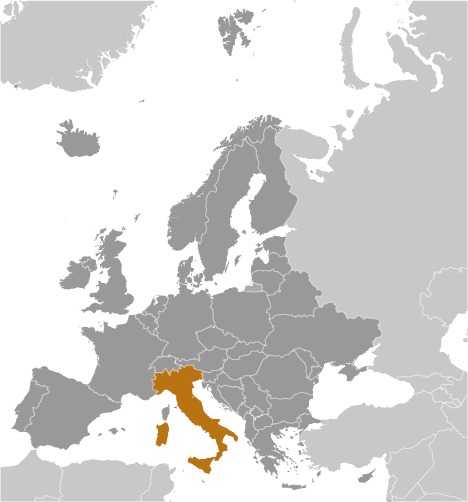
Italy - IT - ITA - ITA - Europe

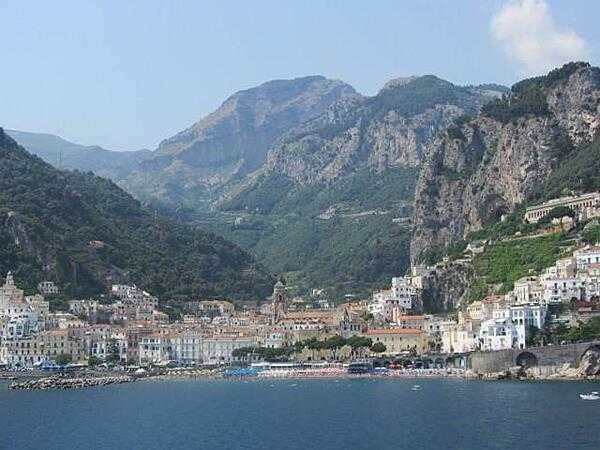
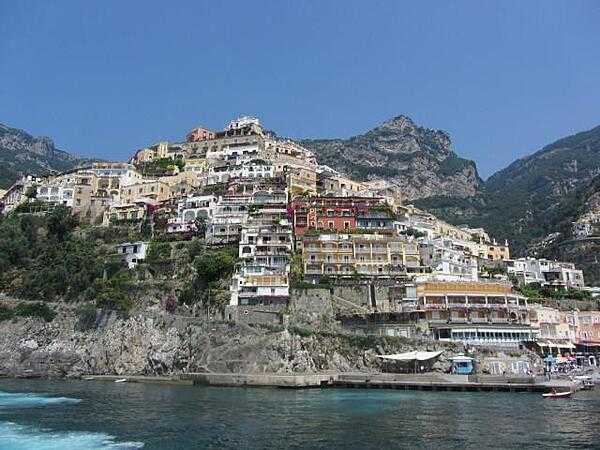
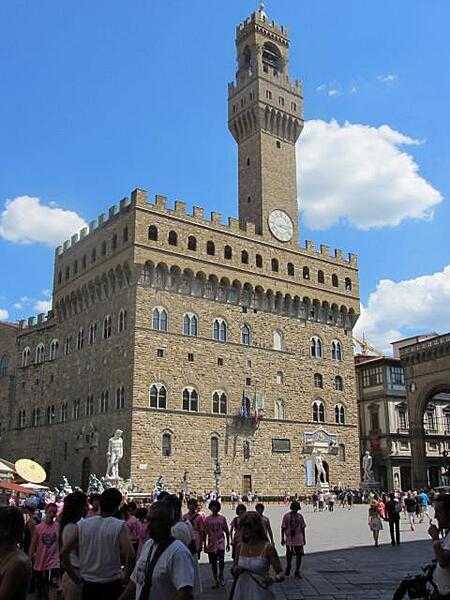
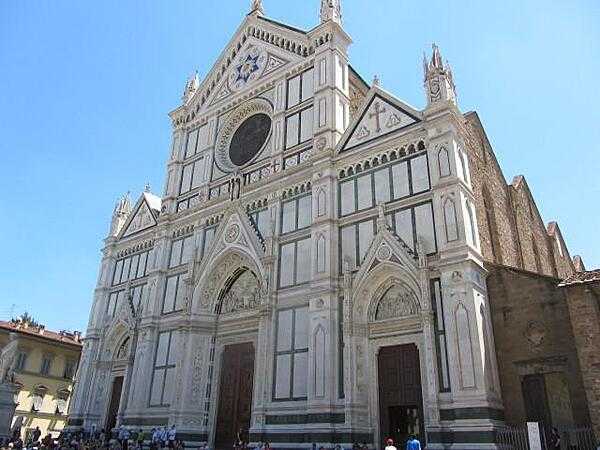
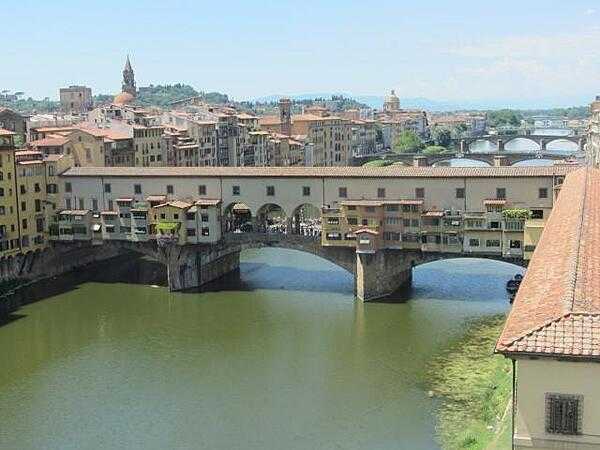
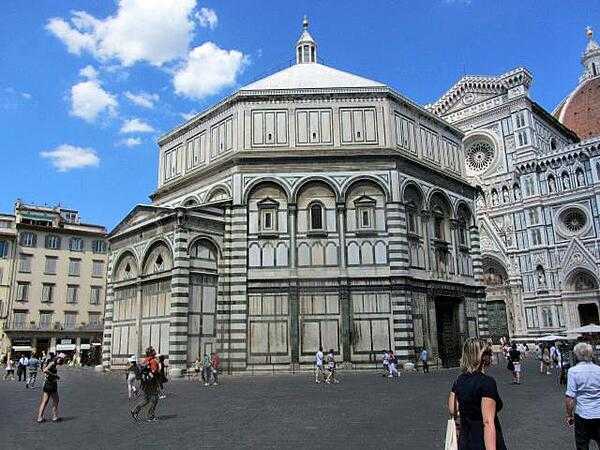
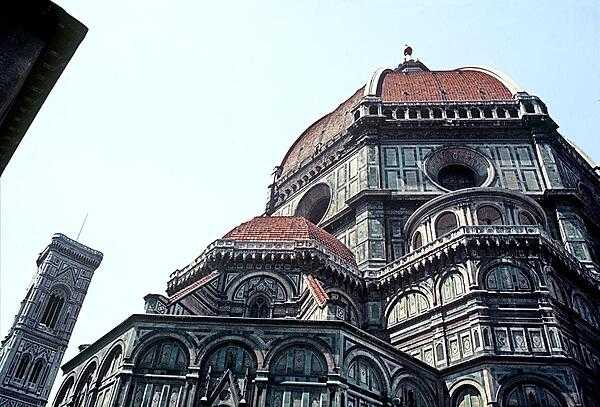
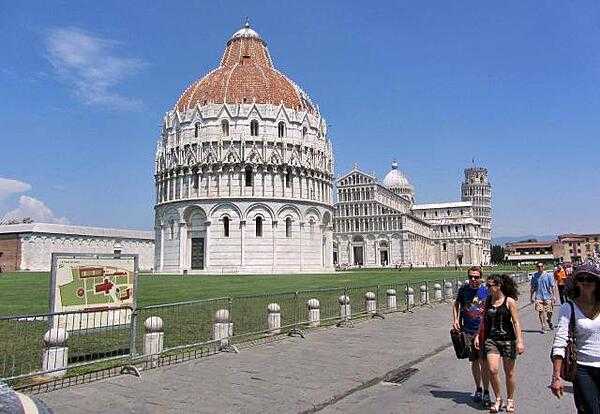
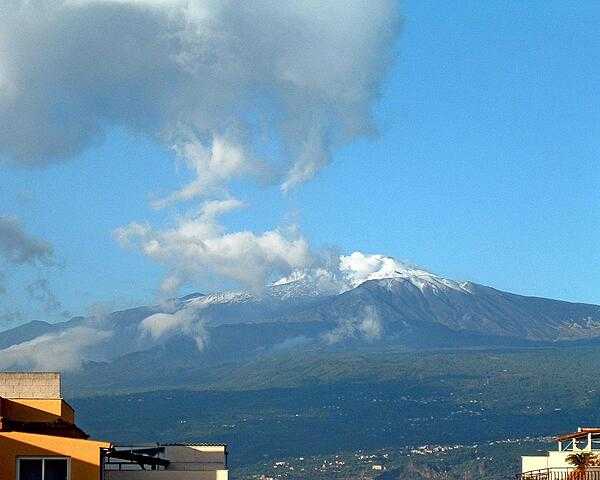
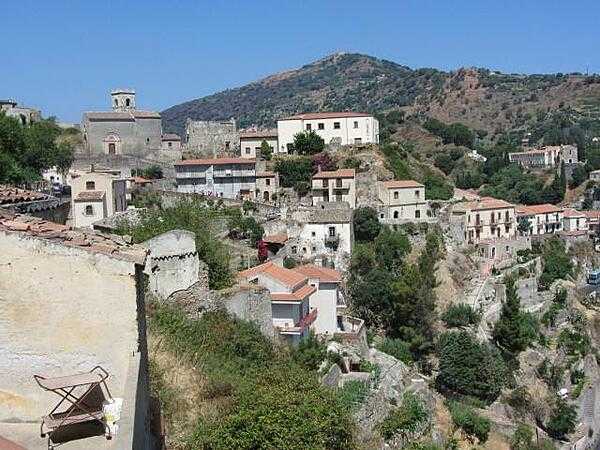
Italy Images
Italy Factbook Data
Diplomatic representation from the US
embassy: via Vittorio Veneto 121, 00187 Roma
mailing address: 9500 Rome Place, Washington DC 20521-9500
telephone: [39] 06-46741
FAX: [39] 06-4674-2244
email address and website:
uscitizenrome@state.gov
https://it.usembassy.gov/
consulate(s) general: Florence, Milan, Naples
Age structure
15-64 years: 64.5% (male 19,378,160/female 19,958,137)
65 years and over: 23.6% (2024 est.) (male 6,336,738/female 8,060,995)
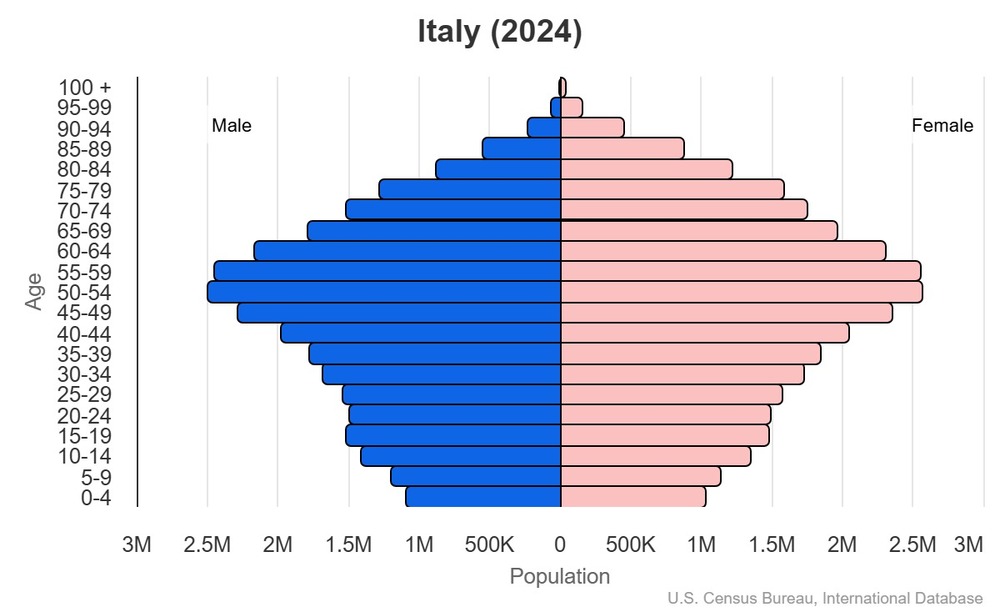
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
Geographic coordinates
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.97 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.79 male(s)/female
total population: 0.93 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Natural hazards
volcanism: significant volcanic activity; Etna (3,330 m) is Europe's most active volcano, and its flank eruptions pose a threat to nearby Sicilian villages; Etna, along with the famous Vesuvius, have both been deemed Decade Volcanoes by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior, worthy of study due to their explosive history and close proximity to human populations; Stromboli, on its namesake island, has also been continuously active with moderate volcanic activity; other historically active volcanoes include Campi Flegrei, Ischia, Larderello, Pantelleria, Vulcano, and Vulsini
Area - comparative
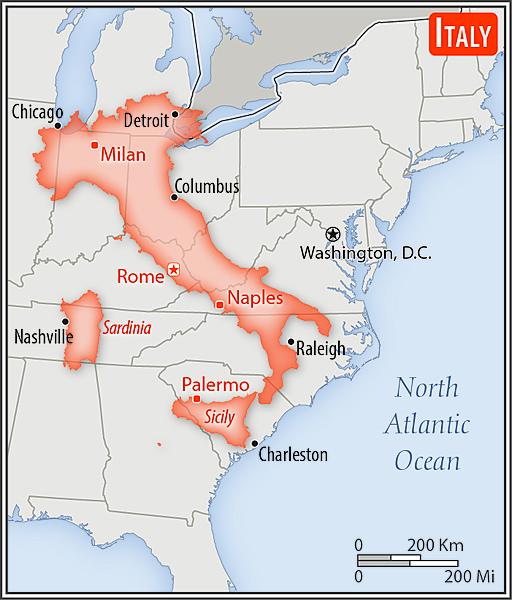
almost twice the size of Georgia; slightly larger than Arizona
Military service age and obligation
note: women serve in all military branches; as of 2023, women made up about 8% of the military's full-time personnel
Background
Italy became a nation-state in 1861 when the regional states of the peninsula, along with Sardinia and Sicily, were united under King Victor EMMANUEL II. An era of parliamentary government came to a close in the early 1920s when Benito MUSSOLINI established a Fascist dictatorship. His alliance with Nazi Germany led to Italy's defeat in World War II. A democratic republic replaced the monarchy in 1946, and economic revival followed. Italy is a charter member of NATO, as well as the European Economic Community (EEC) and its successors, the EC and the EU. It has been at the forefront of European economic and political unification, joining the Economic and Monetary Union in 1999. Persistent problems include sluggish economic growth, high youth and female unemployment, organized crime, corruption, and economic disparities between southern Italy and the more prosperous north.
Environmental issues
International environmental agreements
signed, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Heavy Metals, Air Pollution-Multi-effect Protocol
Military expenditures
1.5% of GDP (2024 est.)
1.5% of GDP (2023 est.)
1.5% of GDP (2022 est.)
1.5% of GDP (2021 est.)
Population below poverty line
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
Household income or consumption by percentage share
highest 10%: 25.3% (2022 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
Exports - commodities
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Exports - partners
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Administrative divisions
regions: Abruzzo, Basilicata, Calabria, Campania, Emilia-Romagna, Lazio (Latium), Liguria, Lombardia, Marche, Molise, Piemonte (Piedmont), Puglia (Apulia), Toscana (Tuscany), Umbria, Veneto
autonomous regions: Friuli Venezia Giulia, Sardegna (Sardinia), Sicilia (Sicily), Trentino-Alto Adige (Trentino-South Tyrol) or Trentino-Suedtirol (German), Valle d'Aosta (Aosta Valley) or Vallée d'Aoste (French)
Agricultural products
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Military and security forces
note 1: the National (or State) Police and Carabinieri (gendarmerie or military police) maintain internal security; the National Police reports to the Ministry of Interior while the Carabinieri reports to the Ministry of Defense but is also under the coordination of the Ministry of Interior; the Carabinieri is primarily a domestic police force organized along military lines, with some overseas responsibilities
note 2: the Financial Guard (Guardia di Finanza) under the Ministry of Economy and Finance is a force with military status and nationwide remit for financial crime investigations, including narcotics trafficking, smuggling, and illegal immigration
Budget
expenditures: $1.104 trillion (2023 est.)
note: central government revenues (excluding grants) and expenditures converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
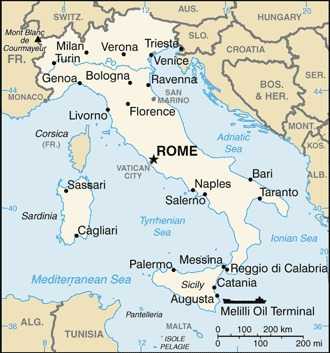
Capital
geographic coordinates: 41 54 N, 12 29 E
time difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
etymology: by tradition, named after Romulus, one of the legendary founders of the city, but the name Romulus may instead derive from the city's name; the name Rome may come from an Etruscan name for the Tiber River, which was Roma or Ruma
Imports - commodities
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Climate
Coastline
Constitution
amendment process: proposed by both houses of Parliament; passage requires two successive debates and approval by absolute majority of each house on the second vote; a referendum is only required when requested by one fifth of the members of either house, by voter petition, or by 5 Regional Councils (elected legislative assemblies of the 15 first-level administrative regions and 5 autonomous regions of Italy); referendum not required if an amendment has been approved by a two-thirds majority in each house in the second vote
Exchange rates
Exchange rates:
0.924 (2024 est.)
0.925 (2023 est.)
0.95 (2022 est.)
0.845 (2021 est.)
0.876 (2020 est.)
Executive branch
head of government: Prime Minister Giorgia MELONI (since 22 October 2022); the prime minister's official title is President of the Council of Ministers
cabinet: Council of Ministers proposed by the prime minister, who is known officially as the President of the Council of Ministers and locally as the premier; nominated by the president
election/appointment process: president indirectly elected by an electoral college consisting of both houses of Parliament and 58 regional representatives for a 7-year term (no term limits); prime minister appointed by the president, confirmed by parliament
most recent election date: 24-29 January 2022 (eight rounds)
election results:
2022: Sergio MATTARELLA (independent) reelected president; electoral college vote count in eighth round - 759 out of 1,009 (505 vote threshold)
2015: Sergio MATTARELLA (independent) elected president; electoral college vote count in fourth round - 665 out of 995 (505 vote threshold)
expected date of next election: 2029
Flag
meaning: colors are those of Milan (red and white) combined with the green uniform color of the Milanese civic guard
history: design inspired by the French flag that Napoleon brought to Italy in 1797
note: similar to the flags of Mexico (longer, darker shades of green and red, and has its coat of arms centered on the white band), Ireland (longer and with orange instead of red), and Cote d'Ivoire (colors reversed)
Independence
note: the Kingdom of Italy proclaimed on 17 March 1861, but Italy was not fully unified until 1871
Industries
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges appointed by the High Council of the Judiciary, headed by the president of the republic; judges may serve for life; Constitutional Court judges - 5 appointed by the president, 5 elected by Parliament, 5 elected by select higher courts; judges serve up to 9 years
subordinate courts: various lower civil and criminal courts (primary and secondary tribunals and courts of appeal)
Land boundaries
border countries (6): Austria 404 km; France 476 km; Holy See (Vatican City) 3.4 km; San Marino 37 km; Slovenia 218 km; Switzerland 698 km
Land use
arable land: 24% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 8.1% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 12.2% (2023 est.)
forest: 31.8% (2023 est.)
other: 24% (2023 est.)
Legal system
Legislative branch
legislative structure: bicameral
Literacy
male: 99.5% (2019 est.)
female: 99.2% (2019 est.)
Maritime claims
continental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
International organization participation
National holiday
Nationality
adjective: Italian
Natural resources
Geography - note
Economic overview
high-income, core EU economy; strong services, manufacturing, and tourism sectors; modest growth supported by net exports, low inflation, and public investments via EU funds; tight labor market with aging workforce and shortages in specialized skills; high public debt levels
Railways
1289.3 0.950-mm gauge (151.3 km electrified)
Suffrage
Terrain
Government type
Country name
conventional short form: Italy
local long form: Repubblica Italiana
local short form: Italia
former: Kingdom of Italy
etymology: derivation is unclear; traditionally said to come from the Vitali, a tribe that settled in what is now Calabria, and whose name is believed to be linked to the Latin word vitulus, or "calf;" alternatively, the name may derive from a local ruler known to the Romans as Italus
Location
Map references
Irrigated land
Diplomatic representation in the US
chancery: 3000 Whitehaven Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 612-4400
FAX: [1] (202) 518-2154
email address and website:
washington.ambasciata@esteri.it
https://ambwashingtondc.esteri.it/ambasciata_washington/en/
consulate(s) general: Boston, Chicago, Houston, Miami, New York, Los Angeles, Philadelphia, San Francisco
consulate(s): Detroit
Internet users
Internet country code
Refugees and internally displaced persons
stateless persons: 3,000 (2024 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
Total renewable water resources
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
male: 16 years (2023 est.)
female: 17 years (2023 est.)
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 0.27% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Broadcast media
Drinking water source
total: 99.9% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
total: 0.1% of population (2022 est.)
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: Goffredo MAMELI/Michele NOVARO
history: adopted 2005; the anthem, originally written in 1847, is also known as "L'Inno di Mameli" (Mameli's Hymn), and "Fratelli d'Italia" (Brothers of Italy)
Major urban areas - population
International law organization participation
Physician density
Hospital bed density
National symbol(s)
Mother's mean age at first birth
GDP - composition, by end use
government consumption: 17.8% (2023 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 22.5% (2023 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.4% (2023 est.)
exports of goods and services: 33.5% (2023 est.)
imports of goods and services: -32.1% (2023 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Italy
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 4 years for EU nationals, 5 years for refugees and specified exceptions, 10 years for all others
Population distribution
Electricity access
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
Sanitation facility access
urban: 100% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 100% of population (2022 est.)
total: 100% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 0% of population (2022 est.)
total: 0% of population (2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
Religions
Languages
major-language sample(s):
L'Almanacco dei fatti del mondo, l'indispensabile fonte per le informazioni di base. (Italian)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Imports - partners
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Elevation
lowest point: Mediterranean Sea 0 m
mean elevation: 538 m
Health expenditure
11.8% of national budget (2022 est.)
Military - note
Italy has been an active member of NATO since its founding in 1948, and the Alliance is a cornerstone of Rome’s national security strategy; it is one of NATO’s leading contributors of military forces and participates in such Alliance missions as Air Policing in the Baltics, the Enhanced Forward Presence in Eastern Europe, and maritime patrols in the Mediterranean and beyond; it hosts NATO’s Joint Force Command in Naples and a NATO Rapid Deployable Corps headquarters in Milan
Italy is also active in European/EU defense cooperation and integration, including hosting the headquarters for the EU’s Mediterranean naval operations force in Rome; in addition, Italy has close defense ties with the US and hosts several US military air, army, and naval bases and facilities (2025)
Military and security service personnel strengths
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
Military deployments
note: since 1960, Italy has committed more than 60,000 troops to UN missions, and it hosts a training center in Vicenza for police personnel destined for peacekeeping missions
Terrorist group(s)
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in the Terrorism reference guide
Total water withdrawal
industrial: 7.7 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
agricultural: 17 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
Waste and recycling
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 39.9% (2022 est.)
Average household expenditures
on alcohol and tobacco: 3.8% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
National heritage
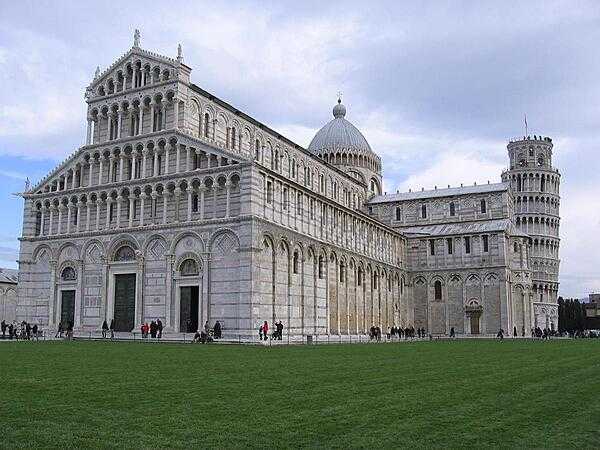
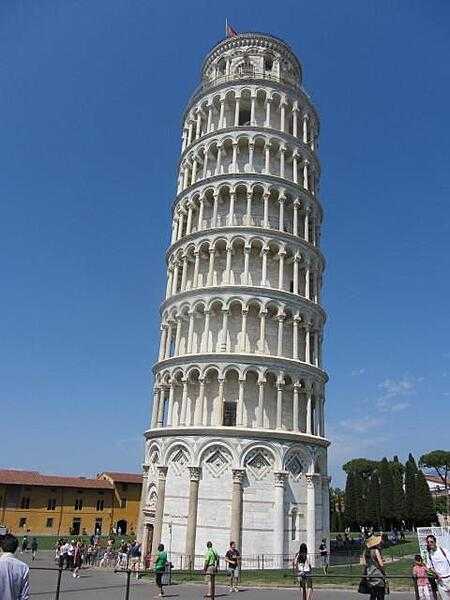
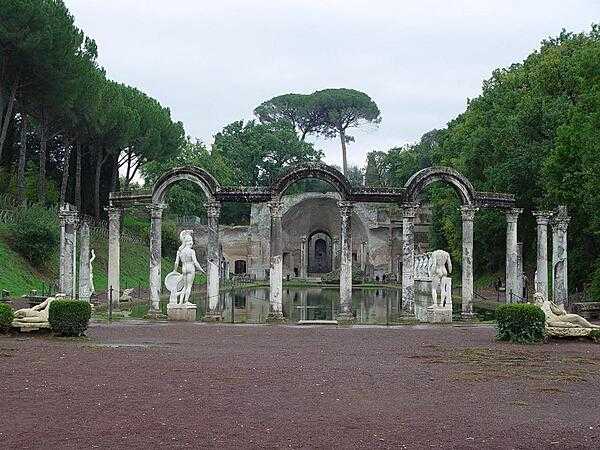
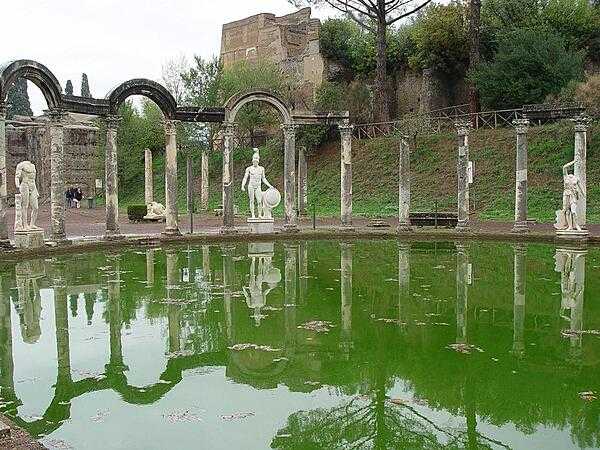
selected World Heritage Site locales: Historic Center of Rome (c); Archaeological Areas of Pompeii, Herculaneum, and Torre Annunziata (c); Venice and its Lagoon (c); Historic Center of Florence (c); Piazza del Duomo, Pisa (c); Historic Centre of Naples (c); Portovenere, Cinque Terre, and the Islands (Palmaria, Tino and Tinetto)(c); Mount Etna (n); Cultural landscape of the Benedictine settlements in medieval Italy (c); Church and Dominican Convent of Santa Maria delle Grazie with “The Last Supper” by Leonardo da Vinci (c); City of Vicenza and the Palladian Villas of the Veneto (c); Crespi d'Adda (c); Early Christian Monuments of Ravenna (c); Historic Centre of the City of Pienza (c); Cathedral, Torre Civica and Piazza Grande, Modena (c); Costiera Amalfitana (c); Villa Romana del Casale (c); Archaeological Area and the Patriarchal Basilica of Aquileia (c); Cilento and Vallo di Diano National Park with the Archeological Sites of Paestum and Velia, and the Certosa di Padula (c); Historic Centre of Urbino (c); Villa Adriana (Tivoli) (c); Assisi, the Basilica of San Francesco and Other Franciscan Sites (c); City of Verona (c); Isole Eolie (Aeolian Islands) (n); Etruscan Necropolises of Cerveteri and Tarquinia (c); Val d'Orcia (c); Mantua and Sabbioneta (c); The Dolomites (n); Prehistoric Pile Dwellings around the Alps (c); Medici Villas and Gardens in Tuscany (c); Venetian Works of Defence between the 16th and 17th Centuries: Stato da Terra – Western Stato da Mar (c); Padua’s fourteenth-century fresco cycles (c); The Porticoes of Bologna (c); Evaporitic Karst and Caves of Northern Apennines (n); Via Appia: Regina Viarum (c); Funerary Tradition in the Prehistory of Sardinia – The domus de janas (c)
Coal
consumption: 12.424 million metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 304,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 12.069 million metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 609.999 million metric tons (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
solar: 12% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
wind: 9.1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 14.7% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
geothermal: 2.1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 6.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Natural gas
consumption: 61.906 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
exports: 2.609 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
imports: 61.851 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 45.76 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Petroleum
refined petroleum consumption: 1.245 million bbl/day (2024 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 497.934 million barrels (2021 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
Remittances
0.5% of GDP (2023 est.)
0.5% of GDP (2022 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
Nuclear energy
Space program overview
Space launch site(s)
the Italian Government has designated the Taranto-Grottaglie Airport as a future spaceport and signed framework agreements with commercial space companies that could lead to suborbital and orbital launches from what would be called the Grottaglie Spaceport (2025)
Space agency/agencies
Geoparks
global geoparks and regional networks: Adamello-Brenta; Alpi Apuane; Aspromonte; Beigua; Cilento, Vallo di Diano e Alburni; Madonie; Maiella; MurGEopark; Pollino; Rocca di Cerere; Sesia Val Grande; Tuscan Mining Park (2025)
Ports
large: 12
medium: 11
small: 71
very small: 28
size unknown: 1
ports with oil terminals: 33
key ports: Brindisi, Civitavecchia, Genova, Gioia Tauro, La Spezia, Livorno, Messina, Napoli, Porto di Lido-Venezia, Siracusa, Taranto, Trieste
Legislative branch - lower chamber
number of seats: 400 (all directly elected)
electoral system: mixed system
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 9/25/2022
parties elected and seats per party: Coalition Brothers of Italy (FdI) - Lega - Forza Italia - Us Moderates (Noi moderati, NM) (237); Democratic Party - Democratic and Progressive Italy (PD-IDP) - Greens and Left Alliance (AVS) - +EUROPA" - Civic Commitment (IC) (84); Five Star Movement (M5s) (52); Action - Italia Viva (21); Other (6)
percentage of women in chamber: 32.8%
expected date of next election: September 2027
Legislative branch - upper chamber
number of seats: 205 (200 directly elected; 5 appointed)
electoral system: mixed system
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 9/25/2022
parties elected and seats per party: Coalition Brothers of Italy (FdI) - Lega - Forza Italia - Us Moderates (Noi moderati, NM) (115); Democratic Party - Democratic and Progressive Italy (PD-IDP) - Greens and Left Alliance (AVS) - +EUROPA" - Civic Commitment (IC) (44); Five Star Movement (M5s) (28); Other (13)
percentage of women in chamber: 36.3%
expected date of next election: September 2027
National color(s)
National coat of arms

Particulate matter emissions
Key space-program milestones
1977 - first domestically built telecommunications/research satellite (Sirio) launched by the US
1990s-2011 - participated in US Space Shuttle program, resulting in first Italian astronaut in space (1992)
1998-present - participated in International Space Station, including the first European astronaut on the station (2001), first Italian to command it (2019-2020), and first woman to command the station (2022)
2012 - first launch of Italian-designed VEGA 3-stage satellite launch vehicle (SLV) for ESA
2020 - signed US-led Artemis Accords for space and lunar exploration
2023 - first Italian all-electric satellite (MicroHETSat) built for the ESA and launched by the US; began developing a habitat for the US-led Artemis Lunar Gateway project
2025 - passed a national space law to govern Italian space operations
Methane emissions
agriculture: 764.9 kt (2019-2021 est.)
waste: 523.4 kt (2019-2021 est.)
other: 35.3 kt (2019-2021 est.)
Labor force
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 19.9% (2024 est.)
female: 24.8% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
Net migration rate
Median age
male: 47.4 years
female: 49.4 years
Maternal mortality ratio
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$247.396 billion (2023 est.)
$224.581 billion (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
Public debt
note: Italy reports its data on public debt according to guidelines set out in the Maastricht Treaty; general government gross debt is defined in the Maastricht Treaty as consolidated general government gross debt at nominal value, outstanding at the end of the year, in the following categories of government liabilities (as defined in ESA95): currency and deposits (AF.2), securities other than shares excluding financial derivatives (AF.3, excluding AF.34), and loans (AF.4); the general government sector comprises central, state, and local government and social security funds
Total fertility rate
Unemployment rate
7.7% (2023 est.)
8.1% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
Carbon dioxide emissions
from coal and metallurgical coke: 26.15 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 162.688 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 118.604 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
Area
land: 294,140 sq km
water: 7,200 sq km
note: includes Sardinia and Sicily
Taxes and other revenues
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$3.11 trillion (2023 est.)
$3.088 trillion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Airports
Infant mortality rate
male: 3.2 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 2.9 deaths/1,000 live births
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
5.6% (2023 est.)
8.2% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
Current account balance
$3.261 billion (2023 est.)
-$36.325 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
Real GDP per capita
$52,700 (2023 est.)
$52,300 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 34 (2023 est.)
Tobacco use
male: 23.2% (2025 est.)
female: 16.6% (2025 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
Energy consumption per capita
Death rate
Birth rate
Electricity
consumption: 290.664 billion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 3.32 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 54.572 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 17.62 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Merchant marine
by type: bulk carrier 17, container ship 6, general cargo 109, oil tanker 95, other 1,049
Imports
$739.646 billion (2023 est.)
$775.518 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
Exports
$774.311 billion (2023 est.)
$737.083 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
Heliports
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 1.99 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 4.83 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.83 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
male: 80.7 years
female: 85.5 years
Real GDP growth rate
0.7% (2023 est.)
4.8% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
Industrial production growth rate
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 21.7% (2024 est.)
services: 65.6% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
Education expenditure
7.4% national budget (2022 est.)
Population growth rate
Political parties
Associative Movement of Italians Abroad or MAIE
Brothers of Italy or FdI
Democratic Party or PD
Five Star Movement or M5S
Forza Italia or FI
Free and Equal (Liberi e Uguali) or LeU
Greens and Left Alliance or AVS
League or Lega
More Europe or +EU
South calls North or ScN
South Tyrolean Peoples Party or SVP
Us Moderates or NM
other minor parties
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 18.1 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 37.2 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 2.7 (2025 est.)
Population
male: 29,383,949
female: 31,540,902
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 133 (2024 est.)
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 34 (2024 est.)





















































