South Sudan - SS - SSD - SSD - Africa

South Sudan Images
South Sudan Factbook Data
Diplomatic representation from the US
embassy: Kololo Road adjacent to the EU's compound, Juba
mailing address: 4420 Juba Place, Washington DC 20521-4420
telephone: [211] 912-105-188
email address and website:
ACSJuba@state.gov
https://ss.usembassy.gov/
Age structure
15-64 years: 55.3% (male 3,568,064/female 3,458,804)
65 years and over: 2.6% (2024 est.) (male 182,757/female 149,534)
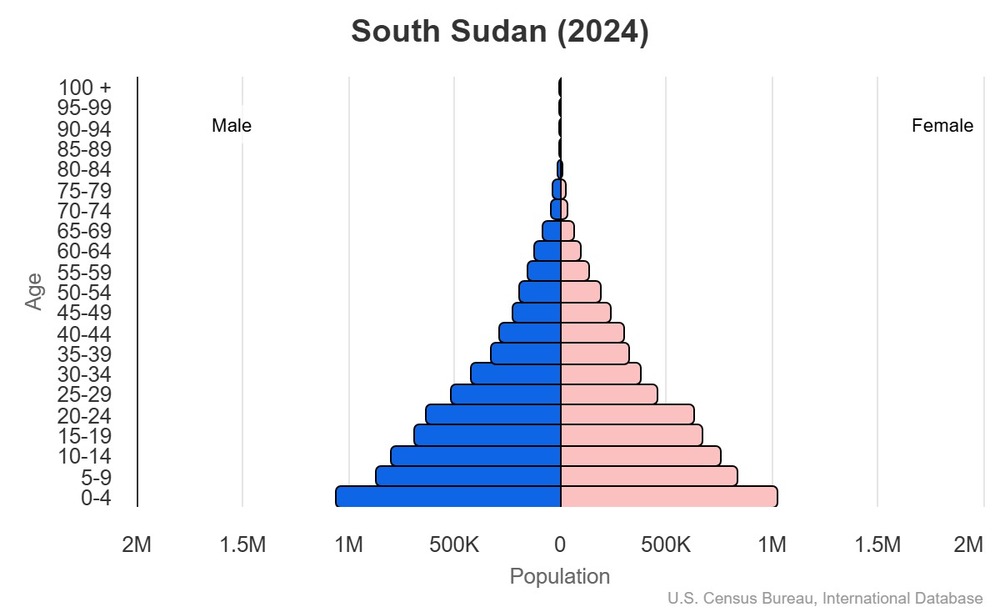
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
Geographic coordinates
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 1.22 male(s)/female
total population: 1.04 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Area - comparative
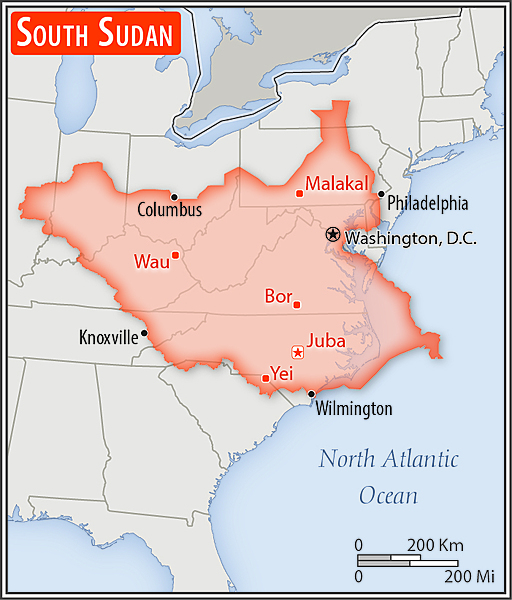
more than four times the size of Georgia; slightly smaller than Texas
Background
South Sudan, which gained independence from Sudan in 2011, is the world’s newest country. Home to a diverse array of mainly Nilotic ethnolinguistic groups that settled in the territory in the 15th through 19th centuries, South Sudanese society is heavily dependent on seasonal migration and seasonal fluctuations in precipitation. Modern-day South Sudan was conquered first by Egypt and later ruled jointly by Egyptian-British colonial administrators in the late 19th century. Christian missionaries helped spread the English language and Christianity in the area, leading to significant cultural differences with the northern part of Sudan, where Arabic and Islam are dominant. When Sudan gained its independence in 1956, the southern region received assurances that it would participate fully in the political system. However, the Arab government in Khartoum reneged on its promises, prompting two periods of civil war (1955-1972 and 1983-2005) in which as many as 2.5 million people died -- mostly civilians -- due largely to starvation and drought. The second Sudanese civil war was one of the deadliest since WWII and left southern Sudanese society devastated. Peace talks resulted in a US-backed Comprehensive Peace Agreement in 2005, which granted the South six years of autonomy followed by a referendum on final status. The result of this referendum, held in 2011, was a vote of 98% in favor of secession.
Since independence, South Sudan has struggled to form a viable governing system and has been plagued by widespread corruption, political conflict, and communal violence. In 2013, conflict erupted between forces loyal to President Salva KIIR, a Dinka, and forces loyal to Vice President Riek MACHAR, a Nuer. The conflict quickly spread through the country along ethnic lines, killing tens of thousands and creating a humanitarian crisis with millions of South Sudanese displaced. KIIR and MACHAR signed a peace agreement in 2015 that created a Transitional Government of National Unity the next year. However, renewed fighting broke out in Juba between KIIR and MACHAR’s forces, plunging the country back into conflict and drawing in additional armed opposition groups. A "revitalized" peace agreement was signed in 2018, mostly ending the fighting and laying the groundwork for a unified national army, a transitional government, and elections. The transitional government was formed in 2020, when MACHAR returned to Juba as first vice president. Since 2020, implementation of the peace agreement has been stalled amid wrangling over power-sharing, which has contributed to an uptick in communal violence and the country’s worst food crisis since independence, with 7 of 11 million South Sudanese citizens in need of humanitarian assistance. The transitional period was extended an additional two years in 2022, pushing elections to late 2024.
Military expenditures
2% of GDP (2023 est.)
2% of GDP (2022 est.)
2% of GDP (2021 est.)
2% of GDP (2020 est.)
Population below poverty line
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
Administrative divisions
note: in 2015, 28 new states were created, and 4 additional states in 2017; after the 2020 peace agreement, the country was again reorganized into the 10 original states, plus 2 administrative areas, Pibor and Ruweng, and 1 special administrative status area, Abyei (which is disputed between South Sudan and Sudan)
Agricultural products
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Military and security forces
Ministry of Interior: South Sudan National Police Service (SSNPS) (2025)
note 1: the NUF are being formed by retraining rebel and pro-government militia fighters into military, police, and other government security forces; the first operational NUF deployed in November 2023
note 2: numerous irregular forces operate in the country with official knowledge, including militias operated by the National Security Service (an internal security force under the Ministry of National Security) and proxy forces
Budget
expenditures: $1.984 billion (2023 est.)
note: central government revenues and expenses (excluding grants/extrabudgetary units/social security funds) converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
Capital
geographic coordinates: 04 51 N, 31 37 E
time difference: UTC+2 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name comes from the name of a small Bari village that was located near the present-day city
Climate
Coastline
Constitution
amendment process: proposed by the National Legislature or by the president of the republic; passage requires submission of the proposal to the Legislature at least one month prior to consideration, approval by at least two-thirds majority vote in both houses of the Legislature, and assent of the president
Exchange rates
Exchange rates:
2,163.104 (2024 est.)
930.331 (2023 est.)
534.511 (2022 est.)
306.355 (2021 est.)
165.907 (2020 est.)
Executive branch
head of government: President Salva KIIR Mayardit (since 9 July 2011)
cabinet: National Council of Ministers appointed by the president, approved by the Transitional National Legislative Assembly
election/appointment process: president directly elected by simple-majority popular vote for a 4-year term (eligible for a second term)
most recent election date: 11-15 April 2010
election results:
2010: Salva KIIR Mayardit elected leader of then-Southern Sudan; percent of vote - Salva KIIR Mayardit (SPLM) 93%, Lam AKOL (SPLM-DC) 7%
expected date of next election: scheduled for 2015 but has been postponed multiple times, currently to be held in December 2026
note: the president is both chief of state and head of government
Flag
meaning: black stands for the people, red for the blood shed in the struggle for freedom, green for the land, and blue for the Nile; the gold star represents the unity of the country's states
note 1: similar to the flag of Kenya
note 2: South Sudan has one of two national flags that display six colors as part of the primary design -- the other is South Africa's
Independence
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: the 2011 Transitional Constitution of South Sudan calls for the establishment of a Judicial Service Council to recommend prospective justices to the president, and for the justices' tenures to be set by the National Legislature
subordinate courts: national level - Courts of Appeal; High Courts; County Courts; state level - High Courts; County Courts; customary courts; other specialized courts and tribunals
note: in mid-2022, the Government of South Sudan inaugurated an ad-hoc judiciary committee, a 12-member body led by two eminent jurists, that is charged with reviewing relevant laws, advising on judicial reform, and restructuring the judiciary
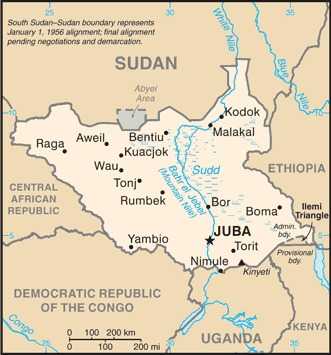
Land boundaries
border countries (6): Central African Republic 1,055 km; Democratic Republic of the Congo 714 km; Ethiopia 1,299 km; Kenya 317 km; Sudan 2,158 km; Uganda 475 km
note: South Sudan-Sudan boundary represents 1 January 1956 alignment; final alignment pending negotiations and demarcation; final sovereignty status of Abyei Area pending negotiations between South Sudan and Sudan
Land use
arable land: 3.9% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 0.1% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 40.8% (2023 est.)
forest: 11.3% (2023 est.)
other: 43.8% (2023 est.)
Legislative branch
legislative structure: bicameral
Maritime claims
International organization participation
National holiday
Nationality
adjective: South Sudanese
Natural resources
Geography - note
Economic overview
Political parties
Democratic Forum or DF
Labour Party or LPSS
South Sudan Opposition Alliance or SSOA
Sudan African National Union or SANU
Sudan People's Liberation Movement or SPLM
Sudan People’s Liberation Movement-In Opposition or SPLM-IO
United Democratic Salvation Front or UDSF
United South Sudan African Party or USSAP
United South Sudan Party or USSP
Railways
note: a narrow gauge, single-track railroad between Babonosa (Sudan) and Wau, the only existing rail system, was repaired in 2010 with $250 million in UN funds, but is not currently operational
Suffrage
Terrain
Government type
Country name
conventional short form: South Sudan
etymology: self-descriptive name from the country's geographic position within Sudan prior to independence; the name Sudan derives from the Arabic balad-as-sudan, meaning "Land of the Black [peoples]"
Location
Map references
Irrigated land
Diplomatic representation in the US
chancery: 1015 31st Street NW, Suite 300, Washington, DC 20007
telephone: [1] (202) 600-2238
FAX: [1] (202) 644-9910
email address and website:
info.ssdembassy@gmail.com
https://www.ssembassydc.org/
Internet country code
Refugees and internally displaced persons
IDPs: 1,359,795 (2024 est.)
stateless persons: 18,000 (2024 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
Trafficking in persons
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 4.12% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Broadcast media
Drinking water source
urban: 70% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 33.6% of population (2022 est.)
total: 41.2% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 30% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 66.4% of population (2022 est.)
total: 58.8% of population (2022 est.)
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: collective/Mido SAMUEL and Juba University students
history: adopted 2011; anthem selected in a national contest
Major urban areas - population
National symbol(s)
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of South Sudan
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years
Population distribution
Electricity access
electrification - urban areas: 15%
electrification - rural areas: 1.7%
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
Sanitation facility access
urban: 60.6% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 15.5% of population (2022 est.)
total: 24.9% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 39.4% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 84.5% of population (2022 est.)
total: 75.1% of population (2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
note: Figures are estimations due to population changes during South Sudan's civil war and the lack of updated demographic studies
Religions
Languages
major-language sample(s):
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information. (English)
كتاب حقائق العالم، المصدر الذي لا يمكن الاستغناء عنه للمعلومات الأساسية (Arabic)
Environmental issues
Elevation
lowest point: White Nile 381 m
Physician density
Health expenditure
2.1% of national budget (2022 est.)
Military - note
the SSPDF, formerly the Sudan People’s Liberation Army (SPLA), was founded as a guerrilla movement against the Sudanese Government in 1983 and participated in the Second Sudanese Civil War (1983-2005); the Juba Declaration that followed the Comprehensive Peace Agreement of 2005 unified the SPLA and the South Sudan Defense Forces (SSDF), the second-largest rebel militia remaining from the civil war, under the SPLA name; in 2017, the SPLA was renamed the South Sudan Defense Forces (SSDF) and in September 2018 was renamed again as the SSPDF
the UN Mission in South Sudan (UNMISS) has operated in the country since 2011 with the objectives of consolidating peace and security and helping establish conditions for the successful economic and political development of South Sudan; UNMISS has about 18,000 personnel assigned; the UN Interim Security Force for Abyei (UNISFA) has operated in the disputed Abyei region along the border between Sudan and South Sudan since 2011; its mission includes ensuring security, protecting civilians, strengthening the capacity of the Abyei Police Service, de-mining, monitoring/verifying the redeployment of armed forces from the area, and facilitating the flow of humanitarian aid; UNISFA has approximately 3,800 personnel assigned (2025)
Military and security service personnel strengths
note: some active SSPDF personnel may be militia; the National/Necessary Unified Forces (NUF) were expected to have up to 80,000 personnel when training and integration is completed; the first batch of approximately 20,000 NUF personnel completed training in late 2022
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
note: South Sudan has been under a UN arms embargo since 2018 (extended for 1 year in May 2025)
Internet users
Total water withdrawal
industrial: 225 million cubic meters (2022 est.)
agricultural: 240 million cubic meters (2022 est.)
Total renewable water resources
Imports - partners
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Imports - commodities
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Exports - partners
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Exports - commodities
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Waste and recycling
International environmental agreements
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Major rivers (by length in km)
note: [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Coal
Electricity generation sources
solar: 6.8% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Petroleum
refined petroleum consumption: 11,000 bbl/day (2023 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 3.75 billion barrels (2021 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
Remittances
0% of GDP (2014 est.)
0% of GDP (2013 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
Household income or consumption by percentage share
highest 10%: 33% (2016 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
Legislative branch - lower chamber
number of seats: 550 (all appointed)
scope of elections: full renewal
most recent election date: 5/10/2021
percentage of women in chamber: 32.4%
expected date of next election: December 2026
Legislative branch - upper chamber
number of seats: 100 (all appointed)
scope of elections: full renewal
most recent election date: 8/2/2021
percentage of women in chamber: 32.1%
expected date of next election: December 2026
National color(s)
Particulate matter emissions
Methane emissions
agriculture: 696 kt (2019-2021 est.)
waste: 120.2 kt (2019-2021 est.)
other: 12.7 kt (2019-2021 est.)
Labor force
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 19.4% (2023 est.)
female: 17.6% (2023 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
Net migration rate
Median age
male: 18.7 years
female: 18.7 years
Maternal mortality ratio
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$94.914 million (2022 est.)
$341.932 million (2021 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
Total fertility rate
Unemployment rate
12.6% (2022 est.)
14.1% (2021 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
Carbon dioxide emissions
from petroleum and other liquids: 1.725 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
Area
land: NA
water: NA
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$6.585 billion (2022 est.)
$6.945 billion (2021 est.)
note: data in 2015 dollars
Airports
Infant mortality rate
male: 65.8 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 54.1 deaths/1,000 live births
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
2.4% (2023 est.)
-6.7% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
Current account balance
-$596.748 million (2022 est.)
-$6.55 million (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
Real GDP per capita
$400 (2022 est.)
$400 (2021 est.)
note: data in 2015 dollars
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: (2023 est.) less than 1
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
Energy consumption per capita
Death rate
Birth rate
Electricity
consumption: 566.034 million kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 23.966 million kWh (2023 est.)
Imports
$6.402 billion (2022 est.)
$4.037 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
Exports
$5.811 billion (2022 est.)
$4.652 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
Heliports
Life expectancy at birth
male: 58.4 years
female: 62.2 years
Real GDP growth rate
-13.9% (2016 est.)
-10.8% (2015 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
Industrial production growth rate
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 33.1% (2015 est.)
services: 56.6% (2015 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
Education expenditure
3.3% national budget (2015 est.)
Population growth rate
Military service age and obligation
note: the UN reports that there are thousands of child soldiers in South Sudan serving in the SSPDF and militia forces although the South Sudanese Government has pledged to end the practice
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 76.3 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 4.8 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 20.8 (2025 est.)
Population
male: 6,765,722
female: 6,534,344
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 47 (2023 est.)
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: (2023 est.) less than 1