India - IN - IND - IND - South Asia

India Images
India Factbook Data
Diplomatic representation from the US
embassy: Shantipath, Chanakyapuri, New Delhi - 110021
mailing address: 9000 New Delhi Place, Washington DC 20521-9000
telephone: [91] (11) 2419-8000
FAX: [91] (11) 2419-0017
email address and website:
acsnd@state.gov
https://in.usembassy.gov/
consulate(s) general: Chennai (Madras), Hyderabad, Kolkata (Calcutta), Mumbai (Bombay)
Age structure
15-64 years: 68.7% (male 500,568,593/female 467,593,781)
65 years and over: 6.8% (2024 est.) (male 44,101,180/female 52,102,662)
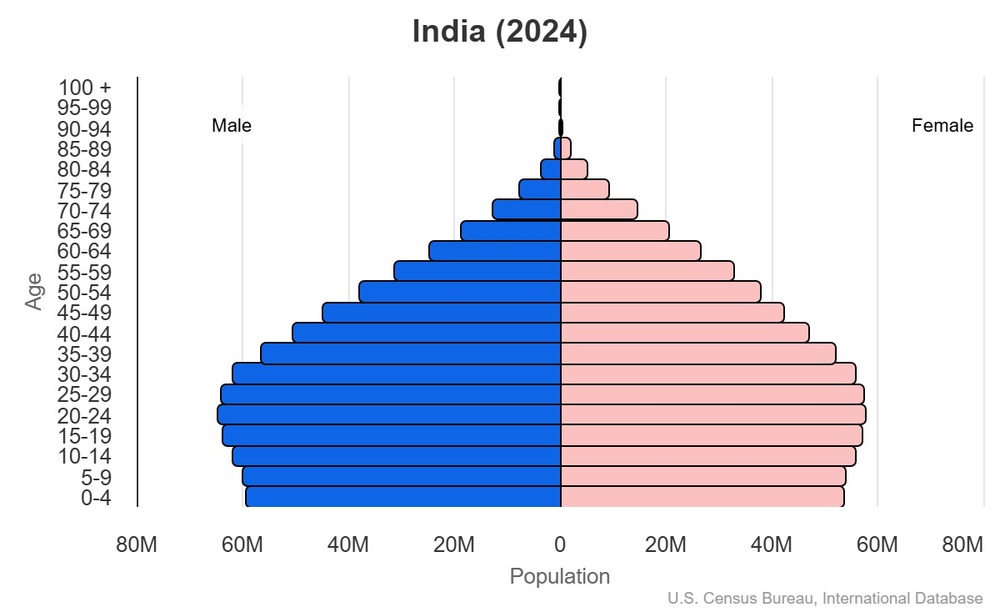
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
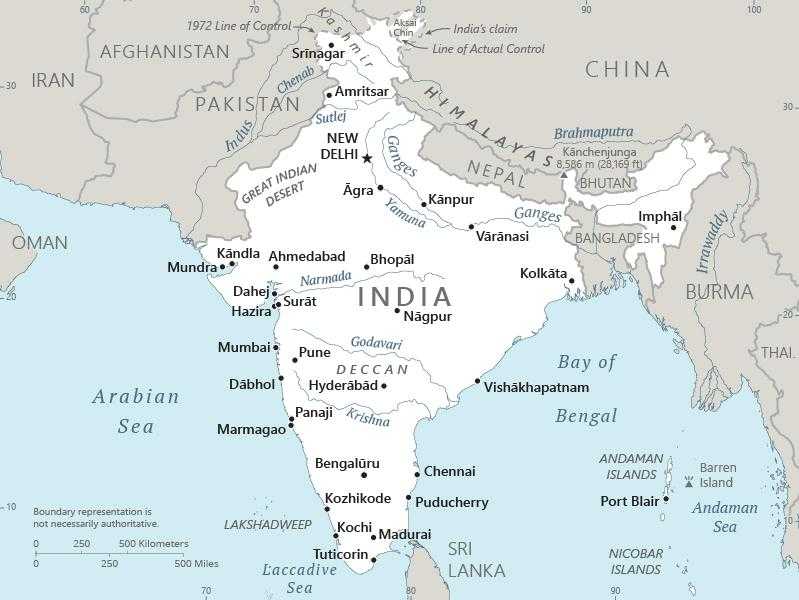
Geographic coordinates
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.11 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.85 male(s)/female
total population: 1.06 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Natural hazards
volcanism: Barren Island (354 m) in the Andaman Sea has been active in recent years
Area - comparative
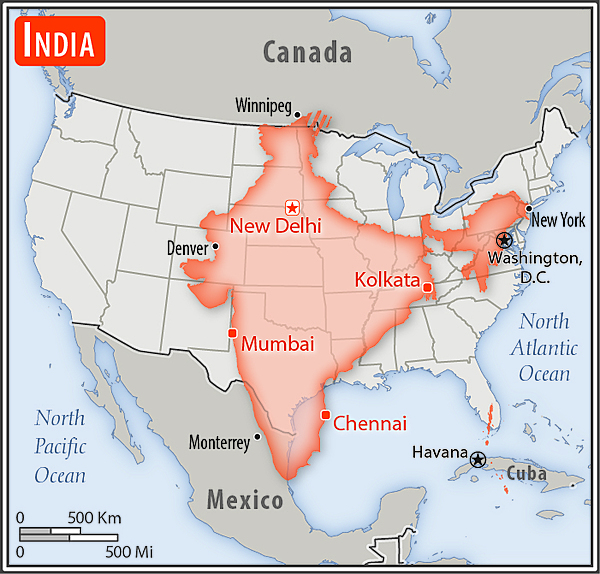
slightly more than one-third the size of the US
Background
The Indus Valley civilization, one of the world's oldest, flourished during the 3rd and 2nd millennia B.C. and extended into northwestern India. Aryan tribes from the northwest infiltrated the Indian subcontinent about 1500 B.C.; their merger with the earlier Dravidian inhabitants created the classical Indian culture. The Maurya Empire of the 4th and 3rd centuries B.C. -- which reached its zenith under ASHOKA -- united much of South Asia. The Gupta dynasty (4th to 6th centuries A.D.) ushered in The Golden Age, which saw a flowering of Indian science, art, and culture. Islam spread across the subcontinent over a period of 700 years. In the 10th and 11th centuries, Turks and Afghans invaded India and established the Delhi Sultanate. In the early 16th century, the Emperor BABUR established the Mughal Dynasty, which ruled large sections of India for more than three centuries. European explorers began establishing footholds in India during the 16th century.
By the 19th century, Great Britain had become the dominant political power on the subcontinent, and India was seen as the "Jewel in the Crown" of the British Empire. The British Indian Army played a vital role in both World Wars. Years of nonviolent resistance to British rule, led by Mohandas GANDHI and Jawaharlal NEHRU, eventually resulted in Indian independence in 1947. Large-scale communal violence took place before and after the subcontinent partition into two separate states -- India and Pakistan. The neighboring countries have fought three wars since independence, the last of which was in 1971 and resulted in East Pakistan becoming the separate nation of Bangladesh. India's nuclear weapons tests in 1998 emboldened Pakistan to conduct its own tests that same year. In 2008, terrorists originating from Pakistan conducted a series of coordinated attacks in Mumbai, India's financial capital. India's economic growth after economic reforms in 1991, a massive youth population, and a strategic geographic location have contributed to the country's emergence as a regional and global power. However, India still faces pressing problems such as extensive poverty, widespread corruption, and environmental degradation, and its restrictive business climate challenges economic growth expectations.
Environmental issues
International environmental agreements
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Military expenditures
2.3% of GDP (2023 est.)
2.1% of GDP (2022 est.)
2.2% of GDP (2021 est.)
2.5% of GDP (2020 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
highest 10%: 22.1% (2022 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
Exports - commodities
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Exports - partners
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Administrative divisions
note: the official name of Delhi is National Capital Territory of Delhi, even though it is considered a union territory
Agricultural products
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Military and security forces
Ministry of Home Affairs: Central Police Organization, Central Armed Police Forces (includes Assam Rifles, Border Security Force, Central Industrial Security Force, Central Reserve Police Force, Indo-Tibetan Border Police, National Security Guards, Sashastra Seema Bal) (2025)
note 1: the Border Security Force (BSF) is responsible for the Indo-Pakistan and Indo-Bangladesh borders; the Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB or Armed Border Force) guards the Indo-Nepal and Indo-Bhutan borders
note 2: the Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) includes a Rapid Reaction Force (RAF) for riot control and the Commando Battalion for Resolute Action (COBRA) for counter-insurgency operations
note 3: the Assam Rifles are under the administrative control of the Ministry of Home Affairs, while operational control falls under the Ministry of Defense (specifically the Indian Army)
Budget
expenditures: $486.598 billion (2022 est.)
note: central government revenues and expenses (excluding grants/extrabudgetary units/social security funds) converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
Capital
geographic coordinates: 28 36 N, 77 12 E
time difference: UTC+5.5 (10.5 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name is of unknown origin; one theory says it may come from the Hindi word dehli (threshold), because of the city's location between the Indus and the Ganges Rivers
Imports - commodities
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Climate
Coastline
Constitution
amendment process: proposed by either the Council of States or the House of the People; passage requires majority participation of the total membership in each house and at least two-thirds majority of voting members of each house, followed by assent of the president of India; proposed amendments to the constitutional amendment procedures also must be ratified by at least one half of the India state legislatures before presidential assent
Exchange rates
Exchange rates:
83.669 (2024 est.)
82.599 (2023 est.)
78.604 (2022 est.)
73.918 (2021 est.)
74.1 (2020 est.)
Executive branch
head of government: Prime Minister Narendra MODI (since 26 May 2014)
cabinet: Union Council of Ministers recommended by the prime minister, appointed by the president
election/appointment process: president indirectly elected for a 5-year term (no term limits) by an electoral college consisting of elected members of both houses of Parliament; vice president indirectly elected for a 5-year term (no term limits) by an electoral college consisting of elected members of both houses of Parliament; following legislative elections, the prime minister is elected by Lok Sabha members of the majority party
most recent election date: president: 18 July 2022
vice president: 5 August 2022
election results:
2022: Droupadi MURMU elected president; percent of electoral college vote - Droupadi MURMU (BJP) 64%, Yashwant SINHA (AITC) 35.9%; Jagdeep DHANKHAR elected vice president; percent of electoral college vote - Jagdeep DHANKHAR (BJP) 74.4%, Margaret ALVA (INC) 25.6%
2017: Ram Nath KOVIND elected president; percent of electoral college vote - Ram Nath KOVIND (BJP) 65.6%, Meira KUMAR (INC) 34.4%; Venkaiah NAIDU elected vice president; percent of electoral college vote - Venkaiah NAIDU (BJP) 67.9%, Gopal-krishna GANDHI 32.1%
expected date of next election: president: July 2027
vice president: August 2027
Flag
meaning: saffron stands for courage, sacrifice, and the spirit of renunciation; white for purity and truth; green for faith and fertility; the chakra symbolizes the wheel of life in movement and death in stagnation
note: similar to the flag of Niger, which has a small orange disk centered in the white band
Illicit drugs
major illicit drug-producing and/or drug-transit country
major precursor-chemical producer (2025)
Independence
Industries
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: justices appointed by the president to serve until age 65
subordinate courts: High Courts; District Courts; Labour Court
Land boundaries
border countries (6): Bangladesh 4,142 km; Bhutan 659 km; Burma 1,468 km; China 2,659 km; Nepal 1,770 km; Pakistan 3,190 km
Land use
arable land: 51.8% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 4.9% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 3.4% (2023 est.)
forest: 24.4% (2023 est.)
other: 15.5% (2023 est.)
Legal system
Legislative branch
legislative structure: bicameral
note: in September 2023, both Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha passed a bill that reserves one third of the House seats for women; implementation could begin for the House election in 2029
Literacy
male: 88.3% (2023 est.)
female: 74.9% (2023 est.)
Maritime claims
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin
International organization participation
National holiday
Nationality
adjective: Indian
Natural resources
Geography - note
Economic overview
largest South Asian economy; strong, sustained GDP growth led by technology and service sectors, foreign investment, and improved regulatory framework; high poverty rate and income inequality; initiatives on infrastructure development, digitization, manufacturing, and financial access
Political parties
All India Trinamool Congress or AITC
Bahujan Samaj Party or BSP
Bharatiya Janata Party or BJP
Biju Janata Dal or BJD
Communist Party of India-Marxist or CPI(M)
Dravida Munnetra Khazhagam
Indian National Congress or INC
Nationalist Congress Party or NCP
Rashtriya Janata Dal or RJD
Samajwadi Party or SP
Shiromani Akali Dal or SAD
Shiv Sena or SS
Telegana Rashtra Samithi or TRS
Telugu Desam Party or TDP
YSR Congress or YSRCP or YCP
Railways
narrow gauge: 1,604 km (2014) 1.000-m gauge
broad gauge: 63,950 km (2014) (39, 329 km electrified)
Suffrage
Terrain
Government type
Country name
conventional short form: India
local long form: Republic of India (English)/ Bharatiya Ganarajya (Hindi)
local short form: India (English)/ Bharat (Hindi)
etymology: the English name derives from the Indus River; the Indian name, Bharat, may derive from the Bharatas tribe mentioned in the Sanskrit Vedas (Hindu religious texts); the name is also associated with Emperor Bharata, the legendary conqueror of India
Location
Map references
Irrigated land
Diplomatic representation in the US
chancery: 2107 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 939-7000
FAX: [1] (202) 265-4351
email address and website:
hoc.washington@mea.gov.in
https://www.indianembassyusa.gov.in/
consulate(s) general: Atlanta, Chicago, Houston, New York, San Francisco, Seattle
Internet users
Internet country code
Refugees and internally displaced persons
IDPs: 642,610 (2024 est.)
stateless persons: 23,262 (2024 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
Total renewable water resources
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
male: 13 years (2024 est.)
female: 13 years (2024 est.)
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 2.33% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Broadcast media
Drinking water source
urban: 95.8% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 91.9% of population (2022 est.)
total: 93.3% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 4.2% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 8.1% of population (2022 est.)
total: 6.7% of population (2022 est.)
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: Rabindranath TAGORE
history: adopted 1950; Rabindranath TAGORE, a Nobel laureate, also wrote Bangladesh's national anthem
Major urban areas - population
International law organization participation
Physician density
Hospital bed density
National symbol(s)
GDP - composition, by end use
government consumption: 10.1% (2024 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 29.6% (2024 est.)
investment in inventories: 3% (2024 est.)
exports of goods and services: 21.2% (2024 est.)
imports of goods and services: -23.5% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 35.6 (2024 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 9.9 (2024 est.)
potential support ratio: 10.1 (2024 est.)
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of India
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Population distribution
Electricity access
electrification - urban areas: 100%
electrification - rural areas: 99.3%
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
Sanitation facility access
urban: 99.4% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 83% of population (2022 est.)
total: 88.9% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0.6% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 17% of population (2022 est.)
total: 11.1% of population (2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
Religions
Languages
major-language sample(s):
विश्व फ़ैक्टबुक, आधारभूत जानकारी का एक अनिवार्य स्रोत (Hindi)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.note 1: there are 22 other recognized languages -- Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Dogri, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Odia, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Santali, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu
note 2: Hindustani is a popular variant of Hindi/Urdu spoken widely throughout northern India but is not an official language
Imports - partners
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Elevation
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 160 m
Health expenditure
4.5% of national budget (2022 est.)
Military - note
the military's chief external focuses are China and Pakistan; the short 1962 Sino-India War left in place one of the World’s longest disputed international borders--known as the Line of Actual Control (LAC)--resulting in occasional standoffs between Indian and Chinese security forces, including lethal clashes in 1975 and 2020; naval competition and influence in the Indian Ocean is also an area of interest
India has fought four wars and several skirmishes with Pakistan; three of the wars have been over the disputed region of Jammu and Kashmir, the status of which has been unsettled since the UK's 1947 withdrawal and the partition and independence of India and Pakistan; a fragile cease-fire in Kashmir was reached in 2003, revised in 2018, and reaffirmed in 2021, although the militarized Line of Control which serves as the border remains contested, and India has accused Pakistan of backing armed separatists and terrorist organizations in Jammu and Kashmir where Indian military and security forces have conducted counterinsurgency operations since the 1980s; in the Spring of 2025, India held Pakistan responsible for a terrorist attack in India-controlled Kashmir and retaliated, sparking a brief cross-border conflict involving aircraft, artillery, drone, and missile strikes
the Kashmir dispute also includes the Siachen Glacier, located in the Karakoram Mountain Range, which was seized by India in 1984 with Pakistan attempting to retake the area several times between 1985 and 1995; despite the 2003 cease-fire, both sides continue to maintain a permanent military presence there with outposts at altitudes above 20,000 feet (over 6,000 meters) where most casualties are due to extreme weather and the hazards of operating in the high mountain terrain of the world’s highest conflict, including avalanches, exposure, and altitude sickness (2025)
Military and security service personnel strengths
Military deployments
note: India has over 6,000 total military and police personnel deployed on UN missions
Terrorist group(s)
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in the Terrorism reference guide
Total water withdrawal
industrial: 17 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
agricultural: 688 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
Waste and recycling
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 17.8% (2022 est.)
Average household expenditures
on alcohol and tobacco: 2% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-49
Major aquifers
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Major rivers (by length in km)
note: [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
National heritage
selected World Heritage Site locales:
Taj Mahal (c); Agra Fort (c); Elphanta Caves (c); Hill Forts of Rajasthan (c); Sundarbans National Park (n); Rock Shelters of Bhimbetka (c); Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park (c); Jaipur (c); Mahabodhi Temple Complex at Bodh Gaya (c); Manas Wildlife Sanctuary (n); Nanda Devi and Valley of Flowers National Parks (n); Khangchendzonga National Park (m); Group of Monuments at Mahabalipuram (c); Sun Temple, Konârak (c); Kaziranga National Park (n); Churches and Convents of Goa (c); Great Living Chola Temples (c); Group of Monuments at Pattadakal (c); Buddhist Monuments at Sanchi (c); Humayun's Tomb, Delhi (c); Qutb Minar and its Monuments, Delhi (c); Great Himalayan National Park Conservation Area (n); Rani-ki-Vav (the Queen’s Stepwell) at Patan, Gujarat (c); Archaeological Site of Nalanda Mahavihara at Nalanda, Bihar (c); Historic City of Ahmadabad (c); Victorian Gothic and Art Deco Ensembles of Mumbai (c); Jaipur City, Rajasthan (c); Kakatiya Rudreshwara (Ramappa) Temple, Telangana (c); Moidams – the Mound-Burial System of the Ahom Dynasty (c); Maratha Military Landscapes of India (c)
Child marriage
women married by age 18: 23.3% (2021)
men married by age 18: 2.6% (2021)
Coal
consumption: 1.262 billion metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 1.632 million metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 243.488 million metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 127.727 billion metric tons (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
nuclear: 2.7% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
solar: 6.6% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
wind: 5.1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 8.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 1.9% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Natural gas
consumption: 62.196 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
exports: 91.921 million cubic meters (2019 est.)
imports: 29.337 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 1.381 trillion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Petroleum
refined petroleum consumption: 5.271 million bbl/day (2023 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 4.605 billion barrels (2021 est.)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
Remittances
3.3% of GDP (2023 est.)
3.3% of GDP (2022 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
Nuclear energy
Number of nuclear reactors under construction: 7 (2025)
Net capacity of operational nuclear reactors: 6.92GW (2025 est.)
Percent of total electricity production: 3.1% (2023 est.)
Space program overview
Space launch site(s)
Space agency/agencies
note: the ISRO is subordinate to the Department of Space (DOS; established 1972)
Ports
large: 4
medium: 4
small: 13
very small: 30
size unknown: 5
ports with oil terminals: 18
key ports: Calcutta, Chennai (Madras), Jawaharlal Nehru Port (Nhava Shiva), Kattupalli Port, Kochi (Cochin), Mumbai (Bombay), New Mangalore, Vishakhapatnam
Legislative branch - lower chamber
number of seats: 545 (543 directly elected; 2 appointed)
electoral system: plurality/majority
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 4/19/2024 to 6/1/2024
parties elected and seats per party: Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) (240); Indian National Congress (INC) (99); Samajwadi Party (SP) (37); All India Trinamool Congress (AITC) (29); Other (138)
percentage of women in chamber: 13.8%
expected date of next election: April 2029
Legislative branch - upper chamber
number of seats: 245 (233 indirectly elected; 12 appointed)
scope of elections: partial renewal
term in office: 6 years
most recent election date: 1/12/2024 to 6/30/2024
percentage of women in chamber: 16.7%
expected date of next election: January 2026
National color(s)
Particulate matter emissions
Key space-program milestones
1975 - first domestically made scientific satellite (Aryabhata) launched by Soviet Union
1979 - first experimental remote sensing (RS) satellite (Bhaskara-I) launched by Soviet Union
1980 - first successful launch of satellite (Rohini) on Indian satellite launch vehicle (SLV)
1984 - first Indian in space on a Soviet rocket
1988 - first operational RS satellite (IRS-1A) launched by Soviet Union
1994 - first successful launch of Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), India’s premier SLV
2008 - first lunar orbiter/probe (Chandrayaan-1) launched, reached lunar orbit, and sent a probe to the surface of the Moon
2014 - first interplanetary probe (Mangalyaan) reached orbit around Mars
2018 - Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (INRSS) became operational
2019 - launched lunar orbiter/probe (Chandrayaan-2) with lander and rover (lander lost when it crash-landed on Moon’s surface)
2023 - successfully landed uncrewed lander/rover mission (Chandrayaan-3) on Moon's surface
2024 - launched satellite (XPoSat) to study black holes and placed solar observatory spacecraft (Aditya-L1) in orbital position to study the Sun
2025 - first docking of two orbiting satellites and sent its first astronaut to the International Space Station
Methane emissions
agriculture: 17,971 kt (2019-2021 est.)
waste: 4,773.7 kt (2019-2021 est.)
other: 644.6 kt (2019-2021 est.)
Labor force
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 15.5% (2024 est.)
female: 17.6% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
Debt - external
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
Maternal mortality ratio
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$627.793 billion (2023 est.)
$567.298 billion (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
Public debt
note: central government debt as a % of GDP
Unemployment rate
4.2% (2023 est.)
4.9% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
Population
male: 725,784,825
female: 683,343,471
Carbon dioxide emissions
from coal and metallurgical coke: 2.054 billion metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 642.909 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 124.226 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
Area
land: 2,973,193 sq km
water: 314,070 sq km
Taxes and other revenues
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$13.377 trillion (2023 est.)
$12.251 trillion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Airports
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 81 (2022 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
5.6% (2023 est.)
6.7% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
Current account balance
-$31.962 billion (2023 est.)
-$79.051 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
Real GDP per capita
$9,300 (2023 est.)
$8,600 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 2 (2022 est.)
Tobacco use
male: 34.1% (2025 est.)
female: 8.9% (2025 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
Energy consumption per capita
Electricity
consumption: 1.5 trillion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 9.529 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 7.843 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 303.066 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Merchant marine
by type: bulk carrier 66, container ship 22, general cargo 607, oil tanker 144, other 1020
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
Imports
$859.507 billion (2023 est.)
$902.304 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
Exports
$773.177 billion (2023 est.)
$767.643 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
Heliports
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 2 (2023 est.)
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 0.23 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 2.85 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
male: 66.5 years
female: 70.1 years
Real GDP growth rate
9.2% (2023 est.)
7.6% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
Industrial production growth rate
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 24.5% (2024 est.)
services: 49.9% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
Education expenditure
14.2% national budget (2022 est.)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
Military service age and obligation
note 1: in 2022, the Indian Government began recruiting men aged 17.5-21 annually to serve on 4-year contracts; at the end of their tenure, 25% would be retained for longer terms of service, while the remainder would be forced to leave the military, although some of those leaving would be eligible to serve in the Coast Guard, the Merchant Navy, civilian positions in the Ministry of Defense, and in the paramilitary forces of the Ministry of Home Affairs
note 2: the Indian military accepts citizens of Nepal and Bhutan; descendants of refugees from Tibet who arrived before 1962 and have resided permanently in India; peoples of Indian origin from nations such as Burma, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Kenya, Malawi, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Tanzania, Uganda, and Vietnam with the intention of permanently settling in India; eligible candidates from “friendly foreign nations” may apply to the Armed Forces Medical Services
note 3: the British began to recruit Nepalese citizens (Gurkhas) into the East India Company Army during the Anglo-Nepalese War (1814-1816), and the Gurkhas subsequently were brought into the British Indian Army; following the partition of India in 1947, an agreement between Nepal, India, and Great Britain allowed for the transfer of the 10 regiments from the British Indian Army to the separate British and Indian armies; six regiments of Gurkhas (aka Gorkhas in India) regiments went to the new Indian Army; a seventh regiment was later added
Gross reproduction rate
Net migration rate
Median age
male: 29.1 years
female: 30.5 years
Total fertility rate
Infant mortality rate
male: 30 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 30.8 deaths/1,000 live births











