Niue - NU - NIU - Australia and Oceania
Niue Images
Niue Factbook Data
Dependency status
Diplomatic representation from the US
note: on 25 September 2023, the US officially established diplomatic relations with Niue
Geographic coordinates
Natural hazards
Area - comparative
Background
Voyagers from Samoa first settled on Niue around A.D. 900, and a second main group of settlers came from Tonga around 1500. With only one reliable source of fresh water, conflict was high on the island. Samoan and Tongan customs heavily influenced Niuean culture, including the formation of an island-wide elected kingship system in the early 1700s. In 1774, British explorer James COOK landed on the island and named it Savage Island because of the Niueans' hostility. Missionaries arrived in 1830 but were also largely unsuccessful at staying on the island until 1846, when a Niuean trained as a Samoan missionary returned to the island and provided a space from which the missionaries could work. In addition to converting the population, the missionaries worked to stop the violent conflicts and helped establish the first parliament in 1849.
Great Britain established a protectorate over Niue in 1900. The following year, Niue was annexed to New Zealand and included as part of the Cook Islands. Niue’s remoteness and cultural and linguistic differences with the Cook Islands led New Zealand to separate Niue into its own administration in 1904. The island became internally self-governing in 1974; it is an independent member of international organizations but is in free association with New Zealand, which is responsible for defense and foreign affairs. In September 2023, the US recognized Niue as a sovereign and independent state.
Environmental issues
International environmental agreements
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Exports - commodities
note: top export commodities based on value in dollars over $500,000
Administrative divisions
Agricultural products
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Military and security forces
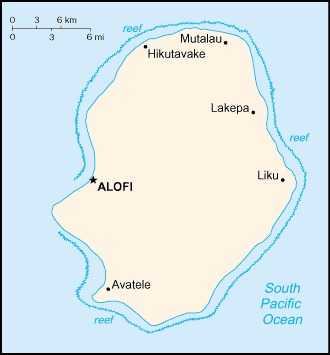
Capital
geographic coordinates: 19 01 S, 169 55 W
time difference: UTC-11 (6 hours behind Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: a traditional name for an area of the island; became the name for the newly declared capital in the 20th century
Imports - commodities
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Climate
Coastline
Constitution
amendment process: proposed by the Assembly; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of the Assembly membership in each of three readings and approval by at least two-thirds majority votes in a referendum; passage of amendments to a number of sections, including Niue’s self-governing status, British nationality and New Zealand citizenship, external affairs and defense, economic and administrative assistance by New Zealand, and amendment procedures, requires at least two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly and at least two thirds of votes in a referendum
Exchange rates
Exchange rates:
1.652 (2024 est.)
1.628 (2023 est.)
1.577 (2022 est.)
1.414 (2021 est.)
1.542 (2020 est.)
Executive branch
head of government: Prime Minister Dalton TAGELAGI; also referred to as premier (since 10 June 2020)
cabinet: Cabinet chosen by the prime minister
election/appointment process: the monarchy is hereditary; prime minister indirectly elected by the Legislative Assembly for a 3-year term
most recent election date: 8 May 2023
election results: Dalton TAGELAGI reelected prime minister; Legislative Assembly vote - Dalton TAGELAGI (independent) 16, O'Love JACOBSEN (independent) 4
expected date of next election: 2026
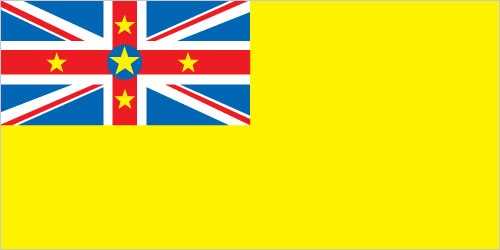
Flag
meaning: the large star represents Niue, and the smaller stars symbolize links with New Zealand; yellow stands for sunshine, as well as the warmth and friendship between Niue and New Zealand
Independence
Industries
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: Niue chief justice appointed by the governor general on the advice of the Cabinet and tendered by the premier; other judges appointed by the governor general on the advice of the Cabinet and tendered by the chief justice and the minister of justice; judges serve until age 68
subordinate courts: High Court
note: the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (in London) is the final appeal court beyond the Niue Court of Appeal
Land boundaries
Land use
arable land: 3.8% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 10.8% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 3.8% (2023 est.)
forest: 72.6% (2023 est.)
other: 9% (2023 est.)
Legal system
Legislative branch
legislative structure: unicameral
number of seats: 20
electoral system: plurality/majority
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 3 years
most recent election date: 29 April 2023
parties elected and seats per party: independents (20)
percentage of women in chamber: 15%
expected date of next election: April 2026
Maritime claims
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
International organization participation
National holiday
Nationality
adjective: Niuean
Natural resources
Geography - note
Economic overview
Political parties
Suffrage
Terrain
Government type
Military - note
Country name
conventional short form: Niue
former: Savage Island
etymology: the origin of the name is obscure; in Niuean, the word translates as "behold the coconut;" the former name, Savage Island, was the result of an acrimonious meeting in 1774 between English explorer Captain James COOK and local people
note: pronunciation falls between nyu-way and new-way, but not like new-wee
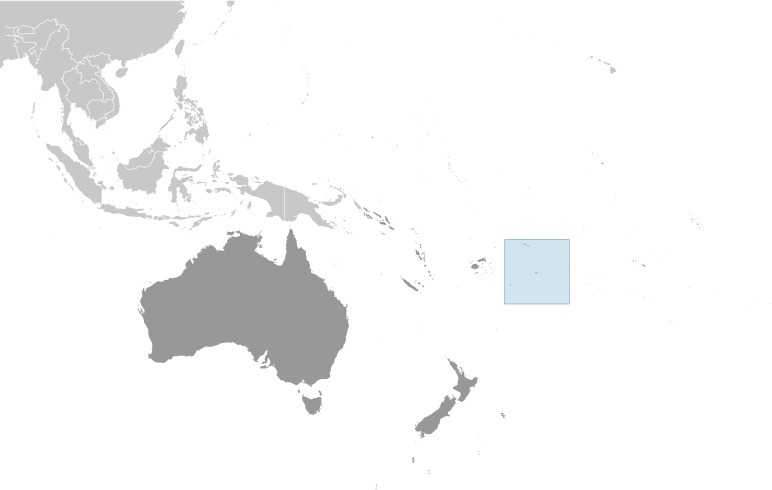
Location
Map references
Irrigated land
Diplomatic representation in the US
Internet users
Internet country code
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 1.43% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Broadcast media
Drinking water source
total: 97% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
total: 3% of population (2022 est.)
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: unknown/unknown, prepared by Sioeli FUSIKATA
history: adopted 1974
title: "God Save the King"
lyrics/music: unknown
history: in use since 1745
Major urban areas - population
National symbol(s)
Population distribution
Sanitation facility access
total: 97.4% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
total: 2.6% of population (2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
note: data represent the resident population
Religions
Languages
Elevation
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
Health expenditure
6.9% of national budget (2022 est.)
Literacy
male: 100% (2022 est.)
female: 100% (2022 est.)
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 38.2 (2024)
elderly dependency ratio: 26.4 (2024)
potential support ratio: 3.8 (2024)
Imports - partners
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Exports - partners
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Electricity generation sources
Petroleum
Ports
large: 0
medium: 0
small: 0
very small: 1
ports with oil terminals: 0
key ports: Alofi
National color(s)
Particulate matter emissions
Population
male: 877 (2024 est.)
female: 938 (2024 est.)
Carbon dioxide emissions
from petroleum and other liquids: 9,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
Area
land: 260 sq km
water: 0 sq km
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$19.9 million (2020 est.)
$20.9 million (2019 est.)
Airports
Real GDP per capita
$11,800 (2020 est.)
$12,400 (2019 est.)
note: data are in 2009 dollars
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
Electricity
consumption: 3 million kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 400,000 kWh (2023 est.)
Merchant marine
by type: bulk carrier 5, container ship 2, general cargo 29, oil tanker 4, other 30
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 4.28 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 1.89 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 2.33 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
female: 75.7 years (2016 est.)
Education expenditure
Population growth rate
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 54 (2022 est.)