British Indian Ocean Territory - IO - IOT - South Asia
Last updated: January 21, 2026

British Indian Ocean Territory Images
British Indian Ocean Territory Factbook Data
Dependency status
overseas territory of the UK; administered by a commissioner, resident in the Foreign, Commonwealth, and Development Office in London
Diplomatic representation from the US
embassy: none (overseas territory of the UK)
Geographic coordinates
6 00 S, 71 30 E
note: Diego Garcia 7 20 S, 72 25 E
note: Diego Garcia 7 20 S, 72 25 E
Natural hazards
none; located outside routes of Indian Ocean cyclones
Area - comparative
land area is about one-third the size of Washington, D.C.
Background
Formerly administered as part of the British Crown Colony of Mauritius, the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) was established as an overseas territory of the UK in 1965. A number of the islands in the territory were later transferred to the Seychelles when it gained independence in 1976. Subsequently, BIOT has consisted of the six main island groups that make up the Chagos Archipelago. Only Diego Garcia, the largest and most southerly of the islands, is inhabited. It contains a joint UK-US naval support facility and hosts one of four dedicated ground antennas that assist in the operation of the Global Positioning System (GPS) navigation system -- the others are on Kwajalein (Marshall Islands); at Cape Canaveral, Florida (US); and on Ascension Island (Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha). The US Air Force also operates a telescope array on Diego Garcia as part of the Ground-Based Electro-Optical Deep Space Surveillance System (GEODSS) for tracking orbital debris, which can be a hazard to spacecraft and astronauts.
Between 1967 and 1973, the former agricultural workers who lived on the islands were relocated, primarily to Mauritius but also to the Seychelles. Negotiations with the UK between 1971 and 1982 resulted in the establishment of a trust fund to compensate the displaced islanders, known as Chagossians. Beginning in 1998, the islanders pursued a series of lawsuits against the British Government, seeking further compensation and the right to return to the territory. British court rulings in 2006 and 2007 invalidated immigration policies that had excluded the islanders from the archipelago, but in 2008, the House of Lords -- the final court of appeal in the UK -- ruled in favor of the British Government by overturning the lower court rulings and finding no right of return for the Chagossians. In 2015, the Permanent Court of Arbitration unanimously held that the marine protected area that the UK declared around the Chagos Archipelago in 2010 violated the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea.
In 2019, the International Court of Justice ruled in an advisory opinion that Britain’s decolonization of Mauritius was not lawful because of continued Chagossian claims. A non-binding 2019 UN General Assembly vote demanded that Britain end its “colonial administration” of the Chagos Archipelago and that it be returned to Mauritius. On 22 May 2025, the United Kingdom and Mauritius signed an agreement that will lead to the transfer of sovereignty of the Chagos Archipelago to Mauritius. Under the agreement, the United Kingdom will lease Diego Garcia from Mauritius for 99 years and maintain full operational control of the joint UK-US military base.
Between 1967 and 1973, the former agricultural workers who lived on the islands were relocated, primarily to Mauritius but also to the Seychelles. Negotiations with the UK between 1971 and 1982 resulted in the establishment of a trust fund to compensate the displaced islanders, known as Chagossians. Beginning in 1998, the islanders pursued a series of lawsuits against the British Government, seeking further compensation and the right to return to the territory. British court rulings in 2006 and 2007 invalidated immigration policies that had excluded the islanders from the archipelago, but in 2008, the House of Lords -- the final court of appeal in the UK -- ruled in favor of the British Government by overturning the lower court rulings and finding no right of return for the Chagossians. In 2015, the Permanent Court of Arbitration unanimously held that the marine protected area that the UK declared around the Chagos Archipelago in 2010 violated the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea.
In 2019, the International Court of Justice ruled in an advisory opinion that Britain’s decolonization of Mauritius was not lawful because of continued Chagossian claims. A non-binding 2019 UN General Assembly vote demanded that Britain end its “colonial administration” of the Chagos Archipelago and that it be returned to Mauritius. On 22 May 2025, the United Kingdom and Mauritius signed an agreement that will lead to the transfer of sovereignty of the Chagos Archipelago to Mauritius. Under the agreement, the United Kingdom will lease Diego Garcia from Mauritius for 99 years and maintain full operational control of the joint UK-US military base.
Environmental issues
wastewater discharge into the lagoon on Diego Garcia
Military and security forces
no regular military forces
Climate
tropical marine; hot, humid, moderated by trade winds
Coastline
698 km
Exchange rates
the US dollar is used
Executive branch
chief of state: King CHARLES III (since 8 September 2022)
head of government: Commissioner Nishi DHOLAKIA (since 16 December 2024); Administrator Bob FAIRWEATHER; both reside in the UK and are represented by Commander Andrew WILLIAMS, RN, the officer commanding British Forces on Diego Garcia (since January 2025)
cabinet: NA
election/appointment process: the monarchy is hereditary; commissioner and administrator appointed by the monarch
head of government: Commissioner Nishi DHOLAKIA (since 16 December 2024); Administrator Bob FAIRWEATHER; both reside in the UK and are represented by Commander Andrew WILLIAMS, RN, the officer commanding British Forces on Diego Garcia (since January 2025)
cabinet: NA
election/appointment process: the monarchy is hereditary; commissioner and administrator appointed by the monarch
Flag
description: white with six wavy blue horizontal stripes; the UK flag is in the upper-left quadrant; the striped section has a palm tree and yellow crown (the territory's symbols) centered on the right half of the flag
meaning: the wavy stripes represent the Indian Ocean; the six blue stripes may stand for the six main atolls of the archipelago
meaning: the wavy stripes represent the Indian Ocean; the six blue stripes may stand for the six main atolls of the archipelago
Land boundaries
total: 0 km
Land use
agricultural land: 0% (2018 est.)
arable land: 0% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 0% (2018 est.)
forest: 0% (2018 est.)
other: 100% (2018 est.)
arable land: 0% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 0% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 0% (2018 est.)
forest: 0% (2018 est.)
other: 100% (2018 est.)
Legal system
the laws of the UK apply
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
Environment (Protection and Preservation) Zone: 200 nm
Environment (Protection and Preservation) Zone: 200 nm
International organization participation
UPU
Natural resources
coconuts, fish, sugarcane
Geography - note
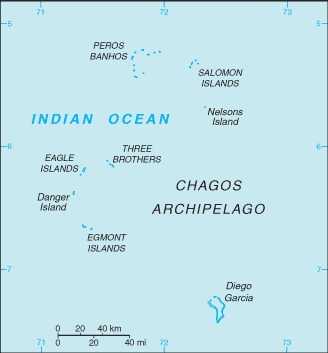
note 1: archipelago of 55 islands; Diego Garcia, the largest and southernmost island, occupies a strategic location in the central Indian Ocean
note 2: Diego Garcia is the only inhabited island of the BIOT
note 2: Diego Garcia is the only inhabited island of the BIOT
Economic overview
small island territory economy; economic activity mainly on Diego Garcia with national military installations; recently settled disputes with Mauritius have increased oil exports; established marine reserve has limited commercial fishing
Terrain
flat and low coral atolls (most areas do not exceed 2 m, or 6.6 ft, in elevation); sits atop the submarine volcanic Chagos-Laccadive Ridge
Country name
conventional long form: British Indian Ocean Territory
conventional short form: none
abbreviation: BIOT
etymology: self-descriptive name specifying the territory's affiliation and location
conventional short form: none
abbreviation: BIOT
etymology: self-descriptive name specifying the territory's affiliation and location
Location
archipelago in the Indian Ocean, south of India, about halfway between Africa and Indonesia
Map references
Political Map of the World
Diplomatic representation in the US
none (overseas territory of the UK)
Internet country code
.io
Broadcast media
Armed Forces Radio and Television Service (AFRTS) broadcasts over 3 frequencies for US and UK military personnel stationed on the islands
Communications - note
Diego Garcia hosts one of four dedicated ground antennas that assist in the operation of the Global Positioning System (GPS) navigation system (the others are on Kwajalein (Marshall Islands), at Cape Canaveral, Florida (US), and on Ascension Island (Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha))
Elevation
highest point: ocean-side dunes on Diego Garcia 9 m
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
Capital
name: administered from London; often regarded as being on Diego Garcia
geographic coordinates: 7 18S, 12 24E
time difference: UTC+6 (12 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
geographic coordinates: 7 18S, 12 24E
time difference: UTC+6 (12 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
Exports - commodities
fish (2023)
note: top export commodities based on value in dollars over $500,000
note: top export commodities based on value in dollars over $500,000
Constitution
history: British Indian Ocean Territory (Constitution) Order 2004
National anthem(s)
title: "God Save the King"
lyrics/music: unknown
history: official anthem, as a UK overseas territory
lyrics/music: unknown
history: official anthem, as a UK overseas territory
Exports - partners
Singapore 86%, Pakistan 8%, USA 1%, South Africa 1%, Czechia 1% (2023)
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, animal products, aluminum structures, insulated wire, prefabricated buildings (2023)
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Imports - partners
Greece 52%, Singapore 38%, USA 4%, Panama 2%, UAE 2% (2023)
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Ports
total ports: 1 (2024)
large: 0
medium: 0
small: 0
very small: 1
ports with oil terminals: 1
key ports: Diego Garcia
large: 0
medium: 0
small: 0
very small: 1
ports with oil terminals: 1
key ports: Diego Garcia
Population
total: no permanent inhabitants
note: Diego Garcia, the largest of the 58 islands, hosts a joint UK-US military facility
note: Diego Garcia, the largest of the 58 islands, hosts a joint UK-US military facility
Area
total : 60 sq km
land: 60 sq km (44 Diego Garcia)
water: 54,340 sq km
note: includes the entire Chagos Archipelago of 55 islands
land: 60 sq km (44 Diego Garcia)
water: 54,340 sq km
note: includes the entire Chagos Archipelago of 55 islands
Airports
1 (2025)
Military - note
defense is the responsibility of the UK; on 22 May 2025, the UK and Mauritius signed an agreement to transfer sovereignty of the Chagos Archipelago to Mauritius; under the agreement, the UK will lease Diego Garcia from Mauritius for 99 years and maintain full operational control of the joint UK-US military base (2025)