Bolivia - BO - BOL - BOL - South America
Last updated: January 05, 2026

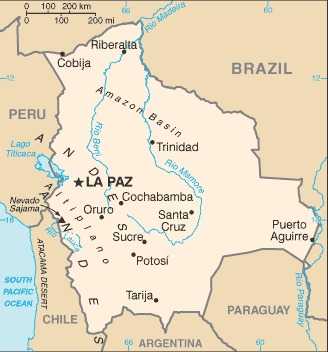
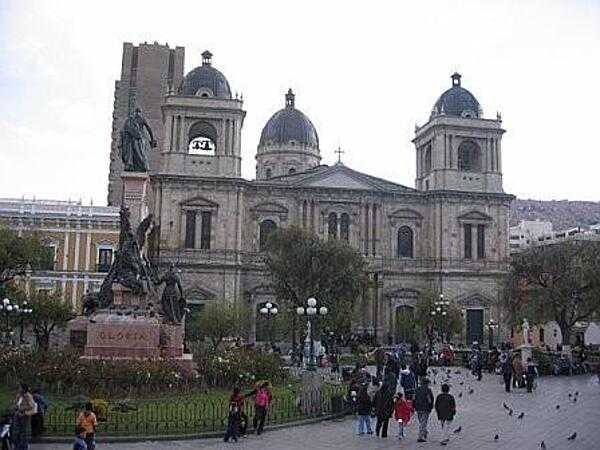
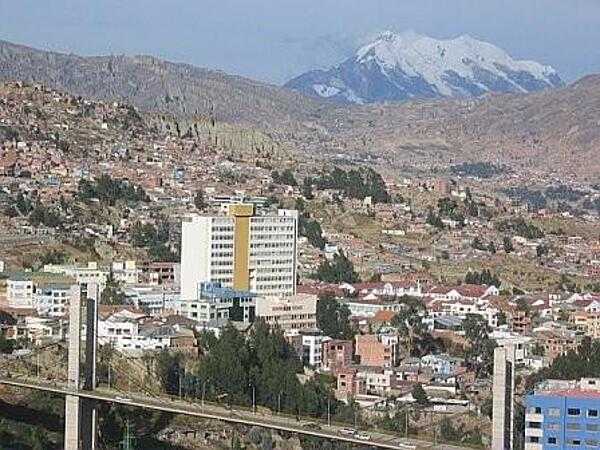
Bolivia Images
Bolivia Factbook Data
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Chargé d'Affaires Debra HEVIA (since September 2023)
embassy: Avenida Arce 2780, Casilla 425, La Paz
mailing address: 3220 La Paz Place, Washington DC 20512-3220
telephone: [591] (2) 216-8000
FAX: [591] (2) 216-8111
email address and website:
ConsularLaPazACS@state.gov
https://bo.usembassy.gov/
note: in September 2008, the Bolivian Government expelled the US Ambassador to Bolivia, Philip GOLDBERG, and both countries have yet to reinstate their ambassadors
embassy: Avenida Arce 2780, Casilla 425, La Paz
mailing address: 3220 La Paz Place, Washington DC 20512-3220
telephone: [591] (2) 216-8000
FAX: [591] (2) 216-8111
email address and website:
ConsularLaPazACS@state.gov
https://bo.usembassy.gov/
note: in September 2008, the Bolivian Government expelled the US Ambassador to Bolivia, Philip GOLDBERG, and both countries have yet to reinstate their ambassadors
Age structure
0-14 years: 28.5% (male 1,792,803/female 1,718,081)
15-64 years: 64.5% (male 4,002,587/female 3,937,953)
65 years and over: 7% (2024 est.) (male 397,384/female 463,166)
15-64 years: 64.5% (male 4,002,587/female 3,937,953)
65 years and over: 7% (2024 est.) (male 397,384/female 463,166)
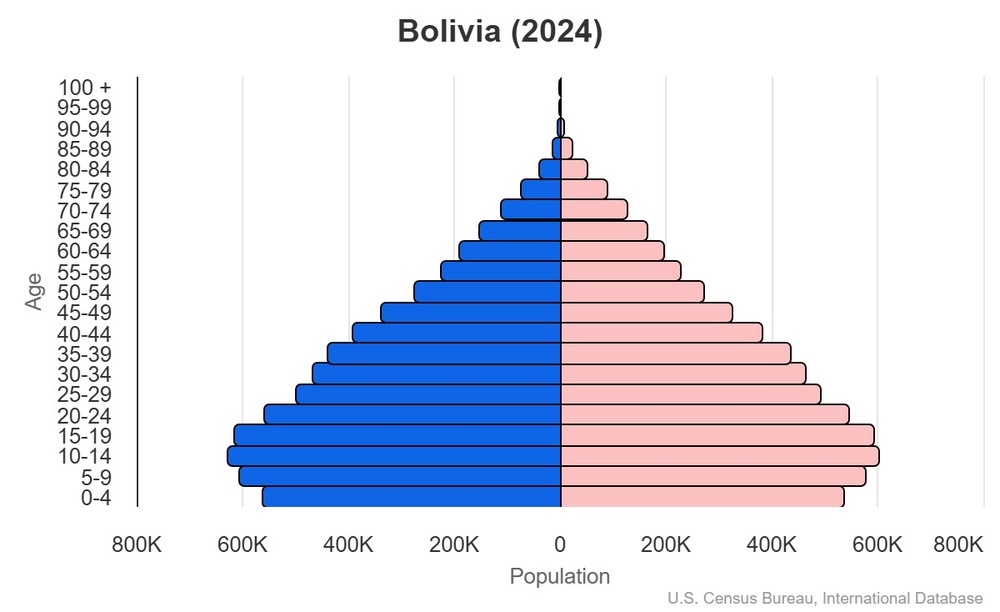
This is the population pyramid for Bolivia. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
Geographic coordinates
17 00 S, 65 00 W
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.86 male(s)/female
total population: 1.01 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.86 male(s)/female
total population: 1.01 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Natural hazards
flooding in the northeast (March to April)
volcanism: volcanic activity in Andes Mountains on the border with Chile; historically active volcanoes in this region are Irruputuncu (5,163 m), which last erupted in 1995, and the Olca-Paruma volcanic complex (5,762 m to 5,167 m)
volcanism: volcanic activity in Andes Mountains on the border with Chile; historically active volcanoes in this region are Irruputuncu (5,163 m), which last erupted in 1995, and the Olca-Paruma volcanic complex (5,762 m to 5,167 m)
Area - comparative
slightly less than three times the size of Montana
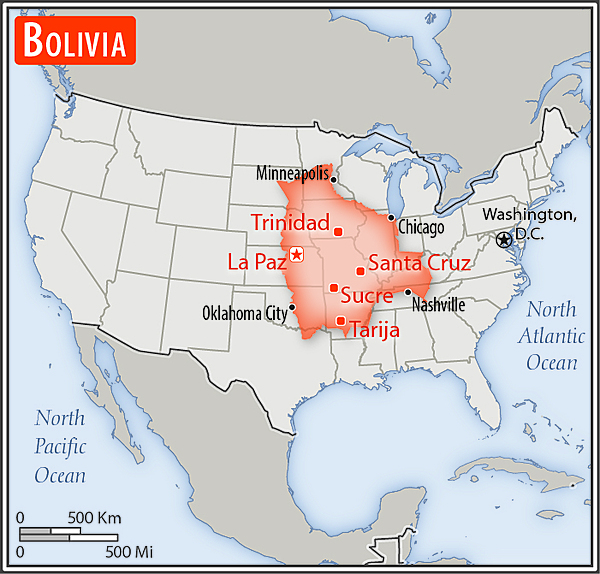
slightly less than three times the size of Montana
Background
Bolivia, named after independence fighter Simón BOLÍVAR, broke away from Spanish rule in 1825. Much of its subsequent history has consisted of a series of coups and countercoups, with the last coup occurring in 1980. Democratic civilian rule was established in 1982, but leaders have faced problems of deep-seated poverty, social unrest, and illegal drug production.
In 2005, Bolivians elected Movement Toward Socialism leader Evo MORALES as president -- by the widest margin of any leader since 1982 -- after he ran on a promise to change the country's traditional political class and empower the poor and indigenous majority. In 2009 and 2014, MORALES easily won reelection, and his party maintained control of the legislative branch. In 2016, MORALES narrowly lost a referendum to approve a constitutional amendment that would have allowed him to compete in the 2019 presidential election. A subsequent Supreme Court ruling stating that term limits violate human rights provided the justification for MORALES to run despite the referendum, but rising violence, pressure from the military, and widespread allegations of electoral fraud ultimately forced him to flee the country. An interim government, led by President Jeanine AÑEZ Chávez, held new elections in 2020, and Luis Alberto ARCE Catacora was elected president.
In 2005, Bolivians elected Movement Toward Socialism leader Evo MORALES as president -- by the widest margin of any leader since 1982 -- after he ran on a promise to change the country's traditional political class and empower the poor and indigenous majority. In 2009 and 2014, MORALES easily won reelection, and his party maintained control of the legislative branch. In 2016, MORALES narrowly lost a referendum to approve a constitutional amendment that would have allowed him to compete in the 2019 presidential election. A subsequent Supreme Court ruling stating that term limits violate human rights provided the justification for MORALES to run despite the referendum, but rising violence, pressure from the military, and widespread allegations of electoral fraud ultimately forced him to flee the country. An interim government, led by President Jeanine AÑEZ Chávez, held new elections in 2020, and Luis Alberto ARCE Catacora was elected president.
Environmental issues
deforestation from agricultural clearing and international demand for timber; soil erosion from overgrazing and poor cultivation methods (including slash-and-burn agriculture); desertification; loss of biodiversity; industrial pollution of water supplies used for drinking and irrigation
International environmental agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Convention, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands,
signed, but not ratified: Environmental Modification, Marine Life Conservation
signed, but not ratified: Environmental Modification, Marine Life Conservation
Military expenditures
1.2% of GDP (2024 est.)
1.2% of GDP (2023 est.)
1.3% of GDP (2022 est.)
1.4% of GDP (2021 est.)
1.4% of GDP (2020 est.)
1.2% of GDP (2023 est.)
1.3% of GDP (2022 est.)
1.4% of GDP (2021 est.)
1.4% of GDP (2020 est.)
Population below poverty line
37.7% (2022 est.)
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 1.8% (2023 est.)
highest 10%: 31.3% (2023 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
highest 10%: 31.3% (2023 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
Exports - commodities
gold, natural gas, precious metal ore, zinc ore, soybean meal (2023)
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Exports - partners
Brazil 15%, India 13%, China 11%, Argentina 11%, UAE 8% (2023)
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Administrative divisions
9 departments (departamentos, singular - departamento); Beni, Chuquisaca, Cochabamba, La Paz, Oruro, Pando, Potosi, Santa Cruz, Tarija
Agricultural products
sugarcane, soybeans, maize, potatoes, sorghum, rice, milk, chicken, plantains, beef (2023)
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Military and security forces
Bolivian Armed Forces (Fuerzas Armadas de Bolivia or FAB): Bolivian Army (Ejercito de Boliviano), Bolivian Navy (Armada Boliviana), Bolivian Air Force (Fuerza Aerea Boliviana)
Ministry of Government: National Police (Policía Nacional de Bolivia, PNB) (2025)
note: the PNB is part of the reserves for the Armed Forces; the police and military share responsibility for border enforcement
Ministry of Government: National Police (Policía Nacional de Bolivia, PNB) (2025)
note: the PNB is part of the reserves for the Armed Forces; the police and military share responsibility for border enforcement
Budget
revenues: $11.796 billion (2019 est.)
expenditures: $14.75 billion (2019 est.)
expenditures: $14.75 billion (2019 est.)
Capital
name: La Paz (administrative capital); Sucre (constitutional [legislative and judicial] capital)
geographic coordinates: 16 30 S, 68 09 W
time difference: UTC-4 (1 hour ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: La Paz is a shortening of the original name of the city, Pueblo Nuevo de Nuestra Señora de La Paz (New Town of Our Lady of Peace); Sucre is named after Antonio José de SUCRE (1795-1830), the second president of Bolivia
note: at approximately 3,630 m above sea level, La Paz's elevation makes it the highest capital city in the world
geographic coordinates: 16 30 S, 68 09 W
time difference: UTC-4 (1 hour ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: La Paz is a shortening of the original name of the city, Pueblo Nuevo de Nuestra Señora de La Paz (New Town of Our Lady of Peace); Sucre is named after Antonio José de SUCRE (1795-1830), the second president of Bolivia
note: at approximately 3,630 m above sea level, La Paz's elevation makes it the highest capital city in the world
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, cars, pesticides, trucks, plastics (2023)
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Climate
varies with altitude; humid and tropical to cold and semiarid
Coastline
0 km (landlocked)
Constitution
history: many previous; latest drafted 6 August 2006 to 9 December 2008, approved by referendum 25 January 2009, effective 7 February 2009
amendment process: proposed through public petition by at least 20% of voters or by the Plurinational Legislative Assembly; passage requires approval by at least two-thirds majority vote of the total membership of the Assembly and approval in a referendum
amendment process: proposed through public petition by at least 20% of voters or by the Plurinational Legislative Assembly; passage requires approval by at least two-thirds majority vote of the total membership of the Assembly and approval in a referendum
Exchange rates
bolivianos (BOB) per US dollar -
Exchange rates:
6.91 (2024 est.)
6.91 (2023 est.)
6.91 (2022 est.)
6.91 (2021 est.)
6.91 (2020 est.)
Exchange rates:
6.91 (2024 est.)
6.91 (2023 est.)
6.91 (2022 est.)
6.91 (2021 est.)
6.91 (2020 est.)
Executive branch
chief of state: President Rodrigo PAZ Pereira (since 8 November 2025)
head of government: President Rodrigo PAZ Pereira (since 8 November 2025)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president
election/appointment process: president and vice president directly elected on the same ballot one of 3 ways: candidate wins at least 50% of the vote, or at least 40% of the vote and 10% more than the next highest candidate; otherwise, a second round is held and the winner determined by simple majority vote; president and vice president are elected by majority vote to serve a 5-year term; no term limits
most recent election date: 17 August 2025
election results:
2025: Rodrigo PAZ Pereira elected president in second round; percent vote in first round - Rodrigo PAZ Pereira (PDC) 32.1%, Jorge Fernando QUIROGA Ramírez (LIBRE) 26.7%, Samuel DORIA MEDINA Auza (UN) 19.7%, Andrónico RODRÌGUEZ Ledezma (AP) 8.5%, Manfred REYES Villa (APB Súmate) 6.8%, Eduardo DEL CASTILLO (MAS) 3.2%, other 3%; percent of vote in second round - Rodrigo PAZ Pereira 55%, Jorge Fernando QUIROGA Ramírez 45%
2020: Luis Alberto ARCE Catacora elected president; percent of vote - Luis Alberto ARCE Catacora (MAS) 55.1%; Carlos Diego MESA Gisbert (CC) 28.8%; Luis Fernando CAMACHO Vaca (Creemos) 14%; other 2.1%
2019: Juan Evo MORALES Ayma reelected president; percent of vote - Juan Evo MORALES Ayma (MAS) 61%; Samuel DORIA MEDINA Arana (UN) 24.5%; Jorge QUIROGA Ramirez (POC) 9.1%; other 5.4%
expected date of next election: 2030
note: the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Rodrigo PAZ Pereira (since 8 November 2025)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president
election/appointment process: president and vice president directly elected on the same ballot one of 3 ways: candidate wins at least 50% of the vote, or at least 40% of the vote and 10% more than the next highest candidate; otherwise, a second round is held and the winner determined by simple majority vote; president and vice president are elected by majority vote to serve a 5-year term; no term limits
most recent election date: 17 August 2025
election results:
2025: Rodrigo PAZ Pereira elected president in second round; percent vote in first round - Rodrigo PAZ Pereira (PDC) 32.1%, Jorge Fernando QUIROGA Ramírez (LIBRE) 26.7%, Samuel DORIA MEDINA Auza (UN) 19.7%, Andrónico RODRÌGUEZ Ledezma (AP) 8.5%, Manfred REYES Villa (APB Súmate) 6.8%, Eduardo DEL CASTILLO (MAS) 3.2%, other 3%; percent of vote in second round - Rodrigo PAZ Pereira 55%, Jorge Fernando QUIROGA Ramírez 45%
2020: Luis Alberto ARCE Catacora elected president; percent of vote - Luis Alberto ARCE Catacora (MAS) 55.1%; Carlos Diego MESA Gisbert (CC) 28.8%; Luis Fernando CAMACHO Vaca (Creemos) 14%; other 2.1%
2019: Juan Evo MORALES Ayma reelected president; percent of vote - Juan Evo MORALES Ayma (MAS) 61%; Samuel DORIA MEDINA Arana (UN) 24.5%; Jorge QUIROGA Ramirez (POC) 9.1%; other 5.4%
expected date of next election: 2030
note: the president is both chief of state and head of government
Flag
description: three equal horizontal bands of red (top), yellow, and green, with the coat of arms centered on the yellow band
meaning: red stands for bravery and the blood of national heroes, yellow for the nation's mineral resources, and green for the land's fertility
history: in 2009, a presidential decree made it mandatory for a wiphala -- a square, multi-colored flag representing the country's ethnic groups -- to be used alongside the national flag
note: similar to the flag of Ghana, which has a large, five-pointed black star centered in the yellow band
meaning: red stands for bravery and the blood of national heroes, yellow for the nation's mineral resources, and green for the land's fertility
history: in 2009, a presidential decree made it mandatory for a wiphala -- a square, multi-colored flag representing the country's ethnic groups -- to be used alongside the national flag
note: similar to the flag of Ghana, which has a large, five-pointed black star centered in the yellow band
Illicit drugs
USG identification:
major illicit drug-producing and/or drug-transit country
major precursor-chemical producer (2025)
major illicit drug-producing and/or drug-transit country
major precursor-chemical producer (2025)
Independence
6 August 1825 (from Spain)
Industries
mining, smelting, electricity, petroleum, food and beverages, handicrafts, clothing, jewelry
Judicial branch
highest court(s): Supreme Court or Tribunal Supremo de Justicia (consists of 12 judges organized into civil, penal, social, and administrative chambers); Plurinational Constitutional Tribunal (consists of 7 primary and 7 alternate magistrates); Plurinational Electoral Organ (consists of 7 members and 6 alternates); National Agro-Environment Court (consists of 5 primary and 5 alternate judges; Council of the Judiciary (consists of 3 primary and 3 alternate judges)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court, Plurinational Constitutional Tribunal, National Agro-Environmental Court, and Council of the Judiciary candidates pre-selected by the Plurinational Legislative Assembly and elected by direct popular vote; judges elected for 6-year terms; Plurinational Electoral Organ judges appointed - 6 by the Legislative Assembly and 1 by the president of the republic; members serve single 6-year terms
subordinate courts: National Electoral Court; District Courts (in each of the 9 administrative departments); agro-environmental lower courts
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court, Plurinational Constitutional Tribunal, National Agro-Environmental Court, and Council of the Judiciary candidates pre-selected by the Plurinational Legislative Assembly and elected by direct popular vote; judges elected for 6-year terms; Plurinational Electoral Organ judges appointed - 6 by the Legislative Assembly and 1 by the president of the republic; members serve single 6-year terms
subordinate courts: National Electoral Court; District Courts (in each of the 9 administrative departments); agro-environmental lower courts
Land boundaries
total: 7,252 km
border countries (5): Argentina 942 km; Brazil 3,403 km; Chile 942 km; Paraguay 753 km; Peru 1,212 km
border countries (5): Argentina 942 km; Brazil 3,403 km; Chile 942 km; Paraguay 753 km; Peru 1,212 km
Land use
agricultural land: 35.8% (2023 est.)
arable land: 5.1% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 0.2% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 30.5% (2023 est.)
forest: 50.6% (2023 est.)
other: 13.5% (2023 est.)
arable land: 5.1% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 0.2% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 30.5% (2023 est.)
forest: 50.6% (2023 est.)
other: 13.5% (2023 est.)
Legal system
civil law system with influences from Roman, Spanish, canon (religious), French, and ethnic groups' pre-colonial law
Legislative branch
legislature name: Plurinational Legislative Assembly (Asamblea Legislativa Plurinacional)
legislative structure: bicameral
legislative structure: bicameral
Literacy
total population: 95.6% (2023 est.)
male: 97.8% (2023 est.)
female: 93.5% (2023 est.)
male: 97.8% (2023 est.)
female: 93.5% (2023 est.)
Maritime claims
none (landlocked)
International organization participation
CAN, CD, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, LAES, LAIA, Mercosur (associate), MIGA, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, NAM, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, UN, UN Security Council (temporary), UNAMID, UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNOOSA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
National holiday
Independence Day, 6 August (1825)
Nationality
noun: Bolivian(s)
adjective: Bolivian
adjective: Bolivian
Natural resources
lithium, tin, natural gas, petroleum, zinc, tungsten, antimony, silver, iron, lead, gold, timber, hydropower
Geography - note
landlocked; shares control of Lago Titicaca, world's highest navigable lake (elevation 3,805 m), with Peru
Economic overview
resource-rich economy benefits during commodity booms; has bestowed juridical rights to Mother Earth, impacting extraction industries; increasing Chinese lithium mining trade relations; hard hit by COVID-19; increased fiscal spending amid poverty increases; rampant banking and finance corruption
Political parties
Autonomy for Bolivia – Súmate or APB Súmate
Christian Democratic Party or PDC
Community Citizen Alliance or ACC
Freedom and Democracy or LIBRE
Front for Victory or FPV
Movement Toward Socialism or MAS
National Unity or UN
Popular Alliance or AP
Revolutionary Left Front or FRI
Revolutionary Nationalist Movement or MNR
Social Democrat Movement or MDS
Third System Movement or MTS
We Believe or Creemos
note: We Believe or Creemos [Luis Fernando CAMACHO Vaca] is a coalition comprised of several opposition parties that participated in the 2020 election, which includes the Christian Democratic Party (PDC) and Solidarity Civic Unity (UCS)
Christian Democratic Party or PDC
Community Citizen Alliance or ACC
Freedom and Democracy or LIBRE
Front for Victory or FPV
Movement Toward Socialism or MAS
National Unity or UN
Popular Alliance or AP
Revolutionary Left Front or FRI
Revolutionary Nationalist Movement or MNR
Social Democrat Movement or MDS
Third System Movement or MTS
We Believe or Creemos
note: We Believe or Creemos [Luis Fernando CAMACHO Vaca] is a coalition comprised of several opposition parties that participated in the 2020 election, which includes the Christian Democratic Party (PDC) and Solidarity Civic Unity (UCS)
Railways
total: 3,960 km (2019)
narrow gauge: 3,960 km (2014) 1.000-m gauge
narrow gauge: 3,960 km (2014) 1.000-m gauge
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal and compulsory
Terrain
rugged Andes Mountains with a highland plateau (Altiplano), hills, lowland plains of the Amazon Basin
Government type
presidential republic
Country name
conventional long form: Plurinational State of Bolivia
conventional short form: Bolivia
local long form: Estado Plurinacional de Bolivia
local short form: Bolivia
former: Upper Peru
etymology: the country is named in honor of Simón BOLÍVAR, a 19th-century leader in the South American wars for independence
conventional short form: Bolivia
local long form: Estado Plurinacional de Bolivia
local short form: Bolivia
former: Upper Peru
etymology: the country is named in honor of Simón BOLÍVAR, a 19th-century leader in the South American wars for independence
Location
Central South America, southwest of Brazil
Map references
South America
Irrigated land
2,972 sq km (2017)
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Chargé d'Affaires Henry BALDELOMAR CHÁVEZ (since 11 October 2023)
chancery: 3014 Massachusetts Ave., NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 483-4410
FAX: [1] (202) 328-3712
email address and website:
embolivia.wdc@gmail.com
https://www.boliviawdc.org/en-us/
consulate(s) general: Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, New York
chancery: 3014 Massachusetts Ave., NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 483-4410
FAX: [1] (202) 328-3712
email address and website:
embolivia.wdc@gmail.com
https://www.boliviawdc.org/en-us/
consulate(s) general: Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, New York
Internet users
percent of population: 70% (2023 est.)
Internet country code
.bo
GDP (official exchange rate)
$49.668 billion (2024 est.)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
Trafficking in persons
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List — Bolivia did not demonstrate overall increasing efforts to eliminate trafficking compared with the previous reporting period and was downgraded to Tier 2 Watch List; for more details, go to: https://www.state.gov/reports/2025-trafficking-in-persons-report/bolivia/
Total renewable water resources
574 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 71.2% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 1.87% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
rate of urbanization: 1.87% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Broadcast media
large number of radio and TV stations broadcasting with private media outlets dominating; state-owned and private radio and TV stations generally operating freely, although both pro-government and anti-government groups have attacked media outlets in response to their reporting (2019)
Drinking water source
improved:
urban: 99.5% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 81% of population (2022 est.)
total: 94.1% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0.5% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 19% of population (2022 est.)
total: 5.9% of population (2022 est.)
urban: 99.5% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 81% of population (2022 est.)
total: 94.1% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0.5% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 19% of population (2022 est.)
total: 5.9% of population (2022 est.)
National anthem(s)
title: "Cancion Patriotica" (Patriotic Song)
lyrics/music: Jose Ignacio de SANJINES/Leopoldo Benedetto VINCENTI
history: adopted 1852
lyrics/music: Jose Ignacio de SANJINES/Leopoldo Benedetto VINCENTI
history: adopted 1852
This is an audio of the National Anthem for Bolivia. The national anthem is generally a patriotic musical composition - usually in the form of a song or hymn of praise - that evokes and eulogizes the history, traditions, or struggles of a nation or its people. National anthems can be officially recognized as a national song by a country's constitution or by an enacted law, or simply by tradition. Although most anthems contain lyrics, some do not.
Major urban areas - population
1.936 million LA PAZ (capital), 1.820 million Santa Cruz, 1.400 million Cochabamba (2022); 278,000 Sucre (constitutional capital) (2018)
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Physician density
1.28 physicians/1,000 population (2021)
Hospital bed density
1.4 beds/1,000 population (2021 est.)
National symbol(s)
llama, Andean condor; two national flowers, the cantuta and the patuju
Mother's mean age at first birth
21.1 years (2008 est.)
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-49
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-49
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 68.5% (2023 est.)
government consumption: 19.3% (2023 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 17.5% (2023 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.1% (2023 est.)
exports of goods and services: 25.5% (2023 est.)
imports of goods and services: -30.9% (2023 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
government consumption: 19.3% (2023 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 17.5% (2023 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.1% (2023 est.)
exports of goods and services: 25.5% (2023 est.)
imports of goods and services: -30.9% (2023 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 55.1 (2024 est.)
youth dependency ratio: 44.2 (2024 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 10.8 (2024 est.)
potential support ratio: 9.2 (2024 est.)
youth dependency ratio: 44.2 (2024 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 10.8 (2024 est.)
potential support ratio: 9.2 (2024 est.)
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: yes
citizenship by descent only: yes
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 3 years
citizenship by descent only: yes
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 3 years
Population distribution
a high-altitude plain in the west between two cordillera of the Andes, known as the Altiplano, is the focal area for most of the population; a dense settlement pattern is also found in and around the city of Santa Cruz, located on the eastern side of the Andes
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 99.9% (2022 est.)
electrification - urban areas: 100%
electrification - rural areas: 95.6%
electrification - urban areas: 100%
electrification - rural areas: 95.6%
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
CP
Sanitation facility access
improved:
urban: 100% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 51.4% of population (2022 est.)
total: 85.8% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 48.6% of population (2022 est.)
total: 14.2% of population (2022 est.)
urban: 100% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 51.4% of population (2022 est.)
total: 85.8% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 48.6% of population (2022 est.)
total: 14.2% of population (2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
Mestizo (mixed White and Indigenous ancestry) 68%, Indigenous 20%, White 5%, Cholo/Chola 2%, African descent 1%, other 1%, unspecified 3%; 44% other Indigenous group, predominantly Quechua or Aymara (2009 est.)
note: results among surveys vary based on the wording of the ethnicity question and the available response choices; the 2001 national census did not provide "Mestizo" as a response choice, resulting in a much higher proportion of respondents identifying themselves as belonging to one of the available indigenous ethnicity choices; the use of "Mestizo" and "Cholo" varies among response choices in surveys, with surveys using the terms interchangeably, providing one or the other as a response choice, or providing the two as separate response choices
note: results among surveys vary based on the wording of the ethnicity question and the available response choices; the 2001 national census did not provide "Mestizo" as a response choice, resulting in a much higher proportion of respondents identifying themselves as belonging to one of the available indigenous ethnicity choices; the use of "Mestizo" and "Cholo" varies among response choices in surveys, with surveys using the terms interchangeably, providing one or the other as a response choice, or providing the two as separate response choices
Religions
Roman Catholic 65%, Protestant 19.6% (Evangelical (non-specific) 11.9%, Evangelical Baptist 2.1%, Evangelical Pentecostal 1.8%, Evangelical Methodist 0.7%, Adventist 2.8%, Protestant (non-specific) 0.3%), Believer (not belonging to the church) 0.9%, other 4.8%, atheist 1.7%, agnostic 0.6%, none 6.1%, unspecified 1.3% (2023 est.)
Languages
Spanish (official) 68.1%, Quechua (official) 17.2%, Aymara (official) 10.5%, Guarani (official) 0.6%, other 1.5%, unspecified 2.1%; note - Spanish and all Indigenous languages are official (2012 est.)
major-language sample(s):
La Libreta Informativa del Mundo, la fuente indispensable de información básica. (Spanish)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
major-language sample(s):
La Libreta Informativa del Mundo, la fuente indispensable de información básica. (Spanish)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Spanish audio sample
Imports - partners
China 22%, Brazil 18%, Chile 13%, USA 7%, Peru 5% (2023)
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees: 1,163 (2024 est.)
IDPs: 12,070 (2024 est.)
IDPs: 12,070 (2024 est.)
Elevation
highest point: Nevado Sajama 6,542 m
lowest point: Rio Paraguay 90 m
mean elevation: 1,192 m
lowest point: Rio Paraguay 90 m
mean elevation: 1,192 m
Health expenditure
8.2% of GDP (2021)
16.4% of national budget (2022 est.)
16.4% of national budget (2022 est.)
Military - note
the Bolivian Armed Forces (FAB) are responsible for territorial defense but also have some internal security duties, particularly counternarcotics and border security; the FAB shares responsibility for border enforcement with the National Police (PNB), and it may be called out to assist the PNB with maintaining public order in critical situations
land-locked Bolivia has a naval force for patrolling some 5,000 miles of navigable rivers to combat narcotics trafficking and smuggling, provide disaster relief, and deliver supplies to remote rural areas, as well as for maintaining a presence on Lake Titicaca; the Navy also exists in part to cultivate a maritime tradition and as a reminder of Bolivia’s defeat at the hands of Chile in the War of the Pacific (1879-1883), and its desire to regain access to the Pacific Ocean; every year on 23 March, the Navy participates in parades and government ceremonies commemorating the Día Del Mar (Day of the Sea) holiday that remembers the loss (2025)
land-locked Bolivia has a naval force for patrolling some 5,000 miles of navigable rivers to combat narcotics trafficking and smuggling, provide disaster relief, and deliver supplies to remote rural areas, as well as for maintaining a presence on Lake Titicaca; the Navy also exists in part to cultivate a maritime tradition and as a reminder of Bolivia’s defeat at the hands of Chile in the War of the Pacific (1879-1883), and its desire to regain access to the Pacific Ocean; every year on 23 March, the Navy participates in parades and government ceremonies commemorating the Día Del Mar (Day of the Sea) holiday that remembers the loss (2025)
Military and security service personnel strengths
approximately 30-35,000 active-duty Armed Forces (2025)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 252.91 million cubic meters (2022 est.)
industrial: 32 million cubic meters (2022 est.)
agricultural: 1.92 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
industrial: 32 million cubic meters (2022 est.)
agricultural: 1.92 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 2.219 million tons (2024 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 34.4% (2022 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 34.4% (2022 est.)
Average household expenditures
on food: 29.3% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
on alcohol and tobacco: 2.2% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
on alcohol and tobacco: 2.2% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
National heritage
total World Heritage Sites: 7 (6 cultural, 1 natural)
selected World Heritage Site locales: City of Potosi (c); El Fuerte de Samaipata (c); Historic Sucre (c); Jesuit Missions of Chiquitos (c); Noel Kempff Mercado National Park (n); Tiahuanacu (c); Qhapaq Ñan/Andean Road System (c)
selected World Heritage Site locales: City of Potosi (c); El Fuerte de Samaipata (c); Historic Sucre (c); Jesuit Missions of Chiquitos (c); Noel Kempff Mercado National Park (n); Tiahuanacu (c); Qhapaq Ñan/Andean Road System (c)
Major aquifers
Amazon Basin
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Atlantic Ocean drainage: Amazon (6,145,186 sq km), Paraná (2,582,704 sq km)
Major lakes (area sq km)
fresh water lake(s): Lago Titicaca (shared with Peru) - 8,030 sq km
salt water lake(s): Lago Poopo - 1,340 sq km
salt water lake(s): Lago Poopo - 1,340 sq km
Child marriage
women married by age 15: 3.4% (2016)
women married by age 18: 19.7% (2016)
men married by age 18: 5.2% (2016)
women married by age 18: 19.7% (2016)
men married by age 18: 5.2% (2016)
Coal
consumption: 9,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 7,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 1 million metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 7,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 1 million metric tons (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 65% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
solar: 2.9% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
wind: 3.7% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 24.9% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 3.5% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
solar: 2.9% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
wind: 3.7% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 24.9% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 3.5% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Natural gas
production: 12.302 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
consumption: 4.025 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
exports: 7.816 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 302.99 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
consumption: 4.025 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
exports: 7.816 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 302.99 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Petroleum
total petroleum production: 58,000 bbl/day (2023 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 100,000 bbl/day (2023 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 240.9 million barrels (2021 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 100,000 bbl/day (2023 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 240.9 million barrels (2021 est.)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
50.2% (2022 est.)
Remittances
3.2% of GDP (2023 est.)
3.3% of GDP (2022 est.)
3.5% of GDP (2021 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
3.3% of GDP (2022 est.)
3.5% of GDP (2021 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
Space program overview
has a small space program focused on acquiring and operating satellites; operates a telecommunications satellite and ground stations; has cooperated with China and India and member states of the Latin American and Caribbean Space Agency (2025)
Space agency/agencies
Bolivian Space Agency (la Agencia Boliviana Espacial, ABE; established 2010 as a national public company under Ministry of Public Works, Services and Housing) (2025)
Terrorist group(s)
Terrorist group(s): Tren de Aragua (TdA)
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in the Terrorism reference guide
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in the Terrorism reference guide
Legislative branch - lower chamber
chamber name: Chamber of Deputies (Cámara de Diputados)
number of seats: 130 (all directly elected)
electoral system: mixed system
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 8/17/2025
parties elected and seats per party: Christian Democratic Party (PDC) (49); LIBRE (39); Unity (26); Popular Alliance (8); Other (8)
percentage of women in chamber: 50.8%
expected date of next election: August 2030
number of seats: 130 (all directly elected)
electoral system: mixed system
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 8/17/2025
parties elected and seats per party: Christian Democratic Party (PDC) (49); LIBRE (39); Unity (26); Popular Alliance (8); Other (8)
percentage of women in chamber: 50.8%
expected date of next election: August 2030
Legislative branch - upper chamber
chamber name: Chamber of Senators (Cámara de Senadores)
number of seats: 36 (all directly elected)
electoral system: proportional representation
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 8/17/2025
parties elected and seats per party: Christian Democratic Party (PDC) (16); LIBRE (12); Unity (7); Other (1)
percentage of women in chamber: 58.3%
expected date of next election: August 2030
number of seats: 36 (all directly elected)
electoral system: proportional representation
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 8/17/2025
parties elected and seats per party: Christian Democratic Party (PDC) (16); LIBRE (12); Unity (7); Other (1)
percentage of women in chamber: 58.3%
expected date of next election: August 2030
National color(s)
red, yellow, green
Key space-program milestones
2013 - first communications satellite (Túpac Katari, TKSAT-1) built and launched by China
2016 - began independently operating the TKSAT-1 satellite
2021 - signed protocols for establishment of the Latin American and Caribbean Space Agency
2016 - began independently operating the TKSAT-1 satellite
2021 - signed protocols for establishment of the Latin American and Caribbean Space Agency
Particulate matter emissions
24.6 micrograms per cubic meter (2019 est.)
Methane emissions
energy: 122.8 kt (2022-2024 est.)
agriculture: 673.4 kt (2019-2021 est.)
waste: 73.1 kt (2019-2021 est.)
other: 150.3 kt (2019-2021 est.)
agriculture: 673.4 kt (2019-2021 est.)
waste: 73.1 kt (2019-2021 est.)
other: 150.3 kt (2019-2021 est.)
Labor force
6.859 million (2024 est.)
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 5.2% (2024 est.)
male: 4.8% (2024 est.)
female: 5.8% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
male: 4.8% (2024 est.)
female: 5.8% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
Debt - external
$11.174 billion (2023 est.)
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
Maternal mortality ratio
146 deaths/100,000 live births (2023 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$1.977 billion (2024 est.)
$1.8 billion (2023 est.)
$3.752 billion (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
$1.8 billion (2023 est.)
$3.752 billion (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
Public debt
49% of GDP (2017 est.)
note: data cover general government debt and includes debt instruments issued by government entities other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data include debt issued by subnational entities
note: data cover general government debt and includes debt instruments issued by government entities other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data include debt issued by subnational entities
Unemployment rate
3.1% (2024 est.)
3.1% (2023 est.)
3.6% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
3.1% (2023 est.)
3.6% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
Population
total: 12,311,974 (2024 est.)
male: 6,192,774
female: 6,119,200
male: 6,192,774
female: 6,119,200
Carbon dioxide emissions
21.552 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 24,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 13.647 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 7.881 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 24,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 13.647 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 7.881 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
Area
total : 1,098,581 sq km
land: 1,083,301 sq km
water: 15,280 sq km
land: 1,083,301 sq km
water: 15,280 sq km
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$122.2 billion (2024 est.)
$120.531 billion (2023 est.)
$116.927 billion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
$120.531 billion (2023 est.)
$116.927 billion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Airports
201 (2025)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
42.1 (2023 est.)
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
5.1% (2024 est.)
2.6% (2023 est.)
1.7% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
2.6% (2023 est.)
1.7% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
Current account balance
-$1.15 billion (2023 est.)
$939.084 million (2022 est.)
$1.581 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
$939.084 million (2022 est.)
$1.581 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
Real GDP per capita
$9,800 (2024 est.)
$9,800 (2023 est.)
$9,700 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
$9,800 (2023 est.)
$9,700 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 1.33 million (2022 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 11 (2022 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 11 (2022 est.)
Tobacco use
total: 11% (2025 est.)
male: 18.9% (2025 est.)
female: 3.2% (2025 est.)
male: 18.9% (2025 est.)
female: 3.2% (2025 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
20.2% (2016)
Energy consumption per capita
29.34 million Btu/person (2023 est.)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 4.375 million kW (2023 est.)
consumption: 10.863 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 1.079 billion kWh (2023 est.)
consumption: 10.863 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 1.079 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Merchant marine
total: 50 (2023)
by type: general cargo 30, oil tanker 2, other 18
by type: general cargo 30, oil tanker 2, other 18
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
3.4% (2016 est.)
Imports
$12.988 billion (2023 est.)
$13.462 billion (2022 est.)
$10.187 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
$13.462 billion (2022 est.)
$10.187 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
Exports
$11.905 billion (2023 est.)
$14.465 billion (2022 est.)
$11.594 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
$14.465 billion (2022 est.)
$11.594 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
Heliports
3 (2025)
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 550,000 (2021 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 4 (2022 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 4 (2022 est.)
Alcohol consumption per capita
total: 2.98 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 2.22 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.14 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.54 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.08 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 2.22 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.14 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.54 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.08 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 72.5 years (2024 est.)
male: 71 years
female: 74 years
male: 71 years
female: 74 years
Real GDP growth rate
1.4% (2024 est.)
3.1% (2023 est.)
3.6% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
3.1% (2023 est.)
3.6% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
Industrial production growth rate
1.1% (2023 est.)
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 13.5% (2023 est.)
industry: 24.2% (2023 est.)
services: 51.1% (2023 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
industry: 24.2% (2023 est.)
services: 51.1% (2023 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
Education expenditure
8.3% of GDP (2023 est.)
10.8% national budget (2024 est.)
10.8% national budget (2024 est.)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the military is equipped with a mix of mostly older Brazilian, Chinese, European, and US armaments (2025)
Military service age and obligation
voluntary service for men and women 18-22 years of age; selective 12-month compulsory service for men, 18-22 (24 months of search and rescue service can be substituted for military service) (2025)
note: as of 2024, women comprised about 11% of the Bolivian military's personnel
note: as of 2024, women comprised about 11% of the Bolivian military's personnel
Gross reproduction rate
1.04 (2025 est.)
Net migration rate
-0.95 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Median age
total: 27 years (2025 est.)
male: 26.2 years
female: 27 years
male: 26.2 years
female: 27 years
Total fertility rate
2.13 children born/woman (2025 est.)
Infant mortality rate
total: 22.1 deaths/1,000 live births (2025 est.)
male: 24.5 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 20 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 24.5 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 20 deaths/1,000 live births
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 12 million (2021 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 100 (2021 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 100 (2021 est.)
Death rate
5.99 deaths/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Birth rate
17.02 births/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Population growth rate
1.01% (2025 est.)

