Iran - IR - IRN - IRI - Middle East

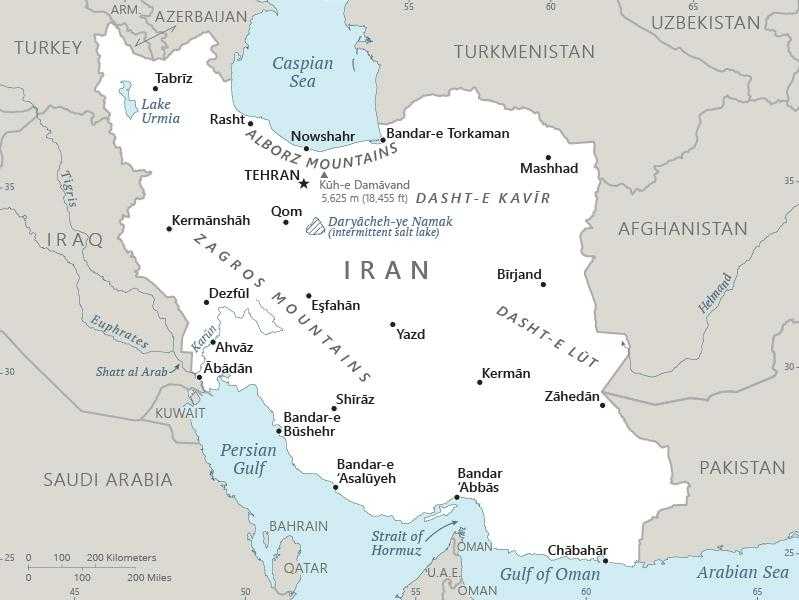
Iran Images
Iran Factbook Data
Diplomatic representation from the US
Age structure
15-64 years: 69.8% (male 31,413,125/female 30,267,241)
65 years and over: 7% (2024 est.) (male 2,869,617/female 3,283,875)
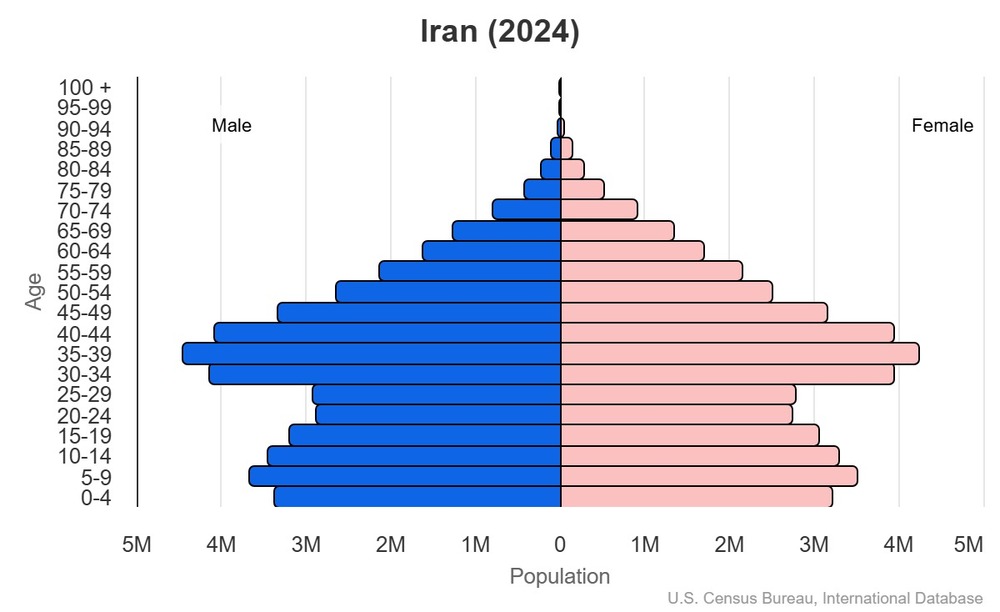
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
Geographic coordinates
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.87 male(s)/female
total population: 1.03 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Natural hazards
Area - comparative
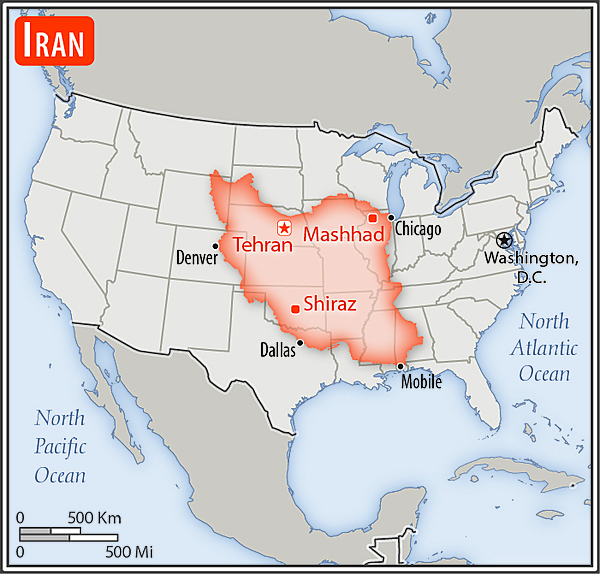
almost 2.5 times the size of Texas; slightly smaller than Alaska
Military service age and obligation
note: conscripts may serve in the Artesh, IRGC, or Law Enforcement
Background
Known as Persia until 1935, Iran became an Islamic republic in 1979 after the ruling monarchy was overthrown and Shah Mohammad Reza PAHLAVI was forced into exile. Conservative clerical forces led by Ayatollah Ruhollah KHOMEINI established a theocratic system of government with ultimate political authority vested in a religious scholar known as the Supreme Leader, who is accountable only to the Assembly of Experts -- an elected 88-member body of clerics. US-Iran relations became strained when Iranian students seized the US Embassy in Tehran in November 1979 and held embassy personnel hostage until mid-January 1981. The US cut off diplomatic relations with Iran in April 1980. From 1980 to 1988, Iran fought a bloody, indecisive war with Iraq that eventually expanded into the Persian Gulf and led to clashes between US Navy and Iranian military forces. Iran has been designated a state sponsor of terrorism since 1984.
After the election of reformer Hojjat ol-Eslam Mohammad KHATAMI as president in 1997 and a reformist Majles (legislature) in 2000, a political reform campaign in response to popular dissatisfaction was initiated, but conservative politicians blocked reform measures while increasing repression. Municipal and legislative elections in 2003 and 2004 saw conservatives reestablish control over Iran's elected government institutions, culminating in the 2005 inauguration of hardliner Mahmud AHMADI-NEJAD as president. His reelection in 2009 sparked nationwide protests over allegations of electoral fraud, and the protests persisted until 2011. In 2013, Iranians elected to the presidency centrist cleric Dr. Hasan Fereidun RUHANI, a longtime senior regime member who promised to reform society and foreign policy. In 2019, Tehran's sudden decision to increase the gasoline price sparked nationwide protests, which the regime violently suppressed. Conservatives won the majority in Majles elections in 2020, and hardline cleric Ebrahim RAISI was elected president in 2021, resulting in a conservative monopoly across the regime's elected and unelected institutions.
Iran continues to be subject to a range of international sanctions and export controls because of its involvement in terrorism, weapons proliferation, human rights abuses, and concerns over the nature of its nuclear program. Iran received nuclear-related sanctions relief in exchange for nuclear concessions under the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action's (JCPOA) Implementation Day beginning in 2016. However, the US reimposed nuclear-related sanctions on Iran after it unilaterally terminated its JCPOA participation in 2018. In October 2023, the EU and the UK also decided to maintain nuclear-proliferation-related measures on Iran, as well as arms and missile embargoes, in response to Iran's non-compliance with its JCPOA commitments.
As president, RAISI has concentrated on deepening Iran's foreign relations with anti-US states -- particularly China and Russia -- to weather US sanctions and diplomatic pressure, while supporting negotiations to restore a nuclear deal that began in 2021. RAISI contended with nationwide protests that began in September 2022 and persisted for over three months after the death of a Kurdish Iranian woman, Mahsa AMINI, in morality police custody. Young people and women led the protests, and demands focused on regime change.
Environmental issues
International environmental agreements
signed, but not ratified: Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Environmental Modification, Law of the Sea, Marine Life Conservation
Military expenditures
2.3% of GDP (2023 est.)
2.5% of GDP (2022 est.)
2.3% of GDP (2021 est.)
2.1% of GDP (2020 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
highest 10%: 28.2% (2023 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
Exports - commodities
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Exports - partners
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Administrative divisions
Agricultural products
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Military and security forces
Artesh: Ground Forces, Navy (includes marines), Air Force, Air Defense Forces
IRGC: Ground Forces, Navy (includes marines), Aerospace Force (controls strategic missile force), Qods Force (aka Quds Force; special operations), Cyber Electronic Command, Basij Paramilitary Forces
Ministry of Interior: Law Enforcement Command (FARAJA)
Ministry of Intelligence and Security (2025)
note 1: the Artesh primarily focuses on defending Iran’s borders and territorial waters from external threats, while the IRGC has a broader mission to defend the Iranian revolution from any foreign or domestic threat
note 2: the Artesh Navy operates Iran’s larger warships and operates in the Gulf of Oman, the Caspian Sea, and deep waters in the region and beyond; the IRGC Navy has responsibility for the closer-in waters of the Persian Gulf and Strait of Hormuz
note 3: the Basij is a volunteer paramilitary group, which sometimes acts as an auxiliary law enforcement unit for the IRGC; it is formally known as the Organization for the Mobilization of the Oppressed and also known as the Popular Mobilization Army
note 4: the Ministry of Intelligence and Security and law enforcement forces under the Interior Ministry, which report to the president, and the IRGC, which reports to the supreme leader, share responsibility for law enforcement and maintaining order
note 5: the FARAJA is the uniformed police of Iran; it includes branches for public security, traffic control, anti-narcotics, special forces (riot control, counterterrorism, hostage rescue, etc), intelligence, and criminal investigations; the FARAJA also has responsibility for border security (Border Guard Command)
Budget
expenditures: $90.238 billion (2019 est.)
Capital
geographic coordinates: 35 42 N, 51 25 E
time difference: UTC+3.5 (8.5 hours ahead of Washington, DC)
daylight saving time: does not observe daylight savings time
etymology: the name probably means "flat" or "lower," referring to its location in the foothills of the Elburz Mountains
Imports - commodities
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Climate
Coastline
note: Iran also borders the Caspian Sea (740 km)
Constitution
amendment process: proposed by the supreme leader – after consultation with the Exigency Council – and submitted as an edict to the "Council for Revision of the Constitution," a body consisting of various executive, legislative, judicial, and academic leaders and members; passage requires absolute majority vote in a referendum and approval of the supreme leader; articles including Iran’s political system, its religious basis, and its form of government cannot be amended
Exchange rates
Exchange rates:
42,000 (2023 est.)
42,000 (2022 est.)
42,000 (2021 est.)
42,000 (2020 est.)
42,000 (2019 est.)
Executive branch
head of government: President Masoud PEZESHKIAN (since 30 July 2024)
cabinet: Council of Ministers selected by the president with legislative approval; the supreme leader has some control over appointments to several ministries
election/appointment process: supreme leader appointed for life by Assembly of Experts; president directly elected by absolute-majority popular vote in 2 rounds, if needed, for a 4-year term (eligible for a second term and an additional nonconsecutive term)
most recent election date: 28 June 2024, with runoff held on 5 July 2024
election results:
2024: first round results - Masoud PEZESHKIAN (independent) 44.4%, Saeed JALILI (Front of Islamic Revolution Stability) 40.4%, Mohammad Baqer QAKIBAF (Progress and Justice Population of Islamic Iran) 14.3%, other 0.9%; second round results - Masoud PEZESHKIAN elected; Masoud PEZESHKIAN 54.8%, Saeed JALILI 45.2%
2021: Ebrahim RAISI elected president; percent of vote - Ebrahim RAISI (independent) 72.4%, Mohsen REZAI (RFII) 13.8%, Abbdolnaser HEMATI (ECP) 9.8%, Amir-Hosein Qazizadeh-HASHEMI (Islamic Law Party) 4%
note: presidential election held early due to the death of President Ebrahim RAISI in a helicopter accident in May 2024
Flag
meaning: green is the color of Islam and also represents growth, white stands for honesty and peace, and red for bravery and martyrdom
Independence
Industries
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court president appointed by the head of the High Judicial Council (HJC), a 5-member body to include the Supreme Court chief justice, the prosecutor general, and 3 clergy, in consultation with judges of the Supreme Court; president appointed for a single, renewable 5-year term; other judges appointed by the HJC; judge tenure NA
subordinate courts: Penal Courts I and II; Islamic Revolutionary Courts; Courts of Peace; Special Clerical Court (functions outside the judicial system and handles cases involving clerics); military courts
Land boundaries
border countries (7): Afghanistan 921 km; Armenia 44 km; Azerbaijan 689 km; Iraq 1,599 km; Pakistan 959 km; Turkey 534 km; Turkmenistan 1,148 km
Land use
arable land: 9.7% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 1.2% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 18.2% (2023 est.)
forest: 6.6% (2023 est.)
other: 64.4% (2023 est.)
Legal system
Legislative branch
legislative structure: unicameral
number of seats: 290 (all directly elected)
electoral system: plurality/majority
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 4 years
most recent election date: 3/1/2024 to 5/10/2024
percentage of women in chamber: 4.9%
expected date of next election: February 2028
note: all candidates to the Majles must be approved by the Council of Guardians, a 12-member group of which 6 are appointed by the supreme leader and 6 are jurists nominated by the judiciary and elected by the Majles
Literacy
male: 90% (2016 est.)
female: 81% (2016 est.)
Maritime claims
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: bilateral agreements or median lines in the Persian Gulf
continental shelf: natural prolongation
International organization participation
National holiday
Nationality
adjective: Iranian
Natural resources
Geography - note
Economic overview
Political parties
Executives of Construction Party
Front of Islamic Revolutionary Stability
Islamic Coalition Party
Progress and Justice Population of Islamic Iran
Militant Clerics Society (Majma-e Ruhaniyoun-e Mobarez) or MRM
Moderation and Development Party
National Trust Party (Hezb-e E'temad-eMelli) or HEM
Progress and Justice Society
Union of Islamic Iran People's Party (Hezb-e Ettehad-e Iran-e Eslami)
Railways
standard gauge: 8,389.5 km (2014) 1.435-m gauge (189.5 km electrified)
broad gauge: 94 km (2014) 1.676-m gauge
Suffrage
Terrain
Government type
Country name
conventional short form: Iran
local long form: Jomhuri-ye Eslami-ye Iran
local short form: Iran
former: Persia
etymology: the name derives from the Sanskrit word arya, referring to people living in a mountainous land, from the root word ar-, or "mountain;" the former name, Persia, was originally "Pars" (or the Arabic-influenced variant "Fars") from the Old Persian parsi, meaning "pure"
Location
Map references
Irrigated land
Diplomatic representation in the US
note: Iran has an Interests Section in the Pakistani Embassy; address: Iranian Interests Section, Embassy of Pakistan, 1250 23rd Street NW, Washington, DC 20037; telephone: [1] (202) 965-4990; FAX [1] (202) 965-1073; email: requests@daftar.org; info@daftarwashington.com; website: https://daftar.org/
Internet users
Internet country code
Refugees and internally displaced persons
IDPs: 421 (2024 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
Trafficking in persons
Total renewable water resources
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
male: 14 years (2020 est.)
female: 14 years (2020 est.)
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 1.32% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Broadcast media
Drinking water source
urban: 98.7% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 94.4% of population (2022 est.)
total: 97.7% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 1.3% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 5.6% of population (2022 est.)
total: 2.3% of population (2022 est.)
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: multiple authors/Hassan RIAHI
history: adopted 1990
note: a recording of the current Iranian national anthem is unavailable because the US Navy Band does not record anthems for countries from which the US does not anticipate official visits; the US does not have diplomatic relations with Iran
Major urban areas - population
International law organization participation
Physician density
Hospital bed density
National symbol(s)
GDP - composition, by end use
government consumption: 12.9% (2024 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 26.7% (2024 est.)
investment in inventories: 13.3% (2024 est.)
exports of goods and services: 22.9% (2024 est.)
imports of goods and services: -26.8% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: the father must be a citizen of Iran
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Population distribution
Electricity access
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
Sanitation facility access
urban: 100% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 100% of population (2022 est.)
total: 100% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 0% of population (2022 est.)
total: 0% of population (2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
Religions
Languages
major-language sample(s):
چکیده نامه جهان، منبعی ضروری برای کسب اطلاعات کلی جهان (Persian)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Imports - partners
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Elevation
lowest point: Caspian Sea -28 m
mean elevation: 1,305 m
Health expenditure
19% of national budget (2022 est.)
Military - note
the Iran-Iraq War (1980–88) transformed the IRGC into more of a conventional fighting force with its own ground, air, naval, and special forces, plus control over Iran’s strategic missile and rocket forces; today, the IRGC is a highly institutionalized and parallel military force to Iran’s regular armed forces (Artesh); it is involved in internal security and has influence in the political and economic spheres of Iranian society, as well as Iran’s foreign policy; on the economic front, it owns factories and corporations and subsidiaries in banking, infrastructure, housing, airlines, tourism and other sectors; its special operations forces, known as the Qods/Quds Force, specialize in foreign missions and have provided advice, funding, guidance, material support, training, and weapons to militants in countries such as Afghanistan, Iraq, Syria, and Yemen, as well as extremist groups, including HAMAS, Hizballah, Kata’ib Hizballah, and Palestine Islamic Jihad; the Qods Force also conducts intelligence and reconnaissance operations; note - both the IRGC and the Qods Force have been designated as foreign terrorist organizations by the US (see Terrorist Organizations under References)
the Supreme Council for National Security (SCNS) is the senior-most body for formulating Iran’s foreign and security policy; it is formally chaired by the president, who also appoints the SCNS secretary; its members include the speaker of the Majles, the head of the judiciary, the chief of the Armed Forces General Staff (chief of defense or CHOD), the commanders of the Artesh (regular forces) and IRGC, and the ministers of defense, foreign affairs, interior, and intelligence; the SCNS reports to the supreme leader; the supreme leader is the commander-in-chief of the armed forces
the Iranian Armed Forces are divided between the regular forces (Artesh) and the IRGC; the Artesh primarily focuses on defending Iran’s borders and territorial waters from external threats, while the IRGC has a broader mission to defend the Iranian revolution from any foreign or domestic threat; in 1989, Iran established the Armed Forces General Staff to coordinate military action across both the Artesh and the IRGC; Iran also has a joint military headquarters, the Khatam ol-Anbia Central Headquarters, to command the Artesh and IRGC in wartime (2024)
Military and security service personnel strengths
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
Military deployments
Terrorist group(s)
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in the Terrorism reference guide
Total water withdrawal
industrial: 1.1 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
agricultural: 86 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
Waste and recycling
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 16.8% (2022 est.)
Average household expenditures
on alcohol and tobacco: 0.5% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Major rivers (by length in km)
note: [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
National heritage
selected World Heritage Site locales: Persepolis (c); Tchogha Zanbil (c); Bam and its Cultural Landscape (c); Golestan Palace (c); Shushtar Historical Hydraulic System (c); Pasargadae (c); Hyrcanian Forests (n); Tabriz Historic Bazaar Complex (c); Meidan Emam, Esfahan (c); Bisotun (c); Takht-e Soleyman (c); Soltaniyeh(c); Bisotun (c); Armenian Monastic Ensembles of Iran(c); Sheikh Safi al-din Khānegāh and Shrine Ensemble in Ardabil (c); The Persian Garden (c); Gonbad-e Qābus (c); Masjed-e Jāmé of Isfahan (c); Shahr-i Sokhta (c); Cultural Landscape of Maymand (c); Susa (c); Lut Desert (n);The Persian Qanat (c); Historic City of Yazd (c); Sassanid Archaeological Landscape of Fars Region (c); Cultural Landscape of Hawraman/Uramanat (c); Trans-Iranian Railway (c); The Persian Caravanserai (c); Hegmataneh (c); Prehistoric Sites of the Khorramabad Valley (c)
Coal
consumption: 3.032 million metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 212,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 1.098 million metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 1.203 billion metric tons (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
nuclear: 1.6% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
solar: 0.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
wind: 0.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 3.4% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Natural gas
consumption: 252.353 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
exports: 14.698 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
imports: 2.274 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 33.987 trillion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Petroleum
refined petroleum consumption: 2.415 million bbl/day (2023 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 208.6 billion barrels (2021 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
Remittances
0% of GDP (2022 est.)
0% of GDP (2021 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
Nuclear energy
Number of nuclear reactors under construction: 1 (2025)
Net capacity of operational nuclear reactors: 0.92GW (2025 est.)
Percent of total electricity production: 1.7% (2023 est.)
Space program overview
Space launch site(s)
Space agency/agencies
note 1: ISA and ISRC are subordinate to the Ministry of Information and Communications Technology; along with the MODAFL, they oversee part of Iran's satellite development programs; they also work with Iranian universities, private industry, and foreign partners to develop satellites
note 2: MODAFL and the IRGC-ARF oversee Iran's satellite/space launch vehicle development program
Geoparks
global geoparks and regional networks: Aras; Qeshm Island; Tabas (2023)
Ports
large: 0
medium: 4
small: 6
very small: 8
ports with oil terminals: 13
key ports: Abadan, Bandar Abbas, Bushehr, Khorramshahr
National color(s)
Particulate matter emissions
Key space-program milestones
2006 - first successful launch of a small, domestically produced communications and research satellite (Omid) on the Safir SLV
2010 - began developing a more capable 2-stage orbital SLV (Simorgh; aka Safir-2)
2011 - launched first domestically produced remote sensing (RS) satellite (Rasad) on Safir SLV
2020 - placed RS microsatellite (Noor) in orbit on 3-stage SLV (Qased or Messenger)
2021 - first launch of road-mobile 3-stage SLV (Zuljanah)
2022 - completed suborbital test of new small-lift SLV (Quam-100)
Methane emissions
agriculture: 819.7 kt (2019-2021 est.)
waste: 832.7 kt (2019-2021 est.)
other: 37.6 kt (2019-2021 est.)
Labor force
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 20% (2024 est.)
female: 35.5% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
Net migration rate
Median age
male: 33.6 years
female: 34.1 years
Debt - external
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
Maternal mortality ratio
Public debt
note: includes publicly guaranteed debt
Total fertility rate
Unemployment rate
9.1% (2023 est.)
9.1% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
Carbon dioxide emissions
from coal and metallurgical coke: 7.136 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 316.922 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 499.306 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
Area
land: 1,531,595 sq km
water: 116,600 sq km
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$1.442 trillion (2023 est.)
$1.373 trillion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Airports
Infant mortality rate
male: 15.4 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 13.2 deaths/1,000 live births
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
44.6% (2023 est.)
43.5% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
Real GDP per capita
$15,900 (2023 est.)
$15,300 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 12 (2023 est.)
Tobacco use
male: 23.8% (2025 est.)
female: 2.8% (2025 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
Energy consumption per capita
Death rate
Birth rate
Electricity
consumption: 335.175 billion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 5.723 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 3.136 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 37.948 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Merchant marine
by type: bulk carrier 32, container ship 28, general cargo 398, oil tanker 86, other 421
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
Imports
$113.21 billion (2023 est.)
$97.729 billion (2022 est.)
note: GDP expenditure basis - imports of goods and services in current dollars
Exports
$97.924 billion (2023 est.)
$105.752 billion (2022 est.)
note: GDP expenditure basis - exports of goods and services in current dollars
Heliports
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.02 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
male: 74.3 years
female: 77.1 years
Real GDP growth rate
5% (2023 est.)
3.8% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
Industrial production growth rate
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 36.4% (2024 est.)
services: 47.9% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
Education expenditure
18.8% national budget (2022 est.)
Population growth rate
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 174 (2024 est.)
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 30.4 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 12.4 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 8.1 (2025 est.)
Population
male: 45,098,223
female: 44,079,134
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 31 (2024 est.)

