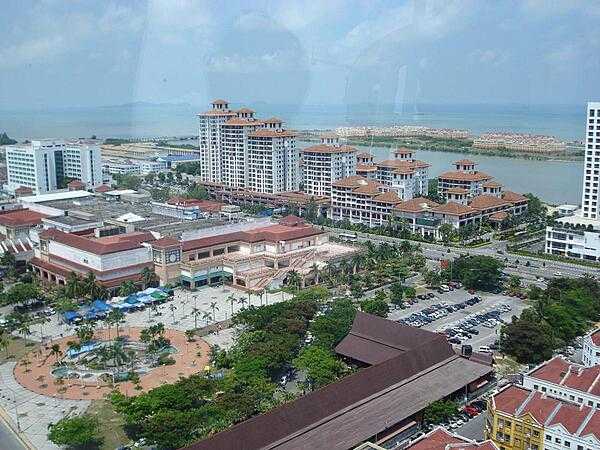
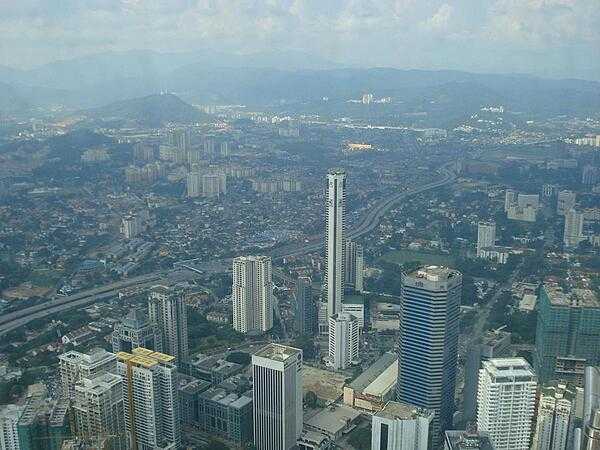
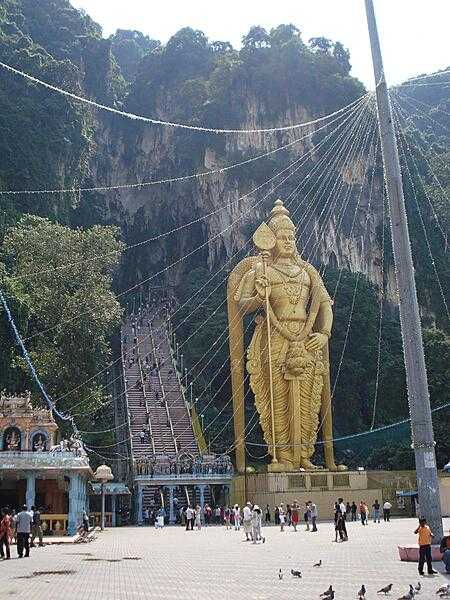
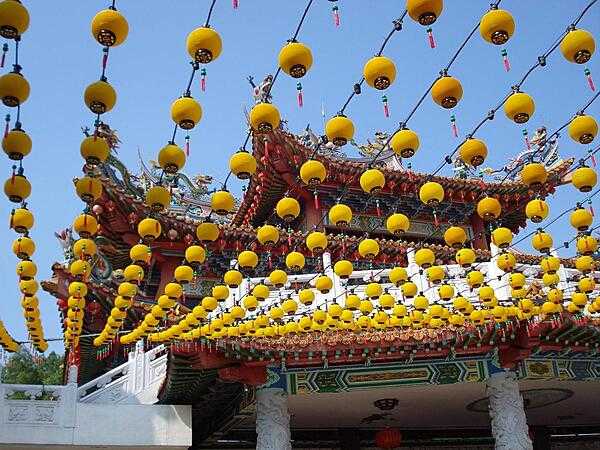
Malaysia - MY - MYS - MAS - East and Southeast Asia

Malaysia Images
Malaysia Factbook Data
Diplomatic representation from the US
embassy: 376 Jalan Tun Razak, 50400 Kuala Lumpur
mailing address: 4210 Kuala Lumpur, Washington DC 20521-4210
telephone: [60] (3) 2168-5000
FAX: [60] (3) 2142-2207
email address and website:
KLACS@state.gov
https://my.usembassy.gov/
Age structure
15-64 years: 69.4% (male 12,308,938/female 11,666,947)
65 years and over: 8.4% (2024 est.) (male 1,409,360/female 1,501,332)
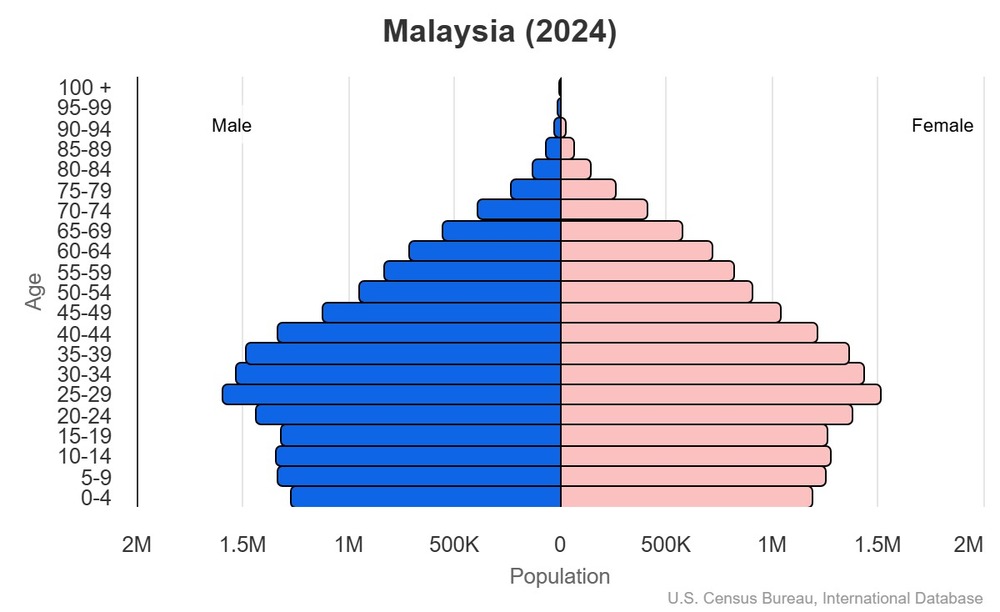
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
Geographic coordinates
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.94 male(s)/female
total population: 1.05 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Natural hazards
Area - comparative
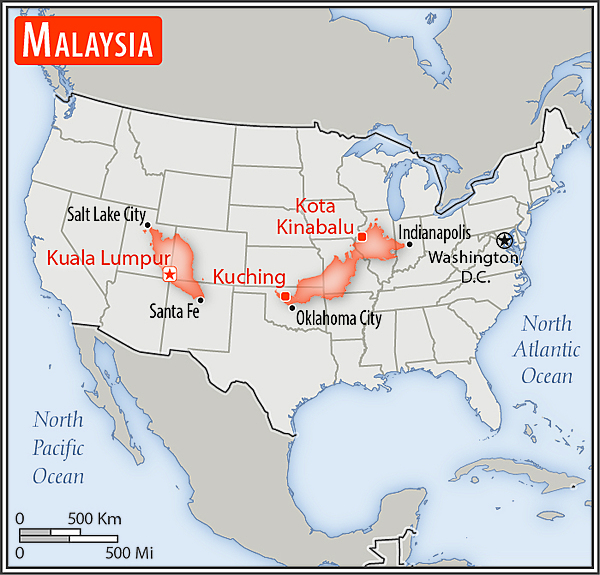
slightly larger than New Mexico
Military service age and obligation
Background
Malaysia’s location has long made it an important cultural, economic, historical, social, and trade link between the islands of Southeast Asia and the mainland. Through the Strait of Malacca, which separates the Malay Peninsula from the archipelago, flowed maritime trade and with it influences from China, India, the Middle East, and the east coast of Africa. Prior to the 14th century, several powerful maritime empires existed in what is modern-day Malaysia, including the Srivijayan, which controlled much of the southern part of the peninsula between the 7th and 13th centuries, and the Majapahit Empire, which took control over most of the peninsula and the Malay Archipelago between the 13th and 14th centuries. The adoption of Islam between the 13th and 17th centuries also saw the rise of a number of powerful maritime states and sultanates on the Malay Peninsula and the island of Borneo, such as the port city of Malacca (Melaka), which at its height in the 15th century had a navy and hosted thousands of Chinese, Arab, Persian, and Indian merchants.
The Portuguese in the 16th century and the Dutch in the 17th century were the first European colonial powers to establish themselves on the Malay Peninsula and in Southeast Asia. However, it was the British who ultimately secured hegemony across the territory and during the late 18th and 19th centuries established colonies and protectorates in the area that is now Malaysia. Japan occupied these holdings from 1942 to 1945. In 1948, the British-ruled territories on the Malay Peninsula (except Singapore) formed the Federation of Malaya, which became independent in 1957. Malaysia was formed in 1963 when the former British colonies of Singapore, as well as Sabah and Sarawak on the northern coast of Borneo, joined the Federation.
A communist insurgency, confrontations with Indonesia, Philippine claims to Sabah, and Singapore's expulsion in 1965 marred the first several years of the country's independence. During the 22-year term of Prime Minister MAHATHIR Mohamad (1981-2003), Malaysia was successful in diversifying its economy from dependence on exports of raw materials to the development of manufacturing, services, and tourism. Former Prime Minister MAHATHIR and a newly formed coalition of opposition parties defeated Prime Minister Mohamed NAJIB bin Abdul Razak's United Malays National Organization (UMNO) in 2018, ending over 60 years of uninterrupted UMNO rule. From 2018-2022, Malaysia underwent considerable political upheaval, with a succession of coalition governments holding power. Following legislative elections in 2022, ANWAR Ibrahim was appointed prime minister after more than 20 years in opposition. His political coalition, Pakatan Harapan (PH), joined its longtime UNMO rival to form a government, but the two groups have remained deeply divided on many issues.
Environmental issues
International environmental agreements
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Military expenditures
0.9% of GDP (2023 est.)
1.1% of GDP (2022 est.)
1% of GDP (2021 est.)
1.1% of GDP (2020 est.)
Population below poverty line
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
Household income or consumption by percentage share
highest 10%: 30.9% (2021 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
Exports - commodities
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Exports - partners
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Administrative divisions
Agricultural products
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Military and security forces
Ministry of Home Affairs: Royal Malaysia Police (RMP or Polis Diraja Malaysia, PDRM), Malaysian Maritime Enforcement Agency (MMEA; aka Malaysian Coast Guard) (2025)
note: the Royal Malaysia Police includes the General Operations Force, a paramilitary force with a variety of roles, including patrolling borders, counterterrorism, maritime security, and counterinsurgency
Budget
expenditures: $89.046 billion (2023 est.)
note: central government revenues and expenses (excluding grants/extrabudgetary units/social security funds) converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
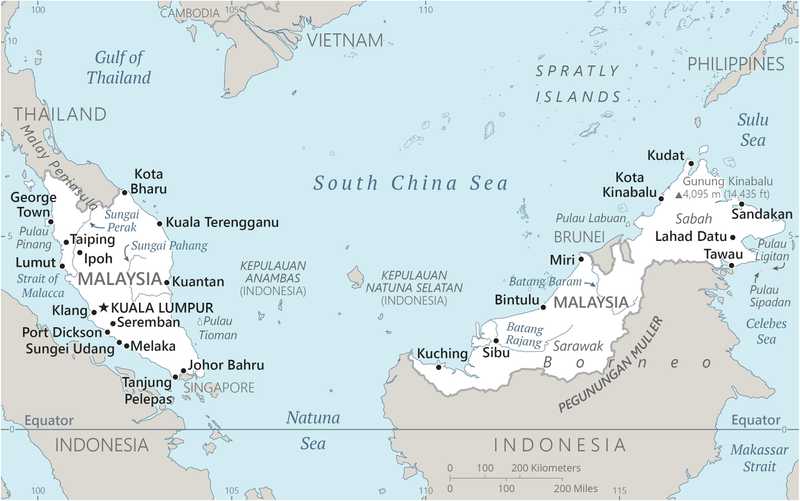
Capital
geographic coordinates: 3 10 N, 101 42 E
time difference: UTC+8 (13 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name means "muddy river junction," referring to the city's location on the confluence of the Kelang and Gombak rivers; it comes from the Malay words kuala (river junction or estuary) and lumpur (mud)
note: nearby Putrajaya is referred to as a federal government administrative center but not as the capital; the legislature meets in Kuala Lumpur
Imports - commodities
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Climate
Coastline
Constitution
amendment process: proposed as a bill by Parliament; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote by the Parliament membership in the bill’s second and third readings; a number of constitutional sections are excluded from amendment or repeal
Exchange rates
Exchange rates:
4.576 (2024 est.)
4.561 (2023 est.)
4.401 (2022 est.)
4.143 (2021 est.)
4.203 (2020 est.)
Executive branch
head of government: Prime Minister ANWAR Ibrahim (since 24 November 2022)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the prime minister from among members of Parliament with the consent of the king
election/appointment process: king elected by and from the hereditary rulers of 9 states for a 5-year term; election is on a rotational basis among rulers of the 9 states; prime minister designated from among members of the House of Representatives; following legislative elections, the leader who has support of the majority of members in the House becomes prime minister
most recent election date: 24 October 2023
expected date of next election: October 2028, with inauguration in January 2029
note: the position of the king is primarily ceremonial, but he is the final arbiter on the appointment of the prime minister
Flag
meaning: the flag is often called Jalur Gemilang (Stripes of Glory); the 14 stripes stand for the equal status of the 13 member states and the federal government; the points on the star represent the unity among these entities; the crescent is a traditional symbol of Islam; blue symbolizes the unity of the Malay people, and yellow is the royal color
note: the design is based on the US flag
Independence
Industries
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: Federal Court justices appointed by the monarch on advice of the prime minister; judges serve until mandatory retirement at age 66 with the possibility of a single 6-month extension
subordinate courts: Court of Appeal; High Court; Sessions Court; Magistrates' Court
note: Malaysia has a dual judicial hierarchy of civil and religious (sharia) courts
Land boundaries
border countries (3): Brunei 266 km; Indonesia 1,881 km; Thailand 595 km
Land use
arable land: 2.4% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 22.7% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 0.9% (2023 est.)
forest: 57.8% (2023 est.)
other: 16% (2023 est.)
Legal system
Legislative branch
legislative structure: bicameral
Literacy
male: 96.8% (2022 est.)
female: 94.7% (2022 est.)
Maritime claims
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation; specified boundary in the South China Sea
International organization participation
National holiday
Nationality
adjective: Malaysian
Natural resources
Geography - note
Economic overview
Political parties
Malaysian Chinese Association (Persatuan Cina Malaysia) or MCA
Malaysian Indian Congress (Kongres India Malaysia) or MIC
United Malays National Organization (Pertubuhan Kebansaan Melayu Bersatu) or UMNO
United Sabah People's Party (Parti Bersatu Rakyat Sabah) or PBRS
Alliance of Hope (Pakatan Harapan) or PH:
Democratic Action Party (Parti Tindakan Demokratik) or DAP
National Trust Party (Parti Amanah Negara) or AMANAH
People's Justice Party (Parti Keadilan Rakyat) or PKR
United Progressive Kinabalu Organization (Pertubuhan Kinabalu Progresif Bersatu) or UPKO
National Alliance (Perikatan Nasional) or PN:
Malaysian People's Movement Party (Parti Gerakan Rakyat Malaysia) or GERAKAN or PGRM
Malaysian United Indigenous Party (Parti Pribumi Bersatu Malaysia) or PPBM or BERSATU
Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (Parti Islam Se-Malaysia) or PAS
Sabah People's Alliance (Gabungan Rakya Sabah) or GRS:
Homeland Solidarity Party (Parti Solidariti Tanah Airku) or STAR
Love Sabah Party (Parti Cinta Sabah) or PCS
Sabah People's Ideas Party (Parti Gagasan Rakyat Sabah) or GAGASAN or PGRS
Sarawak Parties Alliance (Gabungan Parti Sarawak) or GPS:
Progressive Democratic Party (Parti Demokratik Progresif) or PDP
Sarawak People's Party (Parti Rakyat Sarawak) or PRS
Sarawak United People's Party (Parti Rakyat Bersatu Sarawak) or SUPP
United Bumiputera Heritage Party (Parti Pesaka Bumiputera Bersata) or PBB
Homeland Movement/Party (Gerakan Tanah Air) or GTA
Homeland Fighter's Party (Parti Pejuang Tanah Air) or PEJUANG
Perkasa Bumiputera Party of Malaysia (Parti Bumiputera Perkasa Malaysia)
All-Malaysian Jemaah Islamiah Front (Barisan Jemaah Islamiah Se-Malaysia)
National All India Muslim Alliance Party (Parti Perikatan India Muslim Nasional)
others:
Malaysian Nation Party (Parti Bangsa Malaysia) or PBM
Heritage Party (Parti Warisan) or WARISAN
Malaysian United Democratic Alliance (Ikatan Demokratik Malaysia) or MUDA
United Sarawak Party (PSB)
Railways
standard gauge: 59 km (2014) 1.435-m gauge (59 km electrified)
narrow gauge: 1,792 km (2014) 1.000-m gauge (339 km electrified)
Suffrage
Terrain
Government type
note: all Peninsular Malaysian states have hereditary rulers (commonly referred to as sultans) except Melaka (Malacca) and Pulau Pinang (Penang); those two states along with Sabah and Sarawak in East Malaysia have governors appointed by government; powers of state governments are limited by the federal constitution; under terms of federation, Sabah and Sarawak retain certain constitutional prerogatives (e.g., right to maintain their own immigration controls)
Country name
conventional short form: Malaysia
local long form: none
local short form: Malaysia
former: British Malaya, Malayan Union, Federation of Malaya
etymology: devised in the early 19th century by British geographers; the suffix -sia was added to the name of the Malay people to form a classical-style name; the name Malay may come from the Tamil word malai, meaning "mountain"
Location
Map references
Irrigated land
Diplomatic representation in the US
chancery: 3516 International Court NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 572-9700
FAX: [1] (202) 572-9882
email address and website:
mwwashington@kln.gov.my
https://www.kln.gov.my/web/usa_washington/home
consulate(s) general: Los Angeles, New York
Internet users
Internet country code
Refugees and internally displaced persons
stateless persons: 120,857 (2024 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
Total renewable water resources
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
male: 11 years (2023 est.)
female: 12 years (2023 est.)
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 1.87% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Broadcast media
Drinking water source
urban: 99.1% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 90.1% of population (2022 est.)
total: 97.2% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0.9% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 9.9% of population (2022 est.)
total: 2.8% of population (2022 est.)
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: collective, led by Tunku ABDUL RAHMAN/Pierre Jean DE BERANGER
history: adopted 1957; full version only performed in the king's presence, the shorter version performed for the queen and lesser officials
Major urban areas - population
International law organization participation
Physician density
Hospital bed density
National symbol(s)
GDP - composition, by end use
government consumption: 12% (2024 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 20.6% (2024 est.)
investment in inventories: 1.3% (2024 est.)
exports of goods and services: 71.4% (2024 est.)
imports of goods and services: -66% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Malaysia
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 10 out 12 years preceding application
Population distribution
Electricity access
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
Sanitation facility access
urban: 100% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 99.9% of population (2022 est.)
total: 100% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 0.1% of population (2022 est.)
total: 0% of population (2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
Religions
Languages
major-language sample(s):
Buku Fakta Dunia, sumber yang diperlukan untuk maklumat asas. (Bahasa Malaysia)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
note: Malaysia has 134 languages (112 indigenous and 22 non-indigenous); in East Malaysia, there are several indigenous languages, and the most widely spoken are Iban and Kadazan
Imports - partners
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Elevation
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 419 m
Health expenditure
8% of national budget (2022 est.)
Military - note
Malaysia is a member of the Five Powers Defense Arrangements (FPDA), a series of mutual assistance agreements reached in 1971 embracing Australia, Malaysia, New Zealand, Singapore, and the UK; the FPDA commits the members to consult with one another in the event or threat of an armed attack on any of the members and to mutually decide what measures should be taken, jointly or separately; there is no specific obligation to intervene militarily (2025)
Military and security service personnel strengths
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
Military deployments
Terrorist group(s)
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in the Terrorism reference guide
Total water withdrawal
industrial: 1.641 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
agricultural: 2.505 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
Waste and recycling
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 22.1% (2022 est.)
Average household expenditures
on alcohol and tobacco: 1.6% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
National heritage
selected World Heritage Site locales: Gunung Mulu National Park (n); Kinabalu Park (n); Melaka and George Town, Historic Cities of the Straits of Melaka (c); Archaeological Heritage of the Lenggong Valley (c); The Archaeological Heritage of Niah National Park’s Caves Complex (c); Forest Research Institute Malaysia Forest Park Selangor (c)
Coal
consumption: 35.741 million metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 462,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 31.706 million metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 226 million metric tons (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
solar: 1.1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 16.3% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 0.6% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Natural gas
consumption: 47.112 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
exports: 37.451 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
imports: 3.359 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 1.189 trillion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Petroleum
refined petroleum consumption: 672,000 bbl/day (2023 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 3.6 billion barrels (2021 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
Remittances
0.4% of GDP (2023 est.)
0.4% of GDP (2022 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
Space program overview
Space launch site(s)
Space agency/agencies
note: MYSA was established through the merging of the National Space Agency (ANGKASA; established 2002) and the Malaysian Remote Sensing Agency (MRSA; established 1998)
Geoparks
global geoparks and regional networks: Kinabalu; Langkawi (2023)
Ports
large: 3
medium: 4
small: 10
very small: 18
ports with oil terminals: 24
key ports: Johor, Kota Kinabalu, Port Dickson, Port Klang, Pulau Pinang, Tanjung Pelepas, Tapis Marine Terminal A
Legislative branch - lower chamber
number of seats: 223 (all directly elected)
electoral system: plurality/majority
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 11/19/2022
parties elected and seats per party: Pakatan Harapan (PH) (76); National Alliance (PN) (52); National Front (BN) (30); Sarawak Parties Alliance (GPS) (23); Pan-Malaysian Islamic Party (PAS) (22); Other (19)
percentage of women in chamber: 13.5%
expected date of next election: November 2027
Legislative branch - upper chamber
number of seats: 70 (26 indirectly elected; 44 appointed)
percentage of women in chamber: 16.1%
National color(s)
Particulate matter emissions
Methane emissions
agriculture: 182.2 kt (2019-2021 est.)
waste: 847.9 kt (2019-2021 est.)
other: 15.3 kt (2019-2021 est.)
Key space-program milestones
2000 - first multipurpose (remote sensing/RS, communications, scientific) microsatellite (TiungSat-1) produced with technology and training from the UK and launched by Russia
2007 - first Malaysian astronaut (trained in Russia) to space on International Space Station
2009 - first RS satellite (RazakSat) built with assistance from South Korea and launched by US
2011 - completed construction of a satellite assembly, integration, and testing facility
2025 - first commercial high-resolution RS satellite (UzmaSat-1) launched by US; signed US-led Artemis Accords
Labor force
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 11.3% (2024 est.)
female: 13.8% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
Net migration rate
Median age
male: 31.7 years
female: 31.9 years
Maternal mortality ratio
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$113.463 billion (2023 est.)
$114.659 billion (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
Public debt
note: central government debt as a % of GDP
Total fertility rate
Unemployment rate
3.9% (2023 est.)
4% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
Carbon dioxide emissions
from coal and metallurgical coke: 76.78 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 90.273 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 92.951 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
Area
land: 328,657 sq km
water: 1,190 sq km
Taxes and other revenues
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$1.153 trillion (2023 est.)
$1.113 trillion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Airports
Infant mortality rate
male: 6.8 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 6 deaths/1,000 live births
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
2.5% (2023 est.)
3.4% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
Current account balance
$6.257 billion (2023 est.)
$12.738 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
Real GDP per capita
$32,800 (2023 est.)
$32,100 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 13 (2023 est.)
Tobacco use
male: 41.8% (2025 est.)
female: 0.6% (2025 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
Energy consumption per capita
Death rate
Birth rate
Electricity
consumption: 178.653 billion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 1.2 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 61.678 million kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 13.188 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Merchant marine
by type: bulk carrier 14, container ship 35, general cargo 169, oil tanker 148, other 1,384
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
Imports
$253.665 billion (2023 est.)
$283.758 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
Exports
$274.1 billion (2023 est.)
$312.88 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
Heliports
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 0.48 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.04 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.11 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.01 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
male: 75 years
female: 78.4 years
Real GDP growth rate
3.6% (2023 est.)
8.9% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
Industrial production growth rate
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 37.1% (2024 est.)
services: 53.6% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
Education expenditure
14.1% national budget (2023 est.)
Population growth rate
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 140 (2024 est.)
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 31.7 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 12.6 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 7.9 (2025 est.)
Population
male: 17,833,074
female: 17,072,201
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 23 (2024 est.)







