Kenya - KE - KEN - KEN - Africa

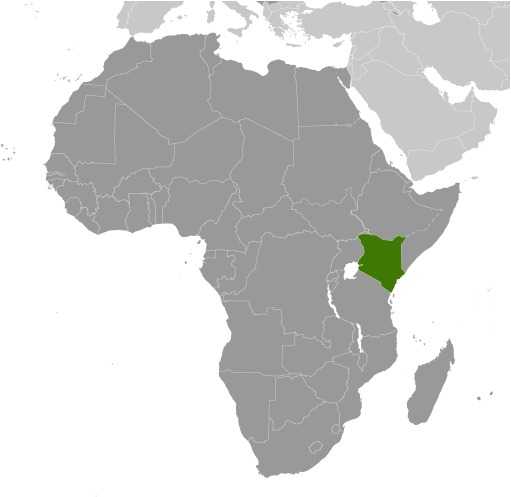
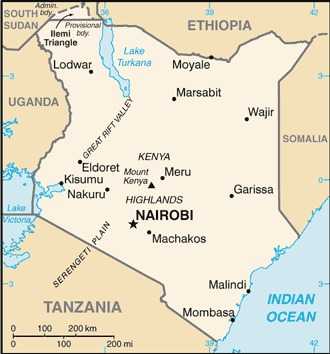
Kenya Images
Kenya Factbook Data
Diplomatic representation from the US
embassy: P.O. Box 606 Village Market, 00621 Nairobi
mailing address: 8900 Nairobi Place, Washington, DC 20521-8900
telephone: [254] (20) 363-6000
FAX: [254] (20) 363-6157
email address and website:
kenya_acs@state.gov
https://ke.usembassy.gov/
Age structure
15-64 years: 60.9% (male 17,731,068/female 17,723,012)
65 years and over: 3.4% (2024 est.) (male 896,348/female 1,064,569)
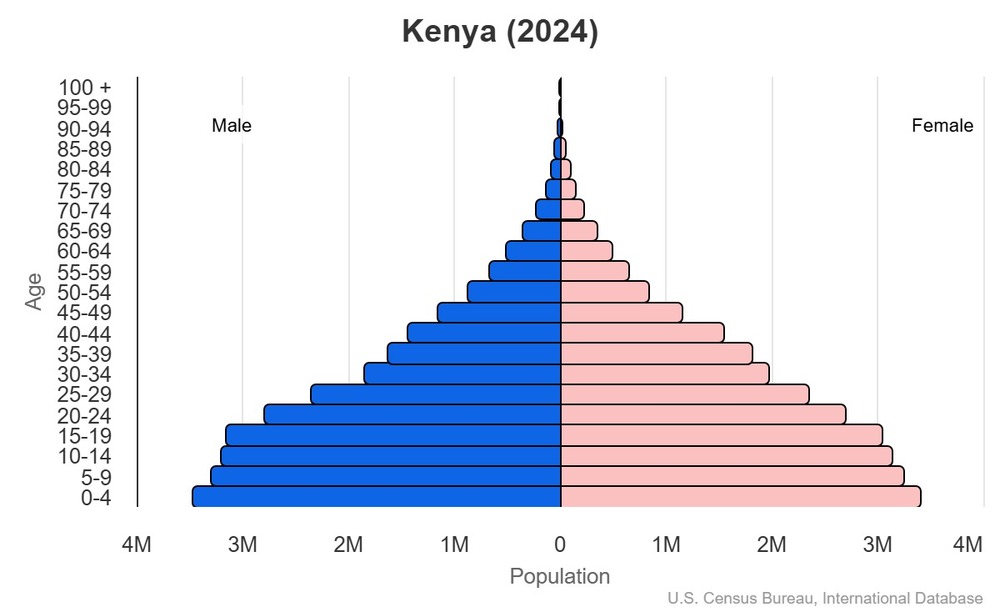
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
Geographic coordinates
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.84 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Natural hazards
volcanism: limited volcanic activity; the Barrier (1,032 m) last erupted in 1921; South Island is the only other historically active volcano
Area - comparative
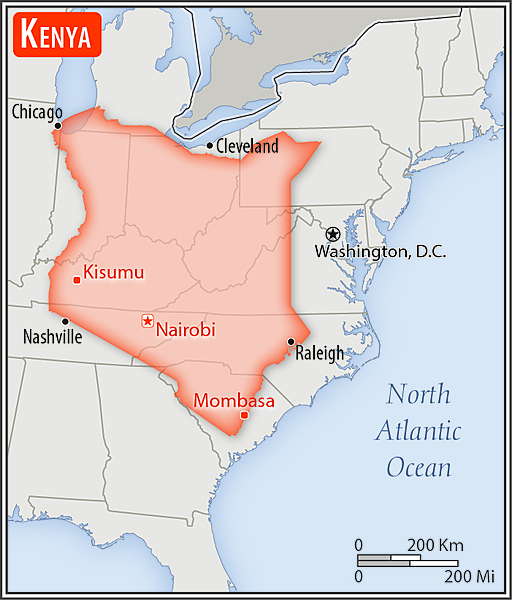
five times the size of Ohio; slightly more than twice the size of Nevada
Military service age and obligation
Background
Trade centers such as Mombasa have existed along the Kenyan and Tanzanian coastlines, known as the Land of Zanj, since at least the 2nd century. These centers traded with the outside world, including China, India, Indonesia, the Middle East, North Africa, and Persia. By around the 9th century, the mix of Africans, Arabs, and Persians who lived and traded there became known as Swahili ("people of the coast") with a distinct language (KiSwahili) and culture. The Portuguese arrived in the 1490s and, using Mombasa as a base, sought to monopolize trade in the Indian Ocean. The Portuguese were pushed out in the late 1600s by the combined forces of Oman and Pate, an island off the coast. In 1890, Germany and the UK divided up the region, with the UK taking the north and the Germans the south, including present-day Tanzania, Burundi, and Rwanda. In 1895, the British established the East Africa Protectorate, which in 1920 was converted into a colony, and named Kenya after its highest mountain. Numerous political disputes between the colony and the UK led to the violent Mau Mau Uprising, which began in 1952, and the eventual declaration of independence in 1963.
Jomo KENYATTA, the founding president and an icon of the liberation struggle, led Kenya from independence in 1963 until his death in 1978, when Vice President Daniel Arap MOI took power in a constitutional succession. The country was a de facto one-party state from 1969 until 1982, after which time the ruling Kenya African National Union (KANU) changed the constitution to make itself the sole legal political party. MOI gave in to internal and external pressure for political liberalization in 1991, but the ethnically fractured opposition failed to dislodge KANU from power in elections in 1992 and 1997, which were marred by violence and fraud. MOI stepped down in 2002 after fair and peaceful elections. Mwai KIBAKI, running as the candidate of the multiethnic, united opposition group, the National Rainbow Coalition (NARC), defeated KANU candidate Uhuru KENYATTA, the son of the founding president, and assumed the presidency following a campaign centered on an anticorruption platform.Opposition candidate Raila ODINGA challenged KIBAKI's reelection in 2007 on the grounds of widespread vote rigging, leading to two months of ethnic violence that caused more than 1,100 deaths and displaced hundreds of thousands. African Union-sponsored mediation resulted in a power-sharing accord that brought ODINGA into the government as prime minister and outlined a reform agenda. In 2010, Kenyans overwhelmingly voted to adopt a new constitution that eliminated the prime minister, introduced additional checks and balances to executive power, and devolved power and resources to 47 newly created counties. Uhuru KENYATTA won the first presidential election under the new constitution in 2013. He won a second and final term in office in 2017 after a contentious repeat election. In 2022, William RUTO won a close presidential election; he assumed the office the following month after the Kenyan Supreme Court upheld the victory.
Environmental issues
International environmental agreements
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Military expenditures
1.1% of GDP (2023 est.)
1.1% of GDP (2022 est.)
1.2% of GDP (2021 est.)
1.2% of GDP (2020 est.)
Population below poverty line
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
Household income or consumption by percentage share
highest 10%: 31.8% (2021 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
Exports - commodities
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Exports - partners
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Administrative divisions
Agricultural products
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Military and security forces
Ministry of Interior: National Police Service, Kenya Coast Guard (2025)
note: the National Police Service maintains internal security and includes a paramilitary General Service Unit and Rapid Deployment Unit, as well as a Border Police Unit
Budget
expenditures: $30.924 billion (2023 est.)
note: central government revenues (excluding grants) and expenditures converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
Capital
geographic coordinates: 1 17 S, 36 49 E
time difference: UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name derives from the Maasai expression meaning "cool waters," which was used to refer to a local water hole, Enkare Nairobi
Imports - commodities
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Climate
Coastline
Constitution
amendment process: amendments can be proposed by either house of Parliament or by petition of at least one million eligible voters; passage of amendments by Parliament requires approval by at least two-thirds majority vote of both houses in each of two readings, approval in a referendum by majority of votes cast by at least 20% of eligible voters in at least one half of Kenya’s counties, and approval by the president; passage of amendments introduced by petition requires approval by a majority of county assemblies, approval by majority vote of both houses, and approval by the president
Exchange rates
Exchange rates:
134.822 (2024 est.)
139.846 (2023 est.)
117.866 (2022 est.)
109.638 (2021 est.)
106.451 (2020 est.)
Executive branch
head of government: President William RUTO (since 13 September 2022)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president, subject to confirmation by the National Assembly
election/appointment process: president and deputy president directly elected on the same ballot by majority vote nationwide and at least 25% of the votes cast in at least 24 of the 47 counties; failure to meet these thresholds requires a runoff between the top two candidates
most recent election date: 9 August 2022
election results:
2022: William RUTO elected president in first round; percent of vote - William RUTO (UDA) 50.5%, Raila ODINGA (ODM) 48.9%, other 0.6%
2017: Uhuru KENYATTA reelected president; percent of vote - Uhuru KENYATTA (JP) 98.3%, Raila ODINGA (ODM) 1%, other 0.7%
expected date of next election: 10 August 2027
note: the president is both chief of state and head of government
Flag
meaning: black stands for the majority population, red for the blood shed in the struggle for freedom, green for natural wealth, and white for peace; the shield and crossed spears symbolize the defense of freedom
Independence
Industries
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: chief and deputy chief justices nominated by Judicial Service Commission (JSC) and appointed by the president with approval of the National Assembly; other judges nominated by the JSC and appointed by president; chief justice serves a nonrenewable 10-year term or until age 70, whichever comes first; other judges serve until age 70
subordinate courts: High Court; Court of Appeal; military courts; magistrates' courts; religious courts
Land boundaries
border countries (5): Ethiopia 867 km; Somalia 684 km; South Sudan 317 km; Tanzania 775 km; Uganda 814 km
Land use
arable land: 11.4% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 1.4% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 36.7% (2023 est.)
forest: 6.5% (2023 est.)
other: 44% (2023 est.)
Legal system
Legislative branch
legislative structure: bicameral
Maritime claims
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
International organization participation
National holiday
note: Madaraka Day, 1 June (1963), marks the day Kenya attained internal self-rule
Nationality
adjective: Kenyan
Natural resources
Geography - note
Economic overview
Political parties
Amani National Congress or ANC
Chama Cha Kazi or CCK
Democratic Action Party or DAP-K
Democratic Party or DP
Forum for the Restoration of Democracy–Kenya or FORD-Kenya
Grand Dream Development Party or GDDP
Jubilee Party or JP
Kenya African National Union or KANU
Kenya Kwanza coalition
Kenya Union Party or KUP
Maendeleo Chap Chap Party or MCC
Movement for Democracy and Growth or MDG
National Agenda Party or NAP-K
National Ordinary People Empowerment Union or NOPEU
Orange Democratic Movement or ODM
Pamoja African Alliance or PAA]
The Service Party or TSP
United Democratic Alliance or UDA
United Democratic Movement or UDM
United Democratic Party or UDP
United Party of Independent Alliance or UPIA
United Progressive Alliance or UPA
Wiper Democratic Movement-Kenya or WDM-K
Railways
standard gauge: 485 km (2018) 1.435-m gauge
narrow gauge: 3,334 km (2018) 1.000-m gauge
Suffrage
Terrain
Government type
Country name
conventional short form: Kenya
local long form: Republic of Kenya (English)/ Jamhuri ya Kenya (Swahili)
local short form: Kenya
former: British East Africa
etymology: named for Mount Kenya; the mountain's name may derive from the Kikuyu word kere nyaga, or "white mountain"
Location
Map references
Irrigated land
Diplomatic representation in the US
chancery: 2249 R St NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 387-6101
FAX: [1] (202) 462-3829
email address and website:
information@kenyaembassydc.org
https://kenyaembassydc.org/#
consulate(s): New York
Internet users
Internet country code
Refugees and internally displaced persons
IDPs: 284,886 (2024 est.)
stateless persons: 9,800 (2024 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
Total renewable water resources
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 4.09% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Broadcast media
Drinking water source
urban: 86.4% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 53.3% of population (2022 est.)
total: 62.9% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 13.6% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 46.7% of population (2022 est.)
total: 37.1% of population (2022 est.)
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: Graham HYSLOP, Thomas KALUME, Peter KIBUKOSYA, Washington OMONDI, and George W. SENOGA-ZAKE/traditional, adapted by Graham HYSLOP, Thomas KALUME, Peter KIBUKOSYA, Washington OMONDI, and George W. SENOGA-ZAKE
history: adopted 1963; based on a traditional Kenyan folk song
Major urban areas - population
International law organization participation
Physician density
Hospital bed density
National symbol(s)
Mother's mean age at first birth
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-49
GDP - composition, by end use
government consumption: 11.5% (2024 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 17.7% (2024 est.)
investment in inventories: -0.9% (2024 est.)
exports of goods and services: 11.1% (2024 est.)
imports of goods and services: -19.2% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 59.8 (2024 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 5.5 (2024 est.)
potential support ratio: 18.3 (2024 est.)
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Kenya
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 4 out of the previous 7 years
Population distribution
Electricity access
electrification - urban areas: 98%
electrification - rural areas: 65.6%
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
Sanitation facility access
urban: 84.7% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 51.1% of population (2022 est.)
total: 60.9% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 15.3% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 48.9% of population (2022 est.)
total: 39.1% of population (2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
Religions
Languages
major-language sample(s):
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information. (English)
The World Factbook, Chanzo cha Lazima Kuhusu Habari ya Msingi. (Kiswahili)
Imports - partners
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Elevation
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 762 m
Health expenditure
8.7% of national budget (2022 est.)
Military - note
the Kenya Military Forces were created following independence in 1963; the current KDF was established and its composition laid out in the 2010 constitution; it is governed by the Kenya Defense Forces Act of 2012; the Army traces its origins back to the Kings African Rifles (KAR), a British colonial regiment raised from Britain's East Africa possessions from 1902 until independence in the 1960s; the KAR conducted both military and internal security functions within the colonial territories, and served outside the territories during both World Wars (2025)
Military and security service personnel strengths
Military deployments
Terrorist group(s)
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in the Terrorism reference guide
Total water withdrawal
industrial: 303 million cubic meters (2022 est.)
agricultural: 3.234 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
Waste and recycling
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 19.9% (2022 est.)
Average household expenditures
on alcohol and tobacco: 3.5% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
Major aquifers
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Major lakes (area sq km)
salt water lake(s): Lake Turkana (shared with Ethiopia) - 6,400 sq km
National heritage
selected World Heritage Site locales: Lake Turkana National Parks (n); Mount Kenya National Park/Natural Forest (n); Lamu Old Town (c); Sacred Mijikenda Kaya Forests (c); Fort Jesus, Mombasa (c); Kenya Lake System in the Great Rift Valley (n); Thimlich Ohinga Archaeological Site (c); The Historic Town and Archaeological Site of Gedi (c)
Coal
exports: 30 metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 1.453 million metric tons (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
solar: 4.5% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
wind: 15.7% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 20.9% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
geothermal: 47.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 1.6% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Petroleum
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
Remittances
3.5% of GDP (2022 est.)
3.4% of GDP (2021 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
Space program overview
Space launch site(s)
Space agency/agencies
note: KSA's predecessor, the National Space Secretariat, was established in 2009
Ports
large: 0
medium: 1
small: 2
very small: 1
ports with oil terminals: 1
key ports: Kilifi, Lamu, Malindi, Mombasa
Legislative branch - lower chamber
number of seats: 350 (all directly elected)
electoral system: plurality/majority
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 8/9/2022
parties elected and seats per party: United Democratic Alliance (UDA) (145); Orange Democratic Movement (ODM) (86); Jubilee Party (JP) (28); Wiper Democratic Movement-Kenya (WDM-K) (26); Others (19); Other (45)
percentage of women in chamber: 23.4%
expected date of next election: August 2027
Legislative branch - upper chamber
number of seats: 68 (all directly elected)
electoral system: plurality/majority
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 8/9/2022
parties elected and seats per party: Kenya Kwanza Alliance (33); Azimio la Umoja - One Kenya Coalition Party (32); Other (1)
percentage of women in chamber: 31.3%
expected date of next election: August 2027
Child marriage
women married by age 18: 12.5% (2022)
men married by age 18: 1.8% (2022)
National color(s)
National coat of arms

Particulate matter emissions
Methane emissions
agriculture: 1,241 kt (2019-2021 est.)
waste: 127.1 kt (2019-2021 est.)
other: 32.8 kt (2019-2021 est.)
Key space-program milestones
2008 - established country's first satellite ground station
2018 - first remote-sensing (RS)/technology-demonstrator cube nanosatellite (1KUNS-PF) produced jointly with Japan and Italy and deployed from the International Space Station
2023 - first domestically designed RS satellite (TAIFA-1) built by Bulgaria and launched by US
Labor force
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 8.3% (2024 est.)
female: 16% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
Debt - external
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
Maternal mortality ratio
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$7.342 billion (2023 est.)
$7.969 billion (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
Unemployment rate
5.6% (2023 est.)
5.8% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
Population
male: 29,091,800
female: 29,154,578
Carbon dioxide emissions
from coal and metallurgical coke: 3.316 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 15.707 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
Area
land: 569,140 sq km
water: 11,227 sq km
Taxes and other revenues
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$314.491 billion (2023 est.)
$297.938 billion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Airports
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 122 (2022 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
7.7% (2023 est.)
7.7% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
Current account balance
-$5.889 billion (2022 est.)
-$5.597 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
Real GDP per capita
$5,700 (2023 est.)
$5,500 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 2 (2023 est.)
Tobacco use
male: 15.5% (2025 est.)
female: 1.9% (2025 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
Energy consumption per capita
Electricity
consumption: 10.002 billion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 34 million kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 316 million kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 3.069 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Merchant marine
by type: oil tanker 4, other 22
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
Imports
$24.606 billion (2022 est.)
$22.001 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
Exports
$13.954 billion (2022 est.)
$11.815 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: (2023 est.) less than 1
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 0.81 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.04 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.81 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.03 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
male: 68.6 years
female: 72.2 years
Real GDP growth rate
5.6% (2023 est.)
4.9% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
Industrial production growth rate
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 16.1% (2024 est.)
services: 55.9% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
Education expenditure
28.5% national budget (2025 est.)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
Gross reproduction rate
Net migration rate
Median age
male: 21.1 years
female: 21.4 years
Total fertility rate
Infant mortality rate
male: 29 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 23.1 deaths/1,000 live births














