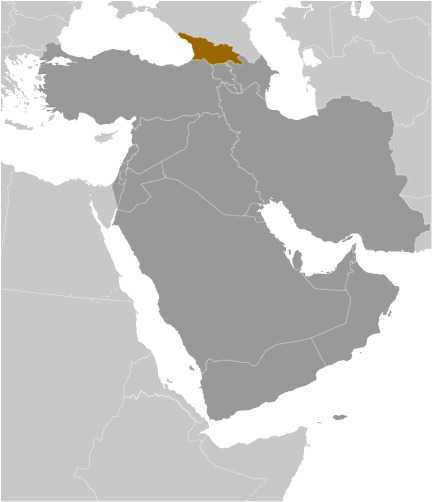
Georgia - GE - GEO - GEO - Central Asia
Last updated: January 05, 2026

Georgia Images
Georgia Factbook Data
Age structure
0-14 years: 20.6% (male 520,091/female 489,882)
15-64 years: 62.7% (male 1,500,036/female 1,572,637)
65 years and over: 16.7% (2024 est.) (male 322,941/female 495,374)
15-64 years: 62.7% (male 1,500,036/female 1,572,637)
65 years and over: 16.7% (2024 est.) (male 322,941/female 495,374)
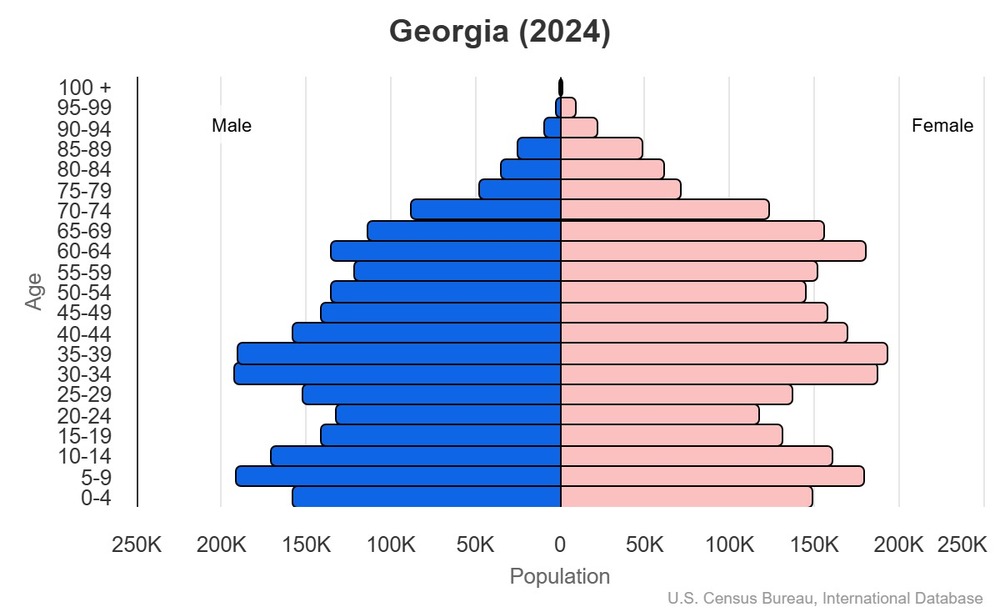
This is the population pyramid for Georgia. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
Geographic coordinates
42 00 N, 43 30 E
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.95 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.65 male(s)/female
total population: 0.92 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.95 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.65 male(s)/female
total population: 0.92 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Natural hazards
earthquakes
Area - comparative
slightly smaller than South Carolina; slightly larger than West Virginia
slightly smaller than South Carolina; slightly larger than West Virginia
Background
The region of present-day Georgia once contained the ancient kingdoms of Colchis (known as Egrisi locally) and Kartli-Iberia. The area came under Roman influence in the first centuries A.D., and Christianity became the state religion in the 330s. Persian, Arab, and Turk domination was followed by a Georgian golden age (11th-13th centuries) that was cut short when the Mongols invaded in 1236. Subsequently, the Ottoman and Persian empires competed for influence in the region. Georgia was absorbed into the Russian Empire in the 19th century. Independent for three years (1918-1921) following the Russian revolution, it was forcibly incorporated into the USSR in 1921 and regained its independence when the Soviet Union dissolved in 1991.
In 2003, mounting public discontent over rampant corruption, ineffective government services, and a government attempt to manipulate parliamentary elections touched off widespread protests that led to the resignation of Eduard SHEVARDNADZE, who had been president since 1995. In the aftermath of this "Rose Revolution," new elections in 2004 swept Mikheil SAAKASHVILI and his United National Movement (UNM) party into power. SAAKASHVILI made progress on market reforms and governance, but he faced accusations of abuse of office. Progress was further complicated when Russian support for the separatist regions of Abkhazia and South Ossetia led to a five-day conflict between Russia and Georgia in August 2008, which included Russia invading large portions of Georgian territory. Russia initially pledged to pull back from most Georgian territory but then unilaterally recognized the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia, and Russian military forces have remained in those regions.
Billionaire Bidzina IVANISHVILI's unexpected entry into politics in 2011 brought the divided opposition together under his Georgian Dream coalition, which won a majority of seats in the 2012 parliamentary elections and removed UNM from power. Conceding defeat, SAAKASHVILI named IVANISHVILI as prime minister and left the country after his presidential term ended in 2013. IVANISHVILI voluntarily resigned from office after the presidential succession, and in the years since, the prime minister position has seen frequent turnover. In 2021, SAAKASHVILI returned to Georgia, where he was immediately arrested to serve six years in prison on outstanding abuse-of-office convictions.
Popular support for integration with the West is high in Georgia. Joining the EU and NATO are among the country's top foreign policy goals, and Georgia applied for EU membership in 2022, becoming a candidate country in December 2023. Georgia and the EU have a Deep and Comprehensive Free Trade Agreement, and since 2017, Georgian citizens have been able to travel to the Schengen area without a visa.
In 2003, mounting public discontent over rampant corruption, ineffective government services, and a government attempt to manipulate parliamentary elections touched off widespread protests that led to the resignation of Eduard SHEVARDNADZE, who had been president since 1995. In the aftermath of this "Rose Revolution," new elections in 2004 swept Mikheil SAAKASHVILI and his United National Movement (UNM) party into power. SAAKASHVILI made progress on market reforms and governance, but he faced accusations of abuse of office. Progress was further complicated when Russian support for the separatist regions of Abkhazia and South Ossetia led to a five-day conflict between Russia and Georgia in August 2008, which included Russia invading large portions of Georgian territory. Russia initially pledged to pull back from most Georgian territory but then unilaterally recognized the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia, and Russian military forces have remained in those regions.
Billionaire Bidzina IVANISHVILI's unexpected entry into politics in 2011 brought the divided opposition together under his Georgian Dream coalition, which won a majority of seats in the 2012 parliamentary elections and removed UNM from power. Conceding defeat, SAAKASHVILI named IVANISHVILI as prime minister and left the country after his presidential term ended in 2013. IVANISHVILI voluntarily resigned from office after the presidential succession, and in the years since, the prime minister position has seen frequent turnover. In 2021, SAAKASHVILI returned to Georgia, where he was immediately arrested to serve six years in prison on outstanding abuse-of-office convictions.
Popular support for integration with the West is high in Georgia. Joining the EU and NATO are among the country's top foreign policy goals, and Georgia applied for EU membership in 2022, becoming a candidate country in December 2023. Georgia and the EU have a Deep and Comprehensive Free Trade Agreement, and since 2017, Georgian citizens have been able to travel to the Schengen area without a visa.
Environmental issues
air pollution, particularly in Rust'avi; heavy water pollution of Mtkvari River and the Black Sea; inadequate supplies of potable water; soil pollution from toxic chemicals; land and forest degradation; biodiversity loss; waste management
International environmental agreements
party to: Air Pollution, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Military expenditures
1.7% of GDP (2024 est.)
1.7% of GDP (2023 est.)
1.6% of GDP (2022 est.)
1.5% of GDP (2021 est.)
1.6% of GDP (2020 est.)
1.7% of GDP (2023 est.)
1.6% of GDP (2022 est.)
1.5% of GDP (2021 est.)
1.6% of GDP (2020 est.)
Population below poverty line
11.8% (2023 est.)
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 2.7% (2023 est.)
highest 10%: 26.9% (2023 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
highest 10%: 26.9% (2023 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
Exports - commodities
cars, copper ore, electricity, garments, wine (2023)
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Exports - partners
Azerbaijan 13%, Turkey 11%, Armenia 11%, Russia 10%, Kyrgyzstan 8% (2023)
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
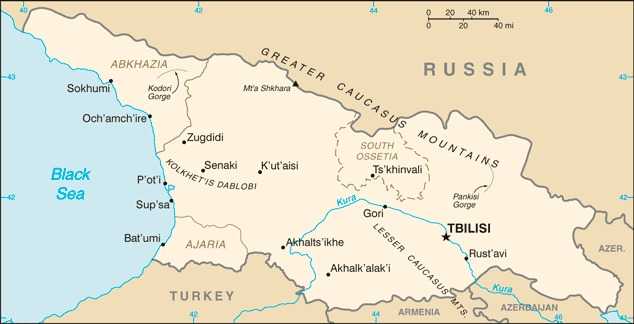
Administrative divisions
9 regions (mkharebi, singular - mkhare), 1 city (kalaki), and 2 autonomous republics (avtomnoy respubliki, singular - avtom respublika)
regions: Guria, Imereti, Kakheti, Kvemo Kartli, Mtskheta Mtianeti, Racha-Lechkhumi and Kvemo Svaneti, Samegrelo and Zemo Svaneti, Samtskhe-Javakheti, Shida Kartli; note - the breakaway region of South Ossetia consists of the northern part of Shida Kartli, eastern slivers of the Imereti region and Racha-Lechkhumi and Kvemo Svaneti, and part of western Mtskheta-Mtianeti
city: Tbilisi
autonomous republics: Abkhazia or Ap'khazet'is Avtonomiuri Respublika (Sokhumi), Ajaria or Acharis Avtonomiuri Respublika (Bat'umi)
note 1: the administrative centers of the two autonomous republics are shown in parentheses
note 2: the United States recognizes the breakaway regions of Abkhazia and South Ossetia as part of Georgia
regions: Guria, Imereti, Kakheti, Kvemo Kartli, Mtskheta Mtianeti, Racha-Lechkhumi and Kvemo Svaneti, Samegrelo and Zemo Svaneti, Samtskhe-Javakheti, Shida Kartli; note - the breakaway region of South Ossetia consists of the northern part of Shida Kartli, eastern slivers of the Imereti region and Racha-Lechkhumi and Kvemo Svaneti, and part of western Mtskheta-Mtianeti
city: Tbilisi
autonomous republics: Abkhazia or Ap'khazet'is Avtonomiuri Respublika (Sokhumi), Ajaria or Acharis Avtonomiuri Respublika (Bat'umi)
note 1: the administrative centers of the two autonomous republics are shown in parentheses
note 2: the United States recognizes the breakaway regions of Abkhazia and South Ossetia as part of Georgia
Agricultural products
milk, grapes, potatoes, maize, wheat, tangerines/mandarins, tomatoes, barley, apples, eggs (2023)
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Military and security forces
Georgian Defense Forces (GDF; aka Defense Forces of Georgia, DFG): Ground Forces, Air Force, Special Operations Forces, National Guard
Ministry of Internal Affairs: Police, Border Police of Georgia, Coast Guard of Georgia (includes naval forces, which were merged with the Coast Guard in 2009) (2025)
Ministry of Internal Affairs: Police, Border Police of Georgia, Coast Guard of Georgia (includes naval forces, which were merged with the Coast Guard in 2009) (2025)
Budget
revenues: $8.686 billion (2023 est.)
expenditures: $9.307 billion (2023 est.)
note: central government revenues (excluding grants) and expenditures converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
expenditures: $9.307 billion (2023 est.)
note: central government revenues (excluding grants) and expenditures converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
Capital
name: Tbilisi
geographic coordinates: 41 41 N, 44 50 E
time difference: UTC+4 (9 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name comes from the Georgian word tbili, meaning "warm" and referring to the hot sulfur springs in the area
geographic coordinates: 41 41 N, 44 50 E
time difference: UTC+4 (9 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name comes from the Georgian word tbili, meaning "warm" and referring to the hot sulfur springs in the area
Imports - commodities
cars, refined petroleum, packaged medicine, natural gas, garments (2023)
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Climate
warm and pleasant; Mediterranean-like on Black Sea coast
Coastline
310 km
Constitution
history: previous 1921, 1978 (based on 1977 Soviet Union constitution); latest approved 24 August 1995, effective 17 October 1995
amendment process: proposed as a draft law supported by more than one half of the Parliament membership or by petition of at least 200,000 voters; passage requires support by at least three fourths of the Parliament membership in two successive sessions three months apart and the signature and promulgation by the president of Georgia
amendment process: proposed as a draft law supported by more than one half of the Parliament membership or by petition of at least 200,000 voters; passage requires support by at least three fourths of the Parliament membership in two successive sessions three months apart and the signature and promulgation by the president of Georgia
Exchange rates
laris (GEL) per US dollar -
Exchange rates:
2.721 (2024 est.)
2.628 (2023 est.)
2.916 (2022 est.)
3.222 (2021 est.)
3.109 (2020 est.)
Exchange rates:
2.721 (2024 est.)
2.628 (2023 est.)
2.916 (2022 est.)
3.222 (2021 est.)
3.109 (2020 est.)
Executive branch
chief of state: President Mikheil KAVELASHVILI (since 29 December 2024)
head of government: Prime Minister Irakli KOBAKHIDZE (since 8 February 2024)
cabinet: Cabinet of Ministers
election/appointment process: president elected by a 300-member College of Electors; prime minister nominated by Parliament, appointed by the president
most recent election date: 14 December 2024
election results:
2024: Mikheil KAVELASHVILI (Georgian Dream Party) was formally inaugurated on 29 December 2024
2024: Irakli KOBAKHIDZE approved as prime minister by Parliamentary vote 84-10
2018: Salome ZOURABICHVILI elected president in second round; percent of vote in second round - Salome ZOURABICHVILI (independent, backed by Georgian Dream) 59.5%, Grigol VASHADZE (UNM) 40.5%; Irakli GARIBASHVILI approved as prime minister by Parliamentary vote 89-2
expected date of next election: 2029
head of government: Prime Minister Irakli KOBAKHIDZE (since 8 February 2024)
cabinet: Cabinet of Ministers
election/appointment process: president elected by a 300-member College of Electors; prime minister nominated by Parliament, appointed by the president
most recent election date: 14 December 2024
election results:
2024: Mikheil KAVELASHVILI (Georgian Dream Party) was formally inaugurated on 29 December 2024
2024: Irakli KOBAKHIDZE approved as prime minister by Parliamentary vote 84-10
2018: Salome ZOURABICHVILI elected president in second round; percent of vote in second round - Salome ZOURABICHVILI (independent, backed by Georgian Dream) 59.5%, Grigol VASHADZE (UNM) 40.5%; Irakli GARIBASHVILI approved as prime minister by Parliamentary vote 89-2
expected date of next election: 2029
Flag
description: white rectangle with a central red cross extending to all four sides of the flag; each of the four quadrants displays a small red bolnur-katskhuri cross (also known as Bolnisi cross), which has equal-length arms that are slightly wider at the end than in the center
history: sometimes referred to as the Five-Cross Flag, the design is based on a 14th-century banner of the Kingdom of Georgia
history: sometimes referred to as the Five-Cross Flag, the design is based on a 14th-century banner of the Kingdom of Georgia
Independence
9 April 1991 (from the Soviet Union); notable earlier date: A.D. 1008 (Georgia unified under King BAGRAT III)
Industries
steel, machine tools, electrical appliances, mining (manganese, copper, gold), chemicals, wood products, wine
Judicial branch
highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of 28 judges organized into several specialized judicial chambers; number of judges determined by the president of Georgia); Constitutional Court (consists of 9 judges)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges nominated by the High Council of Justice (a 14-member body consisting of the Supreme Court chairperson, common court judges, and appointees of the president of Georgia) and appointed by Parliament; judges appointed for life; Constitutional Court judges appointed 3 each by the president, by Parliament, and by the Supreme Court judges; judges appointed for 10-year terms
subordinate courts: Courts of Appeal; regional (town) and district courts
note: the Abkhazian and Ajarian Autonomous republics each have a supreme court and a hierarchy of lower courts
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges nominated by the High Council of Justice (a 14-member body consisting of the Supreme Court chairperson, common court judges, and appointees of the president of Georgia) and appointed by Parliament; judges appointed for life; Constitutional Court judges appointed 3 each by the president, by Parliament, and by the Supreme Court judges; judges appointed for 10-year terms
subordinate courts: Courts of Appeal; regional (town) and district courts
note: the Abkhazian and Ajarian Autonomous republics each have a supreme court and a hierarchy of lower courts
Land boundaries
total: 1,814 km
border countries (4): Armenia 219 km; Azerbaijan 428 km; Russia 894 km; Turkey 273 km
border countries (4): Armenia 219 km; Azerbaijan 428 km; Russia 894 km; Turkey 273 km
Land use
agricultural land: 34.1% (2023 est.)
arable land: 4.4% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 1.8% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 27.9% (2023 est.)
forest: 44.6% (2023 est.)
other: 21.2% (2023 est.)
arable land: 4.4% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 1.8% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 27.9% (2023 est.)
forest: 44.6% (2023 est.)
other: 21.2% (2023 est.)
Legal system
civil law system
Legislative branch
legislature name: Parliament (Sakartvelos Parlamenti)
legislative structure: unicameral
number of seats: 150 (all directly elected)
electoral system: proportional representation
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 4 years
most recent election date: 10/26/2024
parties elected and seats per party: Georgian Dream (89); Coalition for Changes (19); Unity - National Movement (16); Strong Georgia – Lelo, For people, For Liberty! (14); For Georgia (12)
percentage of women in chamber: 16.8%
expected date of next election: October 2028
legislative structure: unicameral
number of seats: 150 (all directly elected)
electoral system: proportional representation
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 4 years
most recent election date: 10/26/2024
parties elected and seats per party: Georgian Dream (89); Coalition for Changes (19); Unity - National Movement (16); Strong Georgia – Lelo, For people, For Liberty! (14); For Georgia (12)
percentage of women in chamber: 16.8%
expected date of next election: October 2028
Literacy
total population: 99.7% (2024 est.)
male: 99.8% (2024 est.)
female: 99.6% (2024 est.)
male: 99.8% (2024 est.)
female: 99.6% (2024 est.)
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
International organization participation
ADB, BSEC, CD, CE, CPLP (associate), EAPC, EBRD, FAO, G-11, GCTU, GUAM, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, OAS (observer), OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE, PFP, SELEC (observer), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
National holiday
Independence Day, 26 May (1918)
note: 26 May 1918 was the date of independence from Soviet Russia; 9 April 1991 was the date of independence from the Soviet Union
note: 26 May 1918 was the date of independence from Soviet Russia; 9 April 1991 was the date of independence from the Soviet Union
Nationality
noun: Georgian(s)
adjective: Georgian
adjective: Georgian
Natural resources
timber, hydropower, manganese deposits, iron ore, copper, minor coal and oil deposits; coastal climate and soils allow for important tea and citrus growth
Geography - note
note 1: strategically located east of the Black Sea, Georgia controls much of the Caucasus Mountains and the routes through them
note 2: the world's four deepest caves are all in Georgia, including two that are the only known caves on earth deeper than 2,000 m: Krubera Cave at -2,197 m (-7,208 ft; reached in 2012) and Veryovkina Cave at -2,212 (-7,257 ft; reached in 2018)
note 2: the world's four deepest caves are all in Georgia, including two that are the only known caves on earth deeper than 2,000 m: Krubera Cave at -2,197 m (-7,208 ft; reached in 2012) and Veryovkina Cave at -2,212 (-7,257 ft; reached in 2018)
Economic overview
upper-middle income, fast-growing South Caucasus economy; regionally focused exporter of cars, metal ores, and energy; financial and migrant inflows resulting from Ukraine conflict; EU accession talks suspended over disputed election and foreign influence law; low inflation but persistent high unemployment
Political parties
Ahali
Citizens
Conservative Party
Droa
European Georgia - Movement for Liberty
For Georgia
For the People
Freedom Square
Georgian Dream
Girchi - More Freedom
Law and Justice
Lelo for Georgia
National Democratic Party
People's Power
Progress and Freedom
Republican Party
State for the People
Strategy Aghmashenebeli
United National Movement or UNM
Citizens
Conservative Party
Droa
European Georgia - Movement for Liberty
For Georgia
For the People
Freedom Square
Georgian Dream
Girchi - More Freedom
Law and Justice
Lelo for Georgia
National Democratic Party
People's Power
Progress and Freedom
Republican Party
State for the People
Strategy Aghmashenebeli
United National Movement or UNM
Railways
total: 1,363 km (2014)
narrow gauge: 37 km (2014) 0.912-m gauge (37 km electrified)
broad gauge: 1,326 km (2014) 1.520-m gauge (1,251 km electrified)
narrow gauge: 37 km (2014) 0.912-m gauge (37 km electrified)
broad gauge: 1,326 km (2014) 1.520-m gauge (1,251 km electrified)
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Terrain
largely mountainous with Great Caucasus Mountains in the north and Lesser Caucasus Mountains in the south; Kolkhet'is Dablobi (Kolkhida Lowland) opens to the Black Sea in the west; Mtkvari River Basin in the east; fertile soils in river valley flood plains and foothills of Kolkhida Lowland
Government type
semi-presidential republic
Military - note
the Defense Forces of Georgia (DFG) are responsible for protecting the independence, sovereignty, and territorial integrity of the country; the DFG also provides units for multinational military operations abroad and supports the Border Police in border protection and civil authorities in counter-terrorist operations, if requested; it is focused primarily on Russia, which maintains military bases and troops in occupied Abkhazia and South Ossetia; a five-day conflict with Russian forces in 2008 resulted in the defeat and expulsion of Georgian forces from the breakaway regions
Georgia is not a member of NATO but has had a relationship with the Alliance since 1992 and declared its aspiration to join in 2002; the military is working to make itself more compatible with NATO and has participated in multinational exercises and security operations abroad with NATO, such as Afghanistan, where it was one of the top non-NATO contributors, and Kosovo; the DFG has also contributed troops to EU and UN missions (2025)
Georgia is not a member of NATO but has had a relationship with the Alliance since 1992 and declared its aspiration to join in 2002; the military is working to make itself more compatible with NATO and has participated in multinational exercises and security operations abroad with NATO, such as Afghanistan, where it was one of the top non-NATO contributors, and Kosovo; the DFG has also contributed troops to EU and UN missions (2025)
Country name
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Georgia
local long form: Republic of Georgia
local short form: Sak'art'velo
former: Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic
etymology: the Western name probably derives from the name of the local people, the Gurz, whose name origin is uncertain; the native name "Sak'art'velo" means "Land of the Kartvelians" and refers to the core central Georgian region of Kartli
conventional short form: Georgia
local long form: Republic of Georgia
local short form: Sak'art'velo
former: Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic
etymology: the Western name probably derives from the name of the local people, the Gurz, whose name origin is uncertain; the native name "Sak'art'velo" means "Land of the Kartvelians" and refers to the core central Georgian region of Kartli
Location
Southwestern Asia, bordering the Black Sea, between Turkey and Russia, with a sliver of land north of the Caucasus extending into Europe; note - Georgia views itself as part of Europe; geopolitically, it can be classified as falling within Europe, the Middle East, or both
Map references
Asia
Irrigated land
4,330 sq km (2012)
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Tamar TALIASHVILI (since 24 July 2025)
chancery: 1824 R Street NW, Washington, DC 20009
telephone: [1] (202) 387-2390
FAX: [1] (202) 387-0864
email address and website:
embgeo.usa@mfa.gov.ge
https://georgiaembassyusa.org/contact/
consulate(s) general: New York, San Francisco
chancery: 1824 R Street NW, Washington, DC 20009
telephone: [1] (202) 387-2390
FAX: [1] (202) 387-0864
email address and website:
embgeo.usa@mfa.gov.ge
https://georgiaembassyusa.org/contact/
consulate(s) general: New York, San Francisco
Internet users
percent of population: 82% (2023 est.)
Internet country code
.ge
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees: 31,791 (2024 est.)
IDPs: 347,754 (2024 est.)
stateless persons: 488 (2024 est.)
IDPs: 347,754 (2024 est.)
stateless persons: 488 (2024 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$33.776 billion (2024 est.)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
Total renewable water resources
63.33 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 16 years (2023 est.)
male: 16 years (2023 est.)
female: 17 years (2023 est.)
male: 16 years (2023 est.)
female: 17 years (2023 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 60.7% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 0.35% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
note: data include Abkhazia and South Ossetia
rate of urbanization: 0.35% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
note: data include Abkhazia and South Ossetia
Broadcast media
state-owned Georgian Public Broadcaster (GPB) includes Channel 1, Channel 2, and Adjara TV; independent commercial TV broadcasters include Imedi, Rustavi 2, Pirveli TV, Maestro, Kavkasia, Georgian Dream Studios (GDS), Obiektivi, Mtavari Arkhi, and TOK TV (Russian language); Tabula and Post TV are web-based TV outlets; Georgian Orthodox Church operates a satellite-based television station called Unanimity; 26 regional TV broadcasters; TV shifted to digital in 2015; several dozen private radio stations; GPB operates 2 radio stations (2019)
Drinking water source
improved:
urban: 99.2% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 88.5% of population (2022 est.)
total: 95% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0.8% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 11.5% of population (2022 est.)
total: 5% of population (2022 est.)
urban: 99.2% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 88.5% of population (2022 est.)
total: 95% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0.8% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 11.5% of population (2022 est.)
total: 5% of population (2022 est.)
National anthem(s)
title: "Tavisupleba" (Liberty)
lyrics/music: Davit MAGRADSE/Zakaria PALIASHVILI (adapted by Joseb KETSCHAKMADSE)
history: adopted 2004, after the Rose Revolution; based on music from the operas "Abesalom da Eteri" and "Daisi"
lyrics/music: Davit MAGRADSE/Zakaria PALIASHVILI (adapted by Joseb KETSCHAKMADSE)
history: adopted 2004, after the Rose Revolution; based on music from the operas "Abesalom da Eteri" and "Daisi"
This is an audio of the National Anthem for Georgia. The national anthem is generally a patriotic musical composition - usually in the form of a song or hymn of praise - that evokes and eulogizes the history, traditions, or struggles of a nation or its people. National anthems can be officially recognized as a national song by a country's constitution or by an enacted law, or simply by tradition. Although most anthems contain lyrics, some do not.
Major urban areas - population
1.082 million TBILISI (capital) (2023)
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Physician density
5.64 physicians/1,000 population (2023)
Hospital bed density
4.9 beds/1,000 population (2020 est.)
National symbol(s)
Saint George, lion
Mother's mean age at first birth
25.9 years (2019 est.)
note: data does not cover Abkhazia and South Ossetia
note: data does not cover Abkhazia and South Ossetia
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 71.3% (2024 est.)
government consumption: 13.4% (2024 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 22% (2024 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.8% (2024 est.)
exports of goods and services: 48.4% (2024 est.)
imports of goods and services: -56% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
government consumption: 13.4% (2024 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 22% (2024 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.8% (2024 est.)
exports of goods and services: 48.4% (2024 est.)
imports of goods and services: -56% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 59.5 (2024 est.)
youth dependency ratio: 32.9 (2024 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 26.6 (2024 est.)
potential support ratio: 3.8 (2024 est.)
youth dependency ratio: 32.9 (2024 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 26.6 (2024 est.)
potential support ratio: 3.8 (2024 est.)
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Georgia
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Georgia
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years
Population distribution
settlement concentrated in the central valley, particularly in the capital city of Tbilisi in the east; smaller urban agglomerations dot the Black Sea coast, with Bat'umi being the largest
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2022 est.)
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
4L
Sanitation facility access
improved:
urban: 96.6% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 72.5% of population (2022 est.)
total: 87.1% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 3.4% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 27.5% of population (2022 est.)
total: 12.9% of population (2022 est.)
urban: 96.6% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 72.5% of population (2022 est.)
total: 87.1% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 3.4% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 27.5% of population (2022 est.)
total: 12.9% of population (2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
Georgian 86.8%, Azeri 6.3%, Armenian 4.5%, other 2.3% (includes Russian, Ossetian, Yazidi, Ukrainian, Kist, Greek) (2014 est.)
Religions
Eastern Orthodox Christian (official) 83.4%, Muslim 10.7%, Armenian Apostolic Christian 2.9%, other 1.2% (includes Roman Catholic Christian, Jehovah's Witness, Yazidi, Protestant Christian, Jewish), none 0.5%, unspecified/no answer 1.2% (2014 est.)
Languages
Georgian (official) 87.6%, Azeri 6.2%, Armenian 3.9%, Russian 1.2%, other 1% (including Abkhaz, the official language in Abkhazia) (2014 est.)
major-language sample(s):
მსოფლიო ფაქტების წიგნი, ძირითადი ინფორმაციის აუცილებელი წყარო. (Georgian)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
major-language sample(s):
მსოფლიო ფაქტების წიგნი, ძირითადი ინფორმაციის აუცილებელი წყარო. (Georgian)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Georgian audio sample
Imports - partners
Turkey 16%, USA 13%, Russia 11%, China 8%, Germany 6% (2023)
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Elevation
highest point: Mt'a Shkhara 5,193 m
lowest point: Black Sea 0 m
mean elevation: 1,432 m
lowest point: Black Sea 0 m
mean elevation: 1,432 m
Health expenditure
7.4% of GDP (2022)
10.5% of national budget (2022 est.)
10.5% of national budget (2022 est.)
Military and security service personnel strengths
the Georgia Defense Forces are authorized up to 37,000 personnel (2025)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 504.96 million cubic meters (2022)
industrial: 354.46 million cubic meters (2022)
agricultural: 433.96 million cubic meters (2022)
industrial: 354.46 million cubic meters (2022)
agricultural: 433.96 million cubic meters (2022)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 800,000 tons (2024 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 19.6% (2022 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 19.6% (2022 est.)
Average household expenditures
on food: 39% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
on alcohol and tobacco: 3.8% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
on alcohol and tobacco: 3.8% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
National heritage
total World Heritage Sites: 4 (3 cultural, 1 natural)
selected World Heritage Site locales: Gelati Monastery (c); Historical Monuments of Mtskheta (c); Upper Svaneti (c); Colchic Rainforests and Wetlands (n)
selected World Heritage Site locales: Gelati Monastery (c); Historical Monuments of Mtskheta (c); Upper Svaneti (c); Colchic Rainforests and Wetlands (n)
Child marriage
women married by age 15: 0.3% (2018)
women married by age 18: 13.9% (2018)
men married by age 18: 0.5% (2018)
women married by age 18: 13.9% (2018)
men married by age 18: 0.5% (2018)
Coal
production: 148,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
consumption: 384,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 80 metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 223,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 900.999 million metric tons (2023 est.)
consumption: 384,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 80 metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 223,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 900.999 million metric tons (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 23.9% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
wind: 0.6% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 75.5% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
wind: 0.6% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 75.5% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Natural gas
production: 10.77 million cubic meters (2023 est.)
consumption: 2.775 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
imports: 2.764 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 8.495 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
consumption: 2.775 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
imports: 2.764 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 8.495 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Petroleum
total petroleum production: 300 bbl/day (2023 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 34,000 bbl/day (2023 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 35 million barrels (2021 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 34,000 bbl/day (2023 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 35 million barrels (2021 est.)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
65.3% (2018 est.)
Remittances
11.8% of GDP (2024 est.)
13.7% of GDP (2023 est.)
15.4% of GDP (2022 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
13.7% of GDP (2023 est.)
15.4% of GDP (2022 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
Ports
total ports: 3 (2024)
large: 0
medium: 0
small: 1
very small: 2
ports with oil terminals: 2
key ports: Batumi, Sokhumi, Supsa Marine Terminal
large: 0
medium: 0
small: 1
very small: 2
ports with oil terminals: 2
key ports: Batumi, Sokhumi, Supsa Marine Terminal
National color(s)
red, white
Particulate matter emissions
18.6 micrograms per cubic meter (2019 est.)
Labor force
1.833 million (2024 est.)
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 29.9% (2024 est.)
male: 28.4% (2024 est.)
female: 32.4% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
male: 28.4% (2024 est.)
female: 32.4% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
Debt - external
$9.085 billion (2023 est.)
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
Maternal mortality ratio
20 deaths/100,000 live births (2023 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$4.447 billion (2024 est.)
$5.002 billion (2023 est.)
$4.886 billion (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
$5.002 billion (2023 est.)
$4.886 billion (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
Public debt
43.4% of GDP (2023 est.)
note: central government debt as a % of GDP
note: central government debt as a % of GDP
Unemployment rate
11.5% (2024 est.)
11.6% (2023 est.)
11.7% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
11.6% (2023 est.)
11.7% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
Population
total: 4,900,961 (2024 est.)
male: 2,343,068
female: 2,557,893
male: 2,343,068
female: 2,557,893
Carbon dioxide emissions
10.7 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 812,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 4.469 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 5.419 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 812,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 4.469 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 5.419 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
Area
total : 69,700 sq km
land: 69,700 sq km
water: 0 sq km
note: approximately 12,560 sq km, or about 18% of Georgia's area, is Russian-occupied; the seized area includes all of Abkhazia and the breakaway region of South Ossetia, which consists of the northern part of Shida Kartli, eastern slivers of the Imereti region, Racha-Lechkhumi, Kvemo Svaneti, and part of western Mtskheta-Mtianeti
land: 69,700 sq km
water: 0 sq km
note: approximately 12,560 sq km, or about 18% of Georgia's area, is Russian-occupied; the seized area includes all of Abkhazia and the breakaway region of South Ossetia, which consists of the northern part of Shida Kartli, eastern slivers of the Imereti region, Racha-Lechkhumi, Kvemo Svaneti, and part of western Mtskheta-Mtianeti
Taxes and other revenues
23.6% (of GDP) (2023 est.)
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$91.849 billion (2024 est.)
$83.935 billion (2023 est.)
$77.838 billion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
$83.935 billion (2023 est.)
$77.838 billion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Airports
21 (2025)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
34.8 (2023 est.)
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
1.1% (2024 est.)
2.5% (2023 est.)
11.9% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
2.5% (2023 est.)
11.9% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
Current account balance
-$1.491 billion (2024 est.)
-$1.709 billion (2023 est.)
-$1.105 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
-$1.709 billion (2023 est.)
-$1.105 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
Real GDP per capita
$25,000 (2024 est.)
$22,600 (2023 est.)
$21,000 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
$22,600 (2023 est.)
$21,000 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 1.1 million (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 29 (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 29 (2023 est.)
Tobacco use
total: 28.7% (2025 est.)
male: 53.9% (2025 est.)
female: 7.5% (2025 est.)
male: 53.9% (2025 est.)
female: 7.5% (2025 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
21.7% (2016)
Energy consumption per capita
56.076 million Btu/person (2023 est.)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 4.526 million kW (2023 est.)
consumption: 12.569 billion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 4.913 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 4.234 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 1.148 billion kWh (2023 est.)
consumption: 12.569 billion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 4.913 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 4.234 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 1.148 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Merchant marine
total: 26 (2023)
by type: general cargo 3, other 23
by type: general cargo 3, other 23
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
2.1% (2018 est.)
Imports
$18.915 billion (2024 est.)
$17.816 billion (2023 est.)
$15.665 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
$17.816 billion (2023 est.)
$15.665 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
Exports
$16.321 billion (2024 est.)
$15.173 billion (2023 est.)
$13.24 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
$15.173 billion (2023 est.)
$13.24 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
Heliports
4 (2025)
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 278,000 (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 7 (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 7 (2023 est.)
Alcohol consumption per capita
total: 7.45 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 1.71 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 3.19 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 2.52 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.02 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 1.71 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 3.19 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 2.52 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.02 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 72.8 years (2024 est.)
male: 68.7 years
female: 77.2 years
male: 68.7 years
female: 77.2 years
Real GDP growth rate
9.4% (2024 est.)
7.8% (2023 est.)
11% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
7.8% (2023 est.)
11% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
Industrial production growth rate
5.4% (2024 est.)
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 5.4% (2024 est.)
industry: 19.1% (2024 est.)
services: 62.8% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
industry: 19.1% (2024 est.)
services: 62.8% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
Education expenditure
4% of GDP (2024 est.)
12.2% national budget (2024 est.)
12.2% national budget (2024 est.)
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Chargé d’Affaires Alan S. PURCELL (since 16 July 2025)
embassy: 29 Georgian-American Friendship Avenue, Didi Dighomi, Tbilisi, 0131
mailing address: 7060 Tbilisi Place, Washington, DC 20521-7060
telephone: [995] (32) 227-70-00
FAX: [995] (32) 253-23-10
email address and website:
askconsultbilisi@state.gov
https://ge.usembassy.gov/
embassy: 29 Georgian-American Friendship Avenue, Didi Dighomi, Tbilisi, 0131
mailing address: 7060 Tbilisi Place, Washington, DC 20521-7060
telephone: [995] (32) 227-70-00
FAX: [995] (32) 253-23-10
email address and website:
askconsultbilisi@state.gov
https://ge.usembassy.gov/
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the majority of the military's inventory consists of Soviet-era weapons and equipment, some of which has been upgraded; it has smaller quantities of mostly secondhand material from such countries as Israel, Poland, Türkiye, and the US, as well as some domestically produced equipment; Georgia has a small defense industry which produces such items as small arms and light armored vehicles (2025)
Military service age and obligation
18-35 years of age for voluntary military service for men and women; conscription was abolished in 2016, but reinstated in 2017 for men 18-27 years of age; conscript service obligation is up to 11 months depending on the assigned ministry, job specialty, and if the service is carried out in a combat unit (2025)
note: conscripts serve in the Defense Forces, the Ministry of Internal Affairs, or the Ministry of Corrections
note: conscripts serve in the Defense Forces, the Ministry of Internal Affairs, or the Ministry of Corrections
Gross reproduction rate
0.94 (2025 est.)
Net migration rate
-3.33 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Median age
total: 38.6 years (2025 est.)
male: 35.9 years
female: 40.6 years
male: 35.9 years
female: 40.6 years
Total fertility rate
1.94 children born/woman (2025 est.)
Infant mortality rate
total: 20.9 deaths/1,000 live births (2025 est.)
male: 23.6 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 19.7 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 23.6 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 19.7 deaths/1,000 live births
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 5.91 million (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 156 (2022 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 156 (2022 est.)
Death rate
12.89 deaths/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Birth rate
11.74 births/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Population growth rate
-0.45% (2025 est.)




