Peru - PE - PER - PER - South America
Last updated: January 21, 2026

Peru Images
Peru Factbook Data
Age structure
0-14 years: 25.8% (male 4,293,229/female 4,119,269)
15-64 years: 66.2% (male 10,546,502/female 11,041,106)
65 years and over: 8% (2024 est.) (male 1,112,825/female 1,487,318)
15-64 years: 66.2% (male 10,546,502/female 11,041,106)
65 years and over: 8% (2024 est.) (male 1,112,825/female 1,487,318)
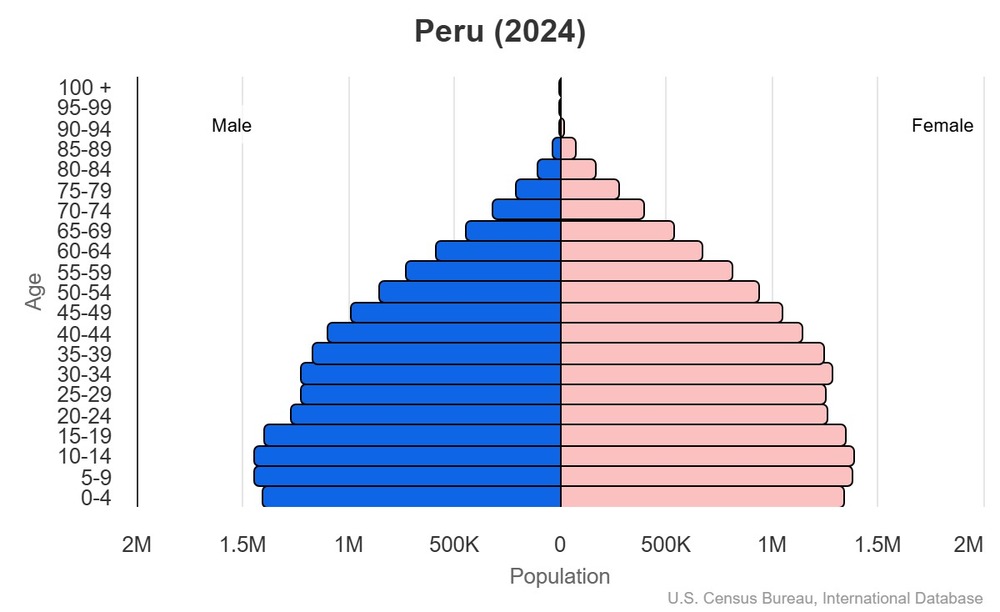
This is the population pyramid for Peru. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
Geographic coordinates
10 00 S, 76 00 W
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.96 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.75 male(s)/female
total population: 0.96 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.96 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.75 male(s)/female
total population: 0.96 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Natural hazards
earthquakes, tsunamis, flooding, landslides, mild volcanic activity
volcanism: volcanic activity in the Andes Mountains; Ubinas (5,672 m) is the country's most active volcano; other historically active volcanoes include El Misti, Huaynaputina, Sabancaya, and Yucamane; see note 2 under "Geography - note"
volcanism: volcanic activity in the Andes Mountains; Ubinas (5,672 m) is the country's most active volcano; other historically active volcanoes include El Misti, Huaynaputina, Sabancaya, and Yucamane; see note 2 under "Geography - note"
Area - comparative
almost twice the size of Texas; slightly smaller than Alaska
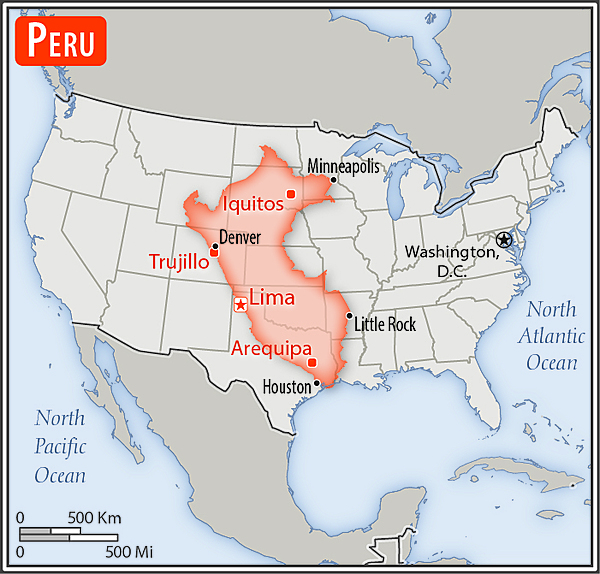
almost twice the size of Texas; slightly smaller than Alaska
Background
Ancient Peru was the seat of several prominent Andean civilizations, most notably that of the Incas whose empire was captured by Spanish conquistadors in 1533. Peru declared its independence in 1821, and remaining Spanish forces were defeated in 1824. After a dozen years of military rule, Peru returned to democratic leadership in 1980 but experienced economic problems and the growth of a violent insurgency. President Alberto FUJIMORI's election in 1990 ushered in a decade that saw a dramatic turnaround in the economy and significant progress in curtailing guerrilla activity. Nevertheless, an economic slump and the president's increasing reliance on authoritarian measures in the late 1990s generated mounting dissatisfaction with his regime, which led to his resignation in 2000.
A caretaker government oversaw a new election in 2001 that installed Alejandro TOLEDO Manrique as the new head of government - Peru's first democratically elected president of indigenous ethnicity. The presidential election of 2006 saw the return of Alan GARCIA Perez who, after a disappointing presidential term from 1985 to 1990, presided over a robust economic rebound. Former army officer Ollanta HUMALA Tasso was elected president in 2011 and carried on the market-oriented economic policies of the three preceding administrations. Pedro Pablo KUCZYNSKI Godard won a very narrow runoff in the 2016 presidential election. Facing impeachment after evidence surfaced of his involvement in a vote-buying scandal, KUCZYNSKI offered his resignation in 2018, and First Vice President Martin Alberto VIZCARRA Cornejo was sworn in as president. In 2019, VIZCARRA invoked his constitutional authority to dissolve Peru's Congress after months of battling with the body over anticorruption reforms. New congressional elections in 2020 resulted in an opposition-led legislature. The Congress impeached VIZCARRA for a second time and removed him from office after accusations of corruption and mishandling of the COVID-19 pandemic. Because of vacancies in the vice-presidential positions, the President of the Peruvian Congress, Manuel MERINO, became the next president. His ascension to office was not well received, and large protests forced his resignation later in 2020. Francisco SAGASTI assumed the position of President of Peru after being appointed President of the Congress the previous day. Jose Pedro CASTILLO Terrones won presidential election in 2021 but was impeached and ousted the following year; his vice president, Dina BOLUARTE, assumed the presidency by constitutional succession in 2022.
A caretaker government oversaw a new election in 2001 that installed Alejandro TOLEDO Manrique as the new head of government - Peru's first democratically elected president of indigenous ethnicity. The presidential election of 2006 saw the return of Alan GARCIA Perez who, after a disappointing presidential term from 1985 to 1990, presided over a robust economic rebound. Former army officer Ollanta HUMALA Tasso was elected president in 2011 and carried on the market-oriented economic policies of the three preceding administrations. Pedro Pablo KUCZYNSKI Godard won a very narrow runoff in the 2016 presidential election. Facing impeachment after evidence surfaced of his involvement in a vote-buying scandal, KUCZYNSKI offered his resignation in 2018, and First Vice President Martin Alberto VIZCARRA Cornejo was sworn in as president. In 2019, VIZCARRA invoked his constitutional authority to dissolve Peru's Congress after months of battling with the body over anticorruption reforms. New congressional elections in 2020 resulted in an opposition-led legislature. The Congress impeached VIZCARRA for a second time and removed him from office after accusations of corruption and mishandling of the COVID-19 pandemic. Because of vacancies in the vice-presidential positions, the President of the Peruvian Congress, Manuel MERINO, became the next president. His ascension to office was not well received, and large protests forced his resignation later in 2020. Francisco SAGASTI assumed the position of President of Peru after being appointed President of the Congress the previous day. Jose Pedro CASTILLO Terrones won presidential election in 2021 but was impeached and ousted the following year; his vice president, Dina BOLUARTE, assumed the presidency by constitutional succession in 2022.
Environmental issues
deforestation (some the result of illegal logging); overgrazing leading to soil erosion; desertification; air pollution in Lima; pollution of rivers and coastal waters from municipal and mining wastes; overfishing
International environmental agreements
party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protection, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Dumping-London Convention, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 2006, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Military expenditures
0.8% of GDP (2024 est.)
1% of GDP (2023 est.)
1.1% of GDP (2022 est.)
1.1% of GDP (2021 est.)
1.2% of GDP (2020 est.)
1% of GDP (2023 est.)
1.1% of GDP (2022 est.)
1.1% of GDP (2021 est.)
1.2% of GDP (2020 est.)
Population below poverty line
27.5% (2022 est.)
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 2% (2023 est.)
highest 10%: 30.6% (2023 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
highest 10%: 30.6% (2023 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
Exports - commodities
copper ore, gold, refined copper, refined petroleum, grapes (2023)
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Exports - partners
China 34%, USA 14%, Canada 5%, India 4%, Switzerland 4% (2023)
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Administrative divisions
24 departments (departamentos, singular - departamento), 1 province* (provincia), and 1 constitutional province** (provincia constitucional); Amazonas, Ancash, Apurimac, Arequipa, Ayacucho, Cajamarca, Callao**, Cusco, Huancavelica, Huánuco, Ica, Junín, La Libertad, Lambayeque, Lima, Lima*, Loreto, Madre de Dios, Moquegua, Pasco, Piura, Puno, San Martin, Tacna, Tumbes, Ucayali
Agricultural products
sugarcane, potatoes, rice, bananas, milk, maize, chicken, oil palm fruit, cassava, grapes (2023)
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Military and security forces
Armed Forces of Peru (Fuerzas Armadas del Perú or FAP): Peruvian Army (Ejercito del Peru), Peruvian Navy (Marina de Guerra del Peru, MGP, includes naval infantry and General Directorate of Captaincies and Coast Guards, DICAPI), Air Force of Peru (Fuerza Aerea del Peru, FAP)
Ministry of the Interior: Peruvian National Police (Policía Nacional del Perú, PNP) (2025)
Ministry of the Interior: Peruvian National Police (Policía Nacional del Perú, PNP) (2025)
Budget
revenues: $48.003 billion (2021 est.)
expenditures: $55.34 billion (2021 est.)
note: central government revenues (excluding grants) and expenditures converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
expenditures: $55.34 billion (2021 est.)
note: central government revenues (excluding grants) and expenditures converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
Capital
name: Lima
geographic coordinates: 12 03 S, 77 03 W
time difference: UTC-5 (same time as Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name is an early Spanish mispronunciation of the Quechua name Rimak, referring to a god and deriving from the word rima (to speak); Quechua priests used to speak to worshippers from inside statues of their gods
geographic coordinates: 12 03 S, 77 03 W
time difference: UTC-5 (same time as Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name is an early Spanish mispronunciation of the Quechua name Rimak, referring to a god and deriving from the word rima (to speak); Quechua priests used to speak to worshippers from inside statues of their gods
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, crude petroleum, cars, trucks, broadcasting equipment (2023)
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Climate
varies from tropical in east to dry desert in west; temperate to frigid in Andes
Coastline
2,414 km
Constitution
history: several previous; latest promulgated 29 December 1993, enacted 31 December 1993
amendment process: proposed by Congress, by the president of the republic with the approval of the Council of Ministers or by petition of at least 0.3% of voters; passage requires absolute majority approval by the Congress membership, followed by approval in a referendum; a referendum is not required if Congress approves the amendment by greater than two-thirds majority vote in each of two successive sessions
amendment process: proposed by Congress, by the president of the republic with the approval of the Council of Ministers or by petition of at least 0.3% of voters; passage requires absolute majority approval by the Congress membership, followed by approval in a referendum; a referendum is not required if Congress approves the amendment by greater than two-thirds majority vote in each of two successive sessions
Exchange rates
nuevo sol (PEN) per US dollar -
Exchange rates:
3.744 (2023 est.)
3.835 (2022 est.)
3.881 (2021 est.)
3.495 (2020 est.)
3.337 (2019 est.)
Exchange rates:
3.744 (2023 est.)
3.835 (2022 est.)
3.881 (2021 est.)
3.495 (2020 est.)
3.337 (2019 est.)
Executive branch
chief of state: President José Enrique JERÍ Oré (since 10 October 2025)
head of government: President José Enrique JERÍ Oré (since 10 October 2025)
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president
election/appointment process: president directly elected by absolute-majority popular vote in 2 rounds, if needed, for a 5-year term (eligible for nonconsecutive terms)
most recent election date: 11 April 2021, with a runoff on 6 June 2021
election results:
2021: Jose Pedro CASTILLO Terrones elected president in second round; percent of vote in first round - Jose Pedro CASTILLO Terrones (PL) 18.9%, Keiko Sofia FUJIMORI Higuchi (FP) 13.4%, Rafael LOPEZ ALIAGA Cazorla (RP) 11.8%, Hernando DE SOTO Polar (Social Integration Party) 11.6%, Yonhy LESCANO Ancieta (AP) 9.1%, Veronika MENDOZA Frisch (JP) 7.9%, Cesar ACUNA Peralta (APP) 6%, George FORSYTH Sommer (VN) 5.7%, Daniel Belizario URRESTI Elera (PP) 5.6%, other 10%; percent of vote second round - Jose Pedro CASTILLO Terrones 50.1%, Keiko Sofia FUJIMORI Higuchi 49.9%
2016: Pedro Pablo KUCZYNSKI Godard elected president in second round; percent of vote in first round - Keiko FUJIMORI Higuchi (FP) 39.9%, Pedro Pablo KUCZYNSKI Godard (PPK) 21.1%, Veronika MENDOZA (FA) 18.7%, Alfredo BARNECHEA (AP) 7%, Alan GARCIA (APRA) 5.8%, other 7.5%; percent of vote in second round - Pedro Pablo KUCZYNSKI Godard 50.1%, Keiko FUJIMORI Higuchi 49.9%
expected date of next election: 12 April 2026
note 1: First Vice President Dina Ercilia BOLUARTE Zegarra assumed the office of the president on 7 December 2022 after President Jose Pedro CASTILLO Terrones was impeached and arrested; on 10 October 2025, the president of the Congress, José Enrique JERÍ Oré, was sworn in as the new president after Congress overwhelmingly voted to remove BOLUARTE from office
note 2: Prime Minister Ernesto ÁLVAREZ (since 14 October 2025) does not exercise executive power; this power rests with the president
note 3: the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President José Enrique JERÍ Oré (since 10 October 2025)
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president
election/appointment process: president directly elected by absolute-majority popular vote in 2 rounds, if needed, for a 5-year term (eligible for nonconsecutive terms)
most recent election date: 11 April 2021, with a runoff on 6 June 2021
election results:
2021: Jose Pedro CASTILLO Terrones elected president in second round; percent of vote in first round - Jose Pedro CASTILLO Terrones (PL) 18.9%, Keiko Sofia FUJIMORI Higuchi (FP) 13.4%, Rafael LOPEZ ALIAGA Cazorla (RP) 11.8%, Hernando DE SOTO Polar (Social Integration Party) 11.6%, Yonhy LESCANO Ancieta (AP) 9.1%, Veronika MENDOZA Frisch (JP) 7.9%, Cesar ACUNA Peralta (APP) 6%, George FORSYTH Sommer (VN) 5.7%, Daniel Belizario URRESTI Elera (PP) 5.6%, other 10%; percent of vote second round - Jose Pedro CASTILLO Terrones 50.1%, Keiko Sofia FUJIMORI Higuchi 49.9%
2016: Pedro Pablo KUCZYNSKI Godard elected president in second round; percent of vote in first round - Keiko FUJIMORI Higuchi (FP) 39.9%, Pedro Pablo KUCZYNSKI Godard (PPK) 21.1%, Veronika MENDOZA (FA) 18.7%, Alfredo BARNECHEA (AP) 7%, Alan GARCIA (APRA) 5.8%, other 7.5%; percent of vote in second round - Pedro Pablo KUCZYNSKI Godard 50.1%, Keiko FUJIMORI Higuchi 49.9%
expected date of next election: 12 April 2026
note 1: First Vice President Dina Ercilia BOLUARTE Zegarra assumed the office of the president on 7 December 2022 after President Jose Pedro CASTILLO Terrones was impeached and arrested; on 10 October 2025, the president of the Congress, José Enrique JERÍ Oré, was sworn in as the new president after Congress overwhelmingly voted to remove BOLUARTE from office
note 2: Prime Minister Ernesto ÁLVAREZ (since 14 October 2025) does not exercise executive power; this power rests with the president
note 3: the president is both chief of state and head of government
Flag
description: three equal vertical bands of red (left side), white, and red, with the coat of arms centered on the white band; the coat of arms has a shield with a vicuna, a cinchona tree, and a yellow cornucopia spilling out coins
meaning: the vicuna represents fauna, the cinchona tree is the source of quinine, and the cornucopia symbolizes mineral wealth; red stands for blood shed for independence, and white for peace
meaning: the vicuna represents fauna, the cinchona tree is the source of quinine, and the cornucopia symbolizes mineral wealth; red stands for blood shed for independence, and white for peace
Illicit drugs
USG identification:
major illicit drug-producing and/or drug-transit country
major precursor-chemical producer (2025)
major illicit drug-producing and/or drug-transit country
major precursor-chemical producer (2025)
Independence
28 July 1821 (from Spain)
Industries
mining and refining of minerals; steel, metal fabrication; petroleum extraction and refining, natural gas and natural gas liquefaction; fishing and fish processing, cement, glass, textiles, clothing, food processing, beer, soft drinks, rubber, machinery, electrical machinery, chemicals, furniture
Judicial branch
highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of 16 judges and divided into civil, criminal, and constitutional-social sectors)
judge selection and term of office: justices proposed by the National Board of Justice (a 7-member independent body), nominated by the president, and confirmed by the Congress; justices can serve until mandatory retirement at age 70
subordinate courts: Court of Constitutional Guarantees; Superior Courts or Cortes Superiores; specialized civil, criminal, and mixed courts; 2 types of peace courts in which professional judges and selected members of the local communities preside
judge selection and term of office: justices proposed by the National Board of Justice (a 7-member independent body), nominated by the president, and confirmed by the Congress; justices can serve until mandatory retirement at age 70
subordinate courts: Court of Constitutional Guarantees; Superior Courts or Cortes Superiores; specialized civil, criminal, and mixed courts; 2 types of peace courts in which professional judges and selected members of the local communities preside
Land boundaries
total: 7,062 km
border countries (5): Bolivia 1,212 km; Brazil 2,659 km; Chile 168 km; Colombia 1,494 km; Ecuador 1,529 km
border countries (5): Bolivia 1,212 km; Brazil 2,659 km; Chile 168 km; Colombia 1,494 km; Ecuador 1,529 km
Land use
agricultural land: 19.1% (2023 est.)
arable land: 3.1% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 1.8% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 14.2% (2023 est.)
forest: 52.9% (2023 est.)
other: 28% (2023 est.)
arable land: 3.1% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 1.8% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 14.2% (2023 est.)
forest: 52.9% (2023 est.)
other: 28% (2023 est.)
Legal system
civil law system
Legislative branch
legislature name: Congress of the Republic (Congreso de la República)
legislative structure: unicameral
number of seats: 130 (all directly elected)
electoral system: proportional representation
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 4/11/2021
parties elected and seats per party: Free Peru (PL) (37); Popular Force (FP) (24); Popular Action (AP) (16); Alliance for Progress (APP) (15); Go on Country - Social Integration Party (AvP) (10); Popular Renewal (RP) (9); We Are Peru" (SP) - Purple Party (PM) (9); Other (10)
percentage of women in chamber: 41.5%
expected date of next election: April 2026
legislative structure: unicameral
number of seats: 130 (all directly elected)
electoral system: proportional representation
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 4/11/2021
parties elected and seats per party: Free Peru (PL) (37); Popular Force (FP) (24); Popular Action (AP) (16); Alliance for Progress (APP) (15); Go on Country - Social Integration Party (AvP) (10); Popular Renewal (RP) (9); We Are Peru" (SP) - Purple Party (PM) (9); Other (10)
percentage of women in chamber: 41.5%
expected date of next election: April 2026
Literacy
total population: 93.7% (2024 est.)
male: 97% (2024 est.)
female: 90.7% (2024 est.)
male: 97% (2024 est.)
female: 90.7% (2024 est.)
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 200 nm; note: the US does not recognize this claim
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm
International organization participation
AIIB, APEC, BIS, CAN, CD, CELAC, EITI (compliant country), FAO, G-24, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAES, LAIA, Mercosur (associate), MIGA, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, NAM, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, Pacific Alliance, PCA, PROSUR, SICA (observer), UN, UNAMID, UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNISFA, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNOOSA, UN Security Council (temporary), UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
National holiday
Independence Day, 28-29 July (1821)
Nationality
noun: Peruvian(s)
adjective: Peruvian
adjective: Peruvian
Natural resources
copper, silver, gold, petroleum, timber, fish, iron ore, coal, phosphate, potash, hydropower, natural gas
Geography - note
note 1: shares control of Lago Titicaca, world's highest navigable lake, with Bolivia; a remote slope of Nevado Mismi, a 5,316-m (17,441-ft) peak, is the ultimate source of the Amazon River
note 2: Peru is one of the countries along the Ring of Fire, which is a belt bordering the Pacific Ocean that contains about 75% of the world's volcanoes and up to 90% of the world's earthquakes
note 3: on 19 February 1600, Mount Huaynaputina in the southern Peruvian Andes erupted in the largest volcanic explosion in South America in historical times; intermittent eruptions lasted until 5 March 1600 and pumped an estimated 16 to 32 million metric tons of particulates into the atmosphere, reducing the amount of sunlight reaching the earth's surface and affecting weather worldwide; over the next two-and-a-half years, millions died around the globe in famines from bitterly cold winters, cool summers, and the loss of crops and animals
note 2: Peru is one of the countries along the Ring of Fire, which is a belt bordering the Pacific Ocean that contains about 75% of the world's volcanoes and up to 90% of the world's earthquakes
note 3: on 19 February 1600, Mount Huaynaputina in the southern Peruvian Andes erupted in the largest volcanic explosion in South America in historical times; intermittent eruptions lasted until 5 March 1600 and pumped an estimated 16 to 32 million metric tons of particulates into the atmosphere, reducing the amount of sunlight reaching the earth's surface and affecting weather worldwide; over the next two-and-a-half years, millions died around the globe in famines from bitterly cold winters, cool summers, and the loss of crops and animals
Economic overview
upper-middle-income South American economy; strong post-COVID rebound tempered by political uncertainty and climate risks; exports driven by mineral extraction and agriculture; large informal sector and uneven access to public services; stable fiscal position and financial sector
Political parties
Advance the Nation (Avanza País) or AvP
Alliance for Progress (Alianza para el Progreso) or APP
Broad Front (Frente Amplio) or FA
Free Peru (Perú Libre) or PL
Front for Hope (Frente Esperanza)
Magisterial Block of National Concentration (Bloque Magisterial de Concertación Nacional) or BMCN
National Victory (Victoria Nacional) or VN
Peru Bicentennial (Perú Bicentenario) or PB
Popular Action (Acción Popular) or AP
Popular Force (Fuerza Popular) or FP
Popular Renewal (Renovación Popular) or RP
Purple Party (Partido Morado)
Social Integration Party (Avanza País - Partido de Integración Social)
Together For Perú (Juntos por el Peru) or JP
We Are Peru (Somos Perú) of SP
We Can Peru (Podemos Perú) or PP
Alliance for Progress (Alianza para el Progreso) or APP
Broad Front (Frente Amplio) or FA
Free Peru (Perú Libre) or PL
Front for Hope (Frente Esperanza)
Magisterial Block of National Concentration (Bloque Magisterial de Concertación Nacional) or BMCN
National Victory (Victoria Nacional) or VN
Peru Bicentennial (Perú Bicentenario) or PB
Popular Action (Acción Popular) or AP
Popular Force (Fuerza Popular) or FP
Popular Renewal (Renovación Popular) or RP
Purple Party (Partido Morado)
Social Integration Party (Avanza País - Partido de Integración Social)
Together For Perú (Juntos por el Peru) or JP
We Are Peru (Somos Perú) of SP
We Can Peru (Podemos Perú) or PP
Railways
total: 1,854.4 km (2017)
standard gauge: 1,730.4 km (2014) 1.435-m gauge (34 km electrified)
narrow gauge: 124 km (2014) 0.914-m gauge
standard gauge: 1,730.4 km (2014) 1.435-m gauge (34 km electrified)
narrow gauge: 124 km (2014) 0.914-m gauge
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal and compulsory until the age of 70
Terrain
western coastal plain (costa), high and rugged Andes in center (sierra), eastern lowland jungle of Amazon Basin (selva)
Government type
presidential republic
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Peru
conventional short form: Peru
local long form: República del Perú
local short form: Perú
etymology: the name may derive from the Guarani word biru, meaning "river"
conventional short form: Peru
local long form: República del Perú
local short form: Perú
etymology: the name may derive from the Guarani word biru, meaning "river"
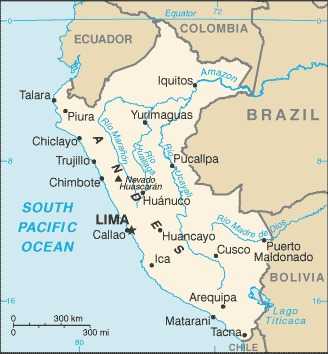
Location
Western South America, bordering the South Pacific Ocean, between Chile and Ecuador
Map references
South America
Irrigated land
25,800 sq km (2012)
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Alfredo Santiago Carlos FERRERO DIEZ CANSECO (since 27 February 2024)
chancery: 1700 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036
telephone: [1] (202) 833-9860
FAX: [1] (202) 659-8124
email address and website:
Webadmin@embassyofperu.us
Embassy of Peru in the United States - E-United States - Platform of the Peruvian State (www.gob.pe)
consulate(s) general: Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Dallas, Denver, Hartford (CT), Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, New York, Paterson (NJ), San Francisco
chancery: 1700 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036
telephone: [1] (202) 833-9860
FAX: [1] (202) 659-8124
email address and website:
Webadmin@embassyofperu.us
Embassy of Peru in the United States - E-United States - Platform of the Peruvian State (www.gob.pe)
consulate(s) general: Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Dallas, Denver, Hartford (CT), Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, New York, Paterson (NJ), San Francisco
Internet users
percent of population: 80% (2023 est.)
Internet country code
.pe
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees: 546,699 (2024 est.)
IDPs: 83,441 (2024 est.)
stateless persons: 32 (2024 est.)
IDPs: 83,441 (2024 est.)
stateless persons: 32 (2024 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$289.222 billion (2024 est.)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
Total renewable water resources
1.88 trillion cubic meters (2022 est.)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 15 years (2017 est.)
male: 15 years (2017 est.)
female: 15 years (2017 est.)
male: 15 years (2017 est.)
female: 15 years (2017 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 78.9% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 1.33% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
rate of urbanization: 1.33% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Broadcast media
10 major TV networks of which only one, Television Nacional de Peru, is state owned; multi-channel cable TV services are available; in excess of 5,000 radio stations including a substantial number of local-language stations (2021)
Drinking water source
improved:
urban: 97.5% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 84.9% of population (2022 est.)
total: 94.8% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 2.5% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 15.1% of population (2022 est.)
total: 5.2% of population (2022 est.)
urban: 97.5% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 84.9% of population (2022 est.)
total: 94.8% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 2.5% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 15.1% of population (2022 est.)
total: 5.2% of population (2022 est.)
National anthem(s)
title: "Himno Nacional del Peru" (National Anthem of Peru)
lyrics/music: Jose DE LA TORRE Ugarte/Jose Bernardo ALZEDO
history: adopted 1821
lyrics/music: Jose DE LA TORRE Ugarte/Jose Bernardo ALZEDO
history: adopted 1821
This is an audio of the National Anthem for Peru. The national anthem is generally a patriotic musical composition - usually in the form of a song or hymn of praise - that evokes and eulogizes the history, traditions, or struggles of a nation or its people. National anthems can be officially recognized as a national song by a country's constitution or by an enacted law, or simply by tradition. Although most anthems contain lyrics, some do not.
Major urban areas - population
11.204 million LIMA (capital), 959,000 Arequipa, 904,000 Trujillo (2023)
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Physician density
1.69 physicians/1,000 population (2023)
Hospital bed density
1.6 beds/1,000 population (2021 est.)
National symbol(s)
vicuna (a camelid related to the llama)
Mother's mean age at first birth
21.9 years (2013 est.)
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-49
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-49
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 61.6% (2024 est.)
government consumption: 13.4% (2024 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 20.8% (2024 est.)
investment in inventories: -1.4% (2024 est.)
exports of goods and services: 28.5% (2024 est.)
imports of goods and services: -22.9% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
government consumption: 13.4% (2024 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 20.8% (2024 est.)
investment in inventories: -1.4% (2024 est.)
exports of goods and services: 28.5% (2024 est.)
imports of goods and services: -22.9% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: yes
citizenship by descent only: yes
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 2 years
citizenship by descent only: yes
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 2 years
Population distribution
approximately one third of the population resides along the desert coastal belt in the west, with a strong focus on the capital city of Lima; the Andean highlands, or sierra, contain roughly half of the population; the eastern slopes of the Andes and adjoining rainforest are sparsely populated
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 96.2% (2022 est.)
electrification - urban areas: 99%
electrification - rural areas: 85.1%
electrification - urban areas: 99%
electrification - rural areas: 85.1%
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
OB
Sanitation facility access
improved:
urban: 94.1% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 65.9% of population (2022 est.)
total: 88.1% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 5.9% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 34.1% of population (2022 est.)
total: 11.9% of population (2022 est.)
urban: 94.1% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 65.9% of population (2022 est.)
total: 88.1% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 5.9% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 34.1% of population (2022 est.)
total: 11.9% of population (2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
Mestizo (mixed Indigenous and White) 60.2%, Indigenous 25.8%, White 5.9%, African descent 3.6%, other (includes Chinese and Japanese descent) 1.2%, unspecified 3.3% (2017 est.)
Religions
Catholic 76%, Evangelical Christian 15.7%, no religion 5.1%, other religions 3.2% (2017 est.)
Languages
Spanish (official) 82.9%, Quechua (official) 13.6%, Aymara (official) 1.6%, Ashaninka 0.3%, other native languages (includes many minor Amazonian languages) 0.8%, other 0.2%, none 0.1%, unspecified 0.7% (2017 est.)
major-language sample(s):
La Libreta Informativa del Mundo, la fuente indispensable de información básica. (Spanish)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
major-language sample(s):
La Libreta Informativa del Mundo, la fuente indispensable de información básica. (Spanish)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Spanish audio sample
Imports - partners
China 26%, USA 21%, Brazil 7%, Argentina 5%, Mexico 3% (2023)
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Elevation
highest point: Nevado Huascaran 6,746 m
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 1,555 m
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 1,555 m
Health expenditure
6.2% of GDP (2021)
16.7% of national budget (2022 est.)
16.7% of national budget (2022 est.)
Military - note
the Peruvian Armed Forces (FAP) are responsible for external defense in addition to some domestic security responsibilities in designated emergency areas and in exceptional circumstances; key areas of focus include counterinsurgency, counternarcotics, cyber defense, disaster relief, and maritime security operations; the FAP supported the police during anti-government protests in early 2023; it has contributed to UN missions since 1958 and has ties to regional militaries, particularly Colombia, as well as those of numerous other countries such as China, Russia, Spain, and the US; the FAP’s last external conflict was a brief border war with Ecuador in 1995
the Special Command of the Valley of the Apurimac, Ene, and Mantaro rivers (CE-VRAEM) is responsible for combating the remnants of the Shining Path terrorist group (aka Sendero Luminoso) and includes several thousand air, ground, naval, police, and special forces personnel; the FAP also provides aircraft, vehicles, and logistical support to the command (2025)
the Special Command of the Valley of the Apurimac, Ene, and Mantaro rivers (CE-VRAEM) is responsible for combating the remnants of the Shining Path terrorist group (aka Sendero Luminoso) and includes several thousand air, ground, naval, police, and special forces personnel; the FAP also provides aircraft, vehicles, and logistical support to the command (2025)
Military and security service personnel strengths
information varies; approximately 85,000 active-duty Armed Forces (50,000 Army; 25,000 Navy; 10,000 Air Force); approximately 75,000 National Police (2025)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the military's inventory consists of mostly older or secondhand armaments originating from a range of countries, including Brazil, China, France, Germany, Italy, Russia/former Soviet Union, South Korea, Spain, and the US; Peru has a small defense industry, including a shipyard that builds and upgrades naval vessels; it also has defense industrial cooperation agreements with several countries, including Russia, South Korea, Spain, and the US (2025)
Military deployments
225 Central African Republic (MINUSCA) (2025)
Terrorist group(s)
Terrorist group(s): Shining Path (Sendero Luminoso); Tren de Aragua (TdA)
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in the Terrorism reference guide
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in the Terrorism reference guide
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 3.141 billion cubic meters (2022)
industrial: 1.666 billion cubic meters (2022)
agricultural: 21.112 billion cubic meters (2022)
industrial: 1.666 billion cubic meters (2022)
agricultural: 21.112 billion cubic meters (2022)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 8.357 million tons (2024 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 9.2% (2022 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 9.2% (2022 est.)
Average household expenditures
on food: 26.9% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
on alcohol and tobacco: 2.5% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
on alcohol and tobacco: 2.5% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
Major aquifers
Amazon Basin
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: Amazon (6,145,186 sq km)
Major lakes (area sq km)
fresh water lake(s): Lago Titicaca (shared with Bolivia) - 8,030 sq km
Major rivers (by length in km)
Amazon river source (shared with Brazil [m]) - 6,400 km
note: [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
note: [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
National heritage
total World Heritage Sites: 13 (9 cultural, 2 natural, 2 mixed)
selected World Heritage Site locales: Cuzco (c); Machu Picchu (m); Chavin (c); Historic Lima (c); Huascarán National Park (n); Chan Chan (c); Manú National Park (n); Lines and Geoglyphs of Nazca (c); Rio Abiseo National Park (m); Historic Arequipa (c); Sacred City of Caral-Supe (c); Qhapaq Ñan/Andean Road System (c)
selected World Heritage Site locales: Cuzco (c); Machu Picchu (m); Chavin (c); Historic Lima (c); Huascarán National Park (n); Chan Chan (c); Manú National Park (n); Lines and Geoglyphs of Nazca (c); Rio Abiseo National Park (m); Historic Arequipa (c); Sacred City of Caral-Supe (c); Qhapaq Ñan/Andean Road System (c)
Child marriage
women married by age 15: 2% (2020)
women married by age 18: 14.1% (2020)
women married by age 18: 14.1% (2020)
Coal
production: 1.382 million metric tons (2023 est.)
consumption: 973,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 1.261 million metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 446,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 1.567 billion metric tons (2023 est.)
consumption: 973,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 1.261 million metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 446,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 1.567 billion metric tons (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 44.8% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
solar: 1.4% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
wind: 3.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 49.6% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
solar: 1.4% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
wind: 3.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 49.6% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Natural gas
production: 14.647 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
consumption: 9.675 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
exports: 4.883 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 300.159 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
consumption: 9.675 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
exports: 4.883 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 300.159 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Petroleum
total petroleum production: 118,000 bbl/day (2023 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 255,000 bbl/day (2023 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 858.89 million barrels (2021 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 255,000 bbl/day (2023 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 858.89 million barrels (2021 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
1.04 (2025 est.)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
52.7% (2022 est.)
Remittances
1.7% of GDP (2023 est.)
1.5% of GDP (2022 est.)
1.6% of GDP (2021 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
1.5% of GDP (2022 est.)
1.6% of GDP (2021 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
Space program overview
focuses on acquiring satellites, applying space applications such as data satellite imagery, and building small rockets; has built a small science/technology satellite; operates satellites and processes satellite imagery data; builds and launches sounding rockets with goal of developing a satellite/space launch vehicle (SLV); researching, developing, and acquiring technologies for manufacturing satellites and satellite payloads, including remote sensing (RS) capabilities; member of Latin American and Caribbean Space Agency (ALCE) since its formation in 2021; cooperates with a variety of foreign space agencies and industries, including those of Brazil, China, the ESA, individual ESA member states (particularly France and Germany), India, Russia, South Korea, Thailand, and the US, as well as other ALCE signatories (2025)
Space launch site(s)
in 2024, Peru announced an initiative to develop a future spaceport in Talara (Piura department)
Space agency/agencies
National Aerospace Research and Development Commission (Comisión Nacional de Investigación y Desarrollo Aeroespacia, CONIDA; established 1974) (2025)
Geoparks
total global geoparks and regional networks: 1
global geoparks and regional networks: Colca y Volcanes de Andagua (2023)
global geoparks and regional networks: Colca y Volcanes de Andagua (2023)
Ports
total ports: 20 (2024)
large: 0
medium: 1
small: 3
very small: 16
ports with oil terminals: 16
key ports: Bahia de Matarani, Iquitos, Puerto del Callao, Talara
large: 0
medium: 1
small: 3
very small: 16
ports with oil terminals: 16
key ports: Bahia de Matarani, Iquitos, Puerto del Callao, Talara
National color(s)
red, white
Particulate matter emissions
31.7 micrograms per cubic meter (2019 est.)
Methane emissions
energy: 233.6 kt (2022-2024 est.)
agriculture: 623.5 kt (2019-2021 est.)
waste: 317 kt (2019-2021 est.)
other: 51.9 kt (2019-2021 est.)
agriculture: 623.5 kt (2019-2021 est.)
waste: 317 kt (2019-2021 est.)
other: 51.9 kt (2019-2021 est.)
Key space-program milestones
2006 - launched first sounding rocket/space probe (Paulet-1)
2013 - first domestically built scientific/research satellite (PUCP-SAT-1) launched by Russia; launched first domestically built rocket (Paulet 1-B) capable of reaching the stratosphere
2016 - first remote sensing satellite (PeruSat-1) acquired from France and launched on European rocket
2024 - signed US-led Artemis Accords on space and lunar exploration
2013 - first domestically built scientific/research satellite (PUCP-SAT-1) launched by Russia; launched first domestically built rocket (Paulet 1-B) capable of reaching the stratosphere
2016 - first remote sensing satellite (PeruSat-1) acquired from France and launched on European rocket
2024 - signed US-led Artemis Accords on space and lunar exploration
Labor force
18.918 million (2024 est.)
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 8.8% (2024 est.)
male: 7.9% (2024 est.)
female: 9.8% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
male: 7.9% (2024 est.)
female: 9.8% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
Net migration rate
-1.16 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Median age
total: 30.4 years (2025 est.)
male: 29.1 years
female: 31.3 years
male: 29.1 years
female: 31.3 years
Debt - external
$38.102 billion (2023 est.)
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
Maternal mortality ratio
51 deaths/100,000 live births (2023 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$79.246 billion (2024 est.)
$71.394 billion (2023 est.)
$72.328 billion (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
$71.394 billion (2023 est.)
$72.328 billion (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
Public debt
35.2% of GDP (2021 est.)
note: central government debt as a % of GDP
note: central government debt as a % of GDP
Total fertility rate
2.12 children born/woman (2025 est.)
Unemployment rate
4.9% (2024 est.)
4.9% (2023 est.)
3.9% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
4.9% (2023 est.)
3.9% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
Carbon dioxide emissions
58.903 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 2.177 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 34.863 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 21.863 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 2.177 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 34.863 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 21.863 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
Area
total : 1,285,216 sq km
land: 1,279,996 sq km
water: 5,220 sq km
land: 1,279,996 sq km
water: 5,220 sq km
Taxes and other revenues
15.9% (of GDP) (2021 est.)
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$535.911 billion (2024 est.)
$518.771 billion (2023 est.)
$520.872 billion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
$518.771 billion (2023 est.)
$520.872 billion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Airports
174 (2025)
Infant mortality rate
total: 10.6 deaths/1,000 live births (2025 est.)
male: 11.9 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 9.7 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 11.9 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 9.7 deaths/1,000 live births
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
40.7 (2023 est.)
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
2% (2024 est.)
6.5% (2023 est.)
8.3% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
6.5% (2023 est.)
8.3% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
Current account balance
$6.39 billion (2024 est.)
$881.934 million (2023 est.)
-$9.972 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
$881.934 million (2023 est.)
-$9.972 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
Real GDP per capita
$15,700 (2024 est.)
$15,300 (2023 est.)
$15,600 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
$15,300 (2023 est.)
$15,600 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 3.53 million (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 10 (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 10 (2023 est.)
Tobacco use
total: 5.7% (2025 est.)
male: 9.5% (2025 est.)
female: 2.1% (2025 est.)
male: 9.5% (2025 est.)
female: 2.1% (2025 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
19.7% (2016)
Energy consumption per capita
30.923 million Btu/person (2023 est.)
Death rate
9.79 deaths/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Birth rate
16.43 births/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 16.164 million kW (2023 est.)
consumption: 53.3 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 47.696 million kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 6.638 billion kWh (2023 est.)
consumption: 53.3 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 47.696 million kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 6.638 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Merchant marine
total: 111 (2023)
by type: general cargo 1, oil tanker 9, other 101
by type: general cargo 1, oil tanker 9, other 101
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
2.7% (2023 est.)
Imports
$67.16 billion (2024 est.)
$63.776 billion (2023 est.)
$69.936 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
$63.776 billion (2023 est.)
$69.936 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
Exports
$83.325 billion (2024 est.)
$72.97 billion (2023 est.)
$71.39 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
$72.97 billion (2023 est.)
$71.39 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
Heliports
7 (2025)
Alcohol consumption per capita
total: 5.74 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 3.01 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.46 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 2.26 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.01 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 3.01 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.46 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 2.26 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.01 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 68.9 years (2024 est.)
male: 65.4 years
female: 72.7 years
male: 65.4 years
female: 72.7 years
Real GDP growth rate
3.3% (2024 est.)
-0.4% (2023 est.)
2.8% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
-0.4% (2023 est.)
2.8% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
Industrial production growth rate
3.1% (2024 est.)
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 6.1% (2024 est.)
industry: 32.2% (2024 est.)
services: 52.7% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
industry: 32.2% (2024 est.)
services: 52.7% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
Education expenditure
4.2% of GDP (2023 est.)
19.2% national budget (2024 est.)
19.2% national budget (2024 est.)
Population growth rate
0.55% (2025 est.)
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador-designate Bernardo NAVARRO; Chargé d’Affaires Joan PERKINS (since 18 April 2025)
embassy: Avenida La Encalada, Cuadra 17 s/n, Surco, Lima 33
mailing address: 3230 Lima Place, Washington DC 20521-3230
telephone: [51] (1) 618-2000
FAX: [51] (1) 618-2724
email address and website:
lima_webmaster@state.gov
https://pe.usembassy.gov/
embassy: Avenida La Encalada, Cuadra 17 s/n, Surco, Lima 33
mailing address: 3230 Lima Place, Washington DC 20521-3230
telephone: [51] (1) 618-2000
FAX: [51] (1) 618-2724
email address and website:
lima_webmaster@state.gov
https://pe.usembassy.gov/
Military service age and obligation
18-30 years of age for voluntary military service (12-24 months) (2025)
note: as of 2024, women made up about 11% of the active-duty military
note: as of 2024, women made up about 11% of the active-duty military
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 50.4 (2025 est.)
youth dependency ratio: 38.4 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 12 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 8.3 (2025 est.)
youth dependency ratio: 38.4 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 12 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 8.3 (2025 est.)
Population
total: 32,768,614 (2025 est.)
male: 16,016,448
female: 16,752,166
male: 16,016,448
female: 16,752,166
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 42.6 million (2024 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 125 (2024 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 125 (2024 est.)
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 1.4 million (2024 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 4 (2024 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 4 (2024 est.)